Related Research Articles
Cartography is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.

Martin Waldseemüller was a German cartographer and humanist scholar. Sometimes known by the Latinized form of his name, Hylacomylus, his work was influential among contemporary cartographers. He and his collaborator Matthias Ringmann are credited with the first recorded usage of the word America to name a portion of the New World in honour of the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci. Waldseemüller was also the first to map South America as a continent separate from Asia, the first to produce a printed globe and the first to create a printed wall map of Europe. A set of his maps printed as an appendix to the 1513 edition of Ptolemy's Geography is considered to be the first example of a modern atlas.

Gerardus Mercator was a 16th-century geographer, cosmographer and cartographer from the County of Flanders. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represented sailing courses of constant bearing as straight lines—an innovation that is still employed in nautical charts.

A world map is a map of most or all of the surface of Earth. World maps, because of their scale, must deal with the problem of projection. Maps rendered in two dimensions by necessity distort the display of the three-dimensional surface of the earth. While this is true of any map, these distortions reach extremes in a world map. Many techniques have been developed to present world maps that address diverse technical and aesthetic goals.

Jodocus Hondius was a Flemish engraver and cartographer. He is sometimes called Jodocus Hondius the Elder to distinguish him from his son Jodocus Hondius II. Hondius is best known for his early maps of the New World and Europe, for re-establishing the reputation of the work of Gerard Mercator, and for his portraits of Francis Drake. One of the notable figures in the Golden Age of Dutch/Netherlandish cartography, he helped establish Amsterdam as the center of cartography in Europe in the 17th century.

"Here be dragons" means dangerous or unexplored territories, in imitation of a medieval practice of putting illustrations of dragons, sea monsters and other mythological creatures on uncharted areas of maps where potential dangers were thought to exist.

Johannes Schöner was a renowned and respected German polymath. It is best to refer to him using the usual 16th-century Latin term "mathematicus", as the areas of study to which he devoted his life were very different from those now considered to be the domain of the mathematician. He was a priest, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, cosmographer, cartographer, mathematician, globe and scientific instrument maker and editor and publisher of scientific tests. In his own time he enjoyed a Europe-wide reputation as an innovative and influential globe maker and cosmographer and as one of the continent's leading and most authoritative astrologers. Today he is remembered as an influential pioneer in the history of globe making, and as a man who played a significant role in the events that led up to the publishing of Copernicus's De revolutionibus orbium coelestium in Nürnberg in 1543.

The Bamberg Apocalypse is an 11th-century richly illuminated manuscript containing the pictorial cycle of the Book of Revelation and a Gospel Lectionary of the books of pericopes. This medieval illuminated manuscript was created during the Ottonian dynasty; it is unknown whether it was commissioned by Otto III or Henry II. It was completed sometime between 1000 and 1020. There is proof that Henry II donated this illuminated manuscript in 1020 to Collegiate Abbey of St. Stephan, on the occasion of its inauguration. The Bamberg Apocalypse is now located in the Bamberg State Library.

The Geography, also known by its Latin names as the Geographia and the Cosmographia, is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, compiling the geographical knowledge of the 2nd-century Roman Empire. Originally written by Claudius Ptolemy in Greek at Alexandria around AD 150, the work was a revision of a now-lost atlas by Marinus of Tyre using additional Roman and Persian gazetteers and new principles. Its translation into Arabic in the 9th century and Latin in 1406 was highly influential on the geographical knowledge and cartographic traditions of the medieval Caliphate and Renaissance Europe.

The Waldseemüller map or Universalis Cosmographia is a printed wall map of the world by German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller, originally published in April 1507. It is known as the first map to use the name "America". The name America is placed on what is now called South America on the main map. As explained in Cosmographiae Introductio, the name was bestowed in honor of the Italian Amerigo Vespucci.

A thematic map is a type of map that portrays the geographic pattern of a particular subject matter (theme) in a geographic area. This usually involves the use of map symbols to visualize selected properties of geographic features that are not naturally visible, such as temperature, language, or population. In this, they contrast with general reference maps, which focus on the location of a diverse set of physical features, such as rivers, roads, and buildings. Alternative names have been suggested for this class, such as special-subject or special-purpose maps, statistical maps, or distribution maps, but these have generally fallen out of common usage. Thematic mapping is closely allied with the field of Geovisualization.

