
The Christian Democratic Party is a Christian democratic political party in Chile. There have been three Christian Democrat presidents in the past, Eduardo Frei Ruiz-Tagle, Patricio Aylwin, and Eduardo Frei Montalva.

The Socialist Party of Chile is a centre-left political party founded in 1933. Its historic leader was President of Chile Salvador Allende, who was deposed in a CIA-backed coup d'état by General Augusto Pinochet in 1973. The military junta immediately banned socialist, Marxist and other leftist political parties. Members of the Socialist party and other leftists were subject to violent suppression, including torture and murder, under the Pinochet dictatorship, and many went into exile. Twenty-seven years after the 1973 coup, Ricardo Lagos Escobar won the Presidency as the Socialist Party candidate in the 1999–2000 Chilean presidential election. Socialist Michelle Bachelet won the 2005–06 Chilean presidential election. She was the first female president of Chile and was succeeded by Sebastián Piñera in 2010. In the 2013 Chilean general election, she was again elected president, leaving office in 2018.

The Concertación, officially the Concertación de Partidos por la Democracia, was a coalition of center-left political parties in Chile, founded in 1988. Presidential candidates under its banner won every election from when military rule ended in 1990 until the conservative candidate Sebastián Piñera won the Chilean presidential election in 2010. In 2013 it was replaced by New Majority coalition.

Popular Unity was a left-wing political alliance in Chile that stood behind the successful candidacy of Salvador Allende for the 1970 Chilean presidential election.
This article gives an overview of liberal and radical parties in Chile. It is limited to liberal and radical parties with substantial support, mainly proved by having had a representation in parliament. The sign ⇒ means a reference to another party in that scheme. For inclusion in this scheme, parties do not necessarily need to have labeled themselves as a liberal party.
This article gives an overview of liberalism and radicalism in Spain. It is limited to liberal and radical parties with substantial support, mainly proved by having been represented in parliament. The sign ⇒ denotes another party in that scheme. For inclusion in this scheme it is not necessary that parties label themselves as a liberal or radical party.

Salvador Allende was the president of Chile from 1970 until his suicide in 1973, and head of the Popular Unity government; he was a Socialist and Marxist elected to the national presidency of a liberal democracy in Latin America. In August 1973 the Chilean Senate declared the Allende administration to be "unlawful," Allende's presidency was ended by a military coup before the end of his term. During Allende's three years, Chile gradually transitioned into a socialist state.

The Citizen Left Party of Chile, known until 2013 as Christian Left Party of Chile was a Chilean left-wing political party. Founded in 1971, in its early days it was suppressed by the Pinochet dictatorship. It was part of the Nueva Mayoría coalition, supporting the presidential candidacy president Michelle Bachelet in 2013.

The Communist Party of Chile is a communist party in Chile. It was founded in 1912 as the Socialist Workers' Party and adopted its current name in 1922. The party established a youth wing, the Communist Youth of Chile, in 1932.

The Radical Democracy, was a Chilean centre-right political party. The party, created in 1969, was dissolved in 1973, and reappeared in 1983 before disbanding permanently in 1990.

The Popular Unitary Action Movement or MAPU was a small leftist political party in Chile. It was part of the Popular Unity coalition during the government of Salvador Allende. MAPU was repressed during the dictatorship of Augusto Pinochet. In this period, some of its most radical members formed the Movimiento Juvenil Lautaro, whose leaders were political prisoners during the dictatorship and with the return to democracy. Another faction of the former members of the party joined the social democratic Party for Democracy in 1987.

The Radical Party was a Chilean political party. It was formed in 1863 in Copiapó by a split in the Liberal Party. Not coincidentally, it was formed shortly after the organization of the Grand Lodge of Chile, and it has maintained a close relationship with Chilean Freemasonry throughout its life. As such, it represented the anticlericalist position in Chilean politics, and was instrumental in producing the "theological reforms" in Chilean law in the early 1880s. These laws removed the cemeteries from the control of the Roman Catholic Church, established a civil registry of births and death in place of the previous recordkeeping of the church, and established a civil law of matrimony, which removed the determination of validity of marriages from the church. Prior to these laws, it was impossible for non-Catholics to contract marriage in Chile, and meant that any children they produced were illegitimate. Non-Catholics had also been barred from burial in Catholic cemeteries, which were virtually the only cemeteries in the country; instead, non-Catholics were buried in the beaches, and even on the Santa Lucia Hill in Santiago, which, in the 19th century, functioned as Santiago's dump.

Parliamentary elections were held in Chile on 4 March 1973, They resulted in a victory for the Confederation of Democracy, an opposition alliance led by the National Party and the Christian Democratic Party. However, they were unable to secure the necessary two-thirds majority in the Senate to remove President Salvador Allende from office.
The Popular Front in Chile was an electoral and political left-wing coalition from 1937 to February 1941, during the Presidential Republic Era (1924–1973). It gathered together the Radical Party, the Socialist Party, the Communist Party, the Democratic Party and the Radical Socialist Party, as well as organizations such as the Confederación de Trabajadores de Chile (CTCH) trade-union, the Mapuche movement which unified itself in the Frente Único Araucano, and the feminist Movimiento Pro-Emancipación de las Mujeres de Chile (MEMCh).

The FRAP was a Chilean left-wing coalition of parties from 1956 to 1969. It presented twice a common candidate, Salvador Allende, for the 1958 and the 1964 presidential elections. Succeeding to the FRENAP formed the preceding year, the FRAP itself was succeeded by the Popular Unity coalition.
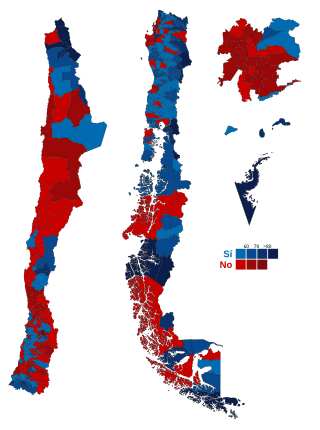
The 1988 Chilean national plebiscite was a presidential election in form, but not in name, as it was officially referred to as a national referendum. Held on October 5, 1988, the plebiscite aimed to determine if Augusto Pinochet, the head of a military dictatorship, should become president for eight years under resumed civilian rule. The "No" side won with 56% of the vote, marking the end of Pinochet's rule of 16 and a half years. Democratic elections were held in 1989, leading to the establishment of a new government in 1990.

The National Democratic Party, known by its acronym PADENA, was a Chilean political party. This party was one of the last political movements linked to the figure of President Carlos Ibáñez del Campo.

Allendism is an ideological current that bases its positions and lines on what was the government of Salvador Allende, former president of Chile who, together with the Popular Unity (UP), ruled the country until the coup d'état of 1973, perpetrated by Augusto Pinochet. Within the political spectrum it is located between the Left-wing and the center left, basing its principles on democratic socialism, institutionalism and reformism. The followers of this current are called allendistas.
















