
USS Thompson (DD-305), a Clemson-class destroyer of the U.S. Navy named in honor of Secretary of the Navy Richard W. Thompson (1809–1900), never saw action against an enemy. She was the first Navy ship of that name; the second, Thompson (DD-627), named for Robert M. Thompson, served during World War II and the Korean War.

The second USS Charleston (C-2) was a United States Navy protected cruiser — the fourth US protected cruiser to be built. Lacking experience in building steel cruisers, the design was purchased from the British company Armstrong, Mitchell and Co. of Newcastle, the construction to be by an American shipyard. In design, she succeeded the "ABC" cruisers Atlanta, Boston, and Chicago with better protection, higher speed, and similar armament.

The seventh USS Washington (ACR-11/CA-11/IX-39), also referred to as "Armored Cruiser No. 11", and later renamed Seattle and reclassified CA-11 and IX-39, was a United States Navy Tennessee-class armored cruiser. She was laid down on 23 September 1903 at Camden, New Jersey, by the New York Shipbuilding Corporation, launched on 18 March 1905, sponsored by Miss Helen Stewart Wilson, daughter of United States Senator John L. Wilson of Washington state, and commissioned at the Philadelphia Navy Yard on 7 August 1906, Captain James D. Adams in command.

The first USS Abarenda (AC-13/AG-14) was a collier in the service of the United States Navy during World War I.

USS Dent (DD–116) was a Wickes-class destroyer in the United States Navy during the World War I and later served as APD-9 in World War II. She was named for Captain John H. Dent.

USS Yorktown was lead ship of her class of steel-hulled, twin-screw gunboats in the United States Navy in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. She was the second U.S. Navy ship named in honor of the American Revolutionary War's Battle of Yorktown.

|} The first USS Tuscarora was a Mohican-class sloop of war in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. Tuscarora was laid down on 27 June 1861 at Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, by Merrick & Sons; launched on 24 August 1861; sponsored by Miss Margaret Lardner; and commissioned on 5 December 1861, Commander Tunis A. M. Craven in command.

Polly Woodside is a Belfast-built, three-masted, iron-hulled barque, preserved in Melbourne, Victoria (Australia), and forming the central feature of the South Wharf precinct. The ship was originally built in Belfast by William J. Woodside and was launched in 1885. Polly Woodside is typical of thousands of smaller iron barques built in the last days of sail, intended for deep water trade around the world and designed to be operated as economically as possible.

The first USS Narragansett was a 2nd class screw sloop in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. Narragansett was built at the Boston Navy Yard, launched on 15 February 1859, and commissioned on 6 November 1859.

Moshulu is a four-masted steel barque, built as Kurt by William Hamilton and Company at Port Glasgow in Scotland in 1904. The largest remaining original windjammer, she is currently a floating restaurant docked in Penn's Landing, Philadelphia, adjacent to the museum ships USS Olympia and USS Becuna.

The second USS Mohican was a steam sloop of war in the United States Navy. She was named for the Mohican tribe.
USS Nyack was a wooden-hulled screw gunboat of the United States Navy that saw action in the American Civil War. After the Civil war, she was transferred to the Pacific where she patrolled the west coast of South America until she was decommissioned in 1871. She was sold and broken up in 1883.

USS Genesee (AOG-8) was a Patapsco-class gasoline tanker acquired by the U.S. Navy for the dangerous task of transporting gasoline to warships in the fleet, and to remote Navy stations.
USS Fredonia was an 800-ton bark that served the U.S. Navy as a transport and as a storeship. After several voyages to California by way of Cape Horn, she became the station warehouse in Arica, where she was destroyed by an earthquake.
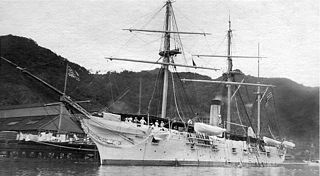
USS Adams was a screw gunboat and the lead ship of the Adams class. She was named for Founding Father and second president of the United States John Adams.
HMCS Integrity was a cutter built by the Colonial Government of New South Wales in 1804. She was the first vessel ever launched from a New South Wales dockyard and carried goods between the colony's coastal settlements of Norfolk Island, Newcastle, New South Wales, Van Diemen's Land and Port Jackson. In 1804 she took part in a series of voyages to Van Diemen's Land with the aim of founding a colony at Port Dalrymple, the site of the modern settlement of George Town, Tasmania.

USS Taganak (AG-45) – also known as USS Lake Shore (ID-1792) – was a commercial cargo ship acquired by the U.S. Navy during World War I as Lake Shore. She was again reacquired during World War II as Taganak. During both wars she carried a variety of cargo for the Navy, including coal, ammunition, and general cargo. She survived both wars and was returned to civilian service after each war.

Carrier Dove was an 1855 medium clipper. She was one of two well-known clippers launched in Baltimore that year, the other being Mary Whitridge.

Esmeralda was a wooden-hulled steam corvette of the Chilean Navy, launched in 1855, and sunk by the Peruvian ironclad Huáscar on 21 May 1879 at the Battle of Iquique during the War of the Pacific.
Portsea was launched at Calcutta in 1807. She was a country ship; that is, she primarily traded east of the Cape of Good Hope. She participated as a transport in the British invasion of Mauritius. She then carried French prisoners of war to France. She also made one voyage to St Helena from Bengal under charter to the British East India Company (EIC). In 1814 a storm dismasted her and she was lengthened, but it is not clear whether before or after the dismasting. She made two voyages as a South Seas whaler between 1828 and 1835. In 1838 she made one voyage transporting convicts to New South Wales. She carried coal to Valparaiso in 1840 and there her owners turned her into a coal hulk. Her final fate is not known.