Henricus Martellus Germanus was a geographer and cartographer from Nuremberg who lived and worked in Florence from 1480 to 1496.
Cartographic censorship is the deliberate modification of publicly available maps in order to disguise, remove, or obfuscate potentially strategic locations or buildings, such as military bases, power plants or transmitters. Sensitive objects and places have been removed from maps since historic times, sometimes as a disinformation tactic in times of war, and also to serve competitive political and economic interests, such as during the Age of Discovery when strategic geographic information was highly sought after. In modern times requests for censorship are sent to Google Earth for certain sites that are deemed to pose security risks for national governments.

The Gough Map or Bodleian Map is a Late Medieval map of the island of Great Britain. Its precise date of production and authorship are unknown. It is named after Richard Gough, who bequeathed the map to the Bodleian Library in 1809. He acquired the map from the estate of the antiquarian Thomas "Honest Tom" Martin in 1774. Numerous copies of it have been made, with an interactive online version created at Queen's University, Belfast. It measures 115 x 56 cm.

Pierre Desceliers was a French cartographer of the Renaissance and an eminent member of the Dieppe School of Cartography. He is considered the father of French hydrography.

A map collection or map library is a storage facility for maps, usually in a library, archive, or museum, or at a map publisher or public-benefit corporation, and the maps and other cartographic items stored within that facility.

The Mercator world map of 1569 is titled Nova et Aucta Orbis Terrae Descriptio ad Usum Navigantium Emendate Accommodata. The title shows that Gerardus Mercator aimed to present contemporary knowledge of the geography of the world and at the same time 'correct' the chart to be more useful to sailors. This 'correction', whereby constant bearing sailing courses on the sphere are mapped to straight lines on the plane map, characterizes the Mercator projection. While the map's geography has been superseded by modern knowledge, its projection proved to be one of the most significant advances in the history of cartography, inspiring map historian Nordenskiöld to write "The master of Rupelmonde stands unsurpassed in the history of cartography since the time of Ptolemy." The projection heralded a new era in the evolution of navigation maps and charts and it is still their basis.
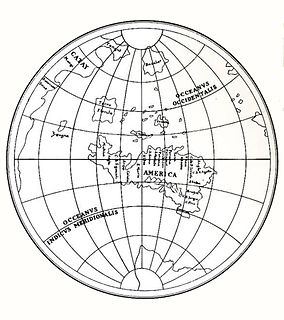
Leonardo's unique equilateral triangular design is applied for a world map. It is a map drawn using the "octant projection" and dates from approximately 1514. It was found loosely inserted among a Codex of Leonardo da Vinci. It features an early use of the name America. The map incorporates information from the travels of Amerigo Vespucci, published in 1503 and 1505. Additionally, the map depicts the Arctic as an ocean and Antarctica as a continent of about the correct size.

Gaspard van der Heyden was a goldsmith, engraver, master printer and builder of precision astronomical instruments including terrestrial and celestial globes from Leuven, Belgium. He was well known among the humanists in Leuven as well as among scientists and mathematicians.

Salvatore de Pilestrina, also known as Salvat de Pilestrina, was a mapmaker in Mallorca in the early 16th century.
References
- ↑ "How I Write History…with Chet Van Duzer". 14 September 2014. Retrieved 1 June 2018.
- ↑ "Chet Van Duzer, Author at Facsimile Finder Blog -". Facsimile Finder Blog. Retrieved 1 June 2018.
- ↑ "People – The Lazarus Project". www.lazarusprojectimaging.com. Retrieved 2018-06-06.
- 1 2 "Chet Van Duzer, Kluge Fellow (Resident Scholars, The John W. Kluge Center at the Library of Congress)". www.loc.gov. Retrieved 1 June 2018.
- ↑ "Apocalyptic cartography : thematic maps and the end of the world in a fifteenth-century manuscript /". Worldcat.org. Retrieved 2018-06-01.
- ↑ "Chet Van Duzer". www.goodreads.com. Retrieved 1 June 2018.