Keykode is an Eastman Kodak Company advancement on edge numbers, which are letters, numbers and symbols placed at regular intervals along the edge of 35 mm and 16 mm film to allow for frame-by-frame specific identification. It was introduced in 1990.

35 mm film is a film gauge used in filmmaking, and the film standard. In motion pictures that record on film, 35 mm is the most commonly used gauge. The name of the gauge is not a direct measurement, and refers to the nominal width of the 35 mm format photographic film, which consists of strips 1.377 ± 0.001 inches (34.976 ± 0.025 mm) wide. The standard image exposure length on 35 mm for movies is four perforations per frame along both edges, which results in 16 frames per foot of film.

16 mm film is a historically popular and economical gauge of film. 16 mm refers to the width of the film ; other common film gauges include 8 mm and 35 mm. It is generally used for non-theatrical film-making, or for low-budget motion pictures. It also existed as a popular amateur or home movie-making format for several decades, alongside 8 mm film and later Super 8 film. Eastman Kodak released the first 16 mm "outfit" in 1923, consisting of a camera, projector, tripod, screen and splicer, for US$335. RCA-Victor introduced a 16 mm sound movie projector in 1932, and developed an optical sound-on-film 16 mm camera, released in 1935.

8 mm film is a motion picture film format in which the film strip is eight millimetres (0.31 in) wide. It exists in two main versions – the original standard 8 mm film, also known as regular 8 mm, and Super 8. Although both standard 8 mm and Super 8 are 8 mm wide, Super 8 has a larger image area because of its smaller and more widely spaced perforations.

Super 8 mm film is a motion-picture film format released in 1965 by Eastman Kodak as an improvement over the older "Double" or "Regular" 8 mm home movie format.

127 is a roll film format for still photography introduced by Kodak in 1912.

110 is a cartridge-based film format used in still photography. It was introduced by Kodak in 1972. 110 is essentially a miniaturized version of Kodak's earlier 126 film format. Each frame is 13 mm × 17 mm, with one registration hole. Cartridges with 12, 20, or 24 frames are available on-line. Production variations sometimes have allowed for an additional image.

Kodachrome is the brand name for a color reversal film introduced by Eastman Kodak in 1935. It was one of the first successful color materials and was used for both cinematography and still photography. For many years, Kodachrome was widely used for professional color photography, especially for images intended for publication in print media.

In photography, reversal film or slide film is a type of photographic film that produces a positive image on a transparent base. Instead of negatives and prints, reversal film is processed to produce transparencies or diapositives. Reversal film is produced in various sizes, from 35 mm to roll film to 8×10 inch sheet film.
C-41 is a chromogenic color print film developing process introduced by Kodak in 1972, superseding the C-22 process. C-41, also known as CN-16 by Fuji, CNK-4 by Konica, and AP-70 by AGFA, is the most popular film process in use, with most, if not all photofinishing labs devoting at least one machine to this development process.
The Cineon System was one of the first computer based digital film systems, created by Kodak in the early 1990s. It was an integrated suite of components consisting a Motion picture film scanner, a film recorder and workstation hardware with software for compositing, visual effects, image restoration and color management.

Photo CD is a system designed by Kodak for digitizing and saving photos onto a CD. Launched in 1991, the discs were designed to hold nearly 100 high quality images, scanned prints and slides using special proprietary encoding. Photo CDs are defined in the Beige Book and conform to the CD-ROM XA and CD-i Bridge specifications as well. They were intended to play on CD-i players, Photo CD players, and any computer with a suitable software.
A standard test image is a digital image file used across different institutions to test image processing and image compression algorithms. By using the same standard test images, different labs are able to compare results, both visually and quantitatively.
Julie Anne Buck is an American film producer, collage artist, photographer, experimental filmmaker, and film archivist.

Color motion picture film refers both to unexposed color photographic film in a format suitable for use in a motion picture camera, and to finished motion picture film, ready for use in a projector, which bears images in color.

Analog photography, also known as film photography, is a term usually applied to photography that uses chemical processes to capture an image, typically on paper, film or a hard plate. These processes were the only methods available to photographers for more than a century prior to the invention of digital photography, which uses electronic sensors to record images to digital media. Analog electronic photography was sometimes used in the late 20th century but soon died out.

A color chart or color reference card is a flat, physical object that has many different color samples present. They can be available as a single-page chart, or in the form of swatchbooks or color-matching fans.
Within the printing industry, the Approval proofer, also known as the Approval Digital Imaging System or Kodak Approval System, was designed for use in Prepress proofing, especially for the highest quality contract proofs.

Technicolor is a series of color motion picture processes, the first version dating back to 1916, and followed by improved versions over several decades.
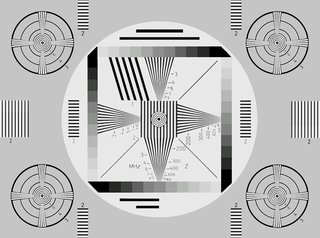
Test film are rolls or loops or slides of photographic film used for testing the quality of equipment. Equipment to be tested could include: telecine, motion picture film scanner, Movie projectors, Image scanners, film-out gear, Film recorders and Film scanners.