
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have special adaptations to take in extra oxygen and to remove salt, which allow them to tolerate conditions that would kill most plants. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in several plant families. They occur worldwide in the tropics and subtropics and even some temperate coastal areas, mainly between latitudes 30° N and 30° S, with the greatest mangrove area within 5° of the equator. Mangrove plant families first appeared during the Late Cretaceous to Paleocene epochs, and became widely distributed in part due to the movement of tectonic plates. The oldest known fossils of mangrove palm date to 75 million years ago.

An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world.

Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families, all in the order Alismatales. Seagrasses evolved from terrestrial plants which recolonised the ocean 70 to 100 million years ago.

Mangrove crabs are crabs that live in and around mangroves. They belong to many different species and families and have been shown to be ecologically significant by burying and consuming leaf litter. Mangrove crabs have a variety of phylogenies because mangrove crab is an umbrella term that encompasses many species of crabs. Two of the most common families are sesarmid and fiddler crabs. They are omnivorous and are predated on by a variety of mammals and fish. They are distributed widely throughout the globe on coasts where mangroves are located. Mangrove crabs have wide variety of ecological and biogeochemical impacts due to the biofilms that live in symbiosis with them as well as their burrowing habits. Like many other crustaceans, they are also a human food source and have been impacted by humans as well as climate change.

Mangrove forests, also called mangrove swamps, mangrove thickets or mangals, are productive wetlands that occur in coastal intertidal zones. Mangrove forests grow mainly at tropical and subtropical latitudes because mangroves cannot withstand freezing temperatures. There are about 80 different species of mangroves, all of which grow in areas with low-oxygen soil, where slow-moving waters allow fine sediments to accumulate.

Monkey River is a coastal watercourse in southern Belize that rises in the Maya Mountains and discharges to the Caribbean Sea near Monkey River Town. One of Belize's major rivers, Monkey River has northern headwaters which originate in the Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary, where the Swasey Branch drains the East Basin of that wildlife sanctuary. Further south, the Bladen Branch watercourse drains the eastern slopes of the Maya Mountains including the ancient Mayan settlement areas of Lubaantun and Nim Li Punit. These two watercourses join to form the Monkey River approximately 16 kilometres upstream from the mouth of the Monkey River. The Monkey River is readily navigated throughout the year using small boats, but navigation above the major confluence becomes more difficult due to lack of depth when the dry season starts about February. Habitats in this watershed provide cover for such diverse species as the ocelot, jaguar, Guatemalan black howler, bare-throated tiger heron, Morelet's crocodile, fer-de-lance and manatee.

The Sesarmidae are a family of crabs, previously included in the Grapsidae by many authors. Several species, namely in Geosesarma, Metopaulias, and Sesarma, are true terrestrial crabs. They do not need to return to the sea even for breeding.

The Coastal and Estuarine Research Federation (CERF) is a private, nonprofit organization created in 1971. At that time, the members of two regionally based organizations, the Atlantic Estuarine Research Society (AERS) and the New England Estuarine Research Society (NEERS) recognized the need for a third estuarine organization that would address national estuarine and coastal issues. Today, CERF is a multidisciplinary federation of members and seven regionally-based Affiliate Societies dedicated to the understanding and wise stewardship of estuaries and coasts worldwide.

The Liquid Jungle Lab (LJL) is a tropical marine research station on the island of Canales de Tierra on the western coast of Pacific Panamá along a primary marine biological corridor. The LJL research campus was completed in 2004 and is part of a private 3,500 hectare reserve composed of primary forest, mangroves, tide pools, and a rocky inter-tidal zone that transitions into fringing coral reefs.

Chiromantes haematocheir is a mudflat crab of the family Sesarmidae, which is endemic to East Asia. It is known under the common names red-clawed crab or akategani (Japanese) and the Latin names Grapsus haematocheir and Sesarma haematocheir. It is quite distinct from the other species placed in the genus Chiromantes, and the genus may be restricted to this one species.

Mangrove ecosystems represent natural capital capable of producing a wide range of goods and services for coastal environments and communities and society as a whole. Some of these outputs, such as timber, are freely exchanged in formal markets. Value is determined in these markets through exchange and quantified in terms of price. Mangroves are important for aquatic life and home for many species of fish.

Cerithidea decollata, common name the truncated mangrove snail, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Potamididae.

Terebralia palustris, common name the giant mangrove whelk, is a species of brackish-water snail, a gastropod mollusk in the family Potamididae. This tropical species which inhabits mangrove environments of the Indo-West Pacific region, has the widest geographic distribution amongst the potamidids extending from eastern Africa to northern Australia. Terebralia palustris is the largest mangrove gastropod, with a maximum shell length of 190 mm recorded from Arnhem Land, Australia.

Ocypode cursor, the tufted ghost crab, is a species of ghost crab found on sandy beaches along the coasts of the eastern Atlantic Ocean and eastern Mediterranean Sea.
Perisesarma guttatum, the red-claw mangrove crab, is a crab species in the genus Parasesarma and the family Sesarmidae. It is distributed in coastal brackish water habitats of the western Indian Ocean.

The marine ecoregions of the South African exclusive economic zone are a set of geographically delineated regions of similar ecological characteristics on a fairly broad scale, covering the exclusive economic zone along the South African coast.
The Port Elizabeth Corals Marine Protected Area is an offshore conservation region south of Port Elizabeth in the exclusive economic zone of South Africa

The Marine biodiversity of South Africa is the variety of living organisms that live in the seas off the coast of South Africa. It includes genetic, species and ecosystems biodiversity in a range of habitats spread over a range of ecologically varied regions, influenced by the geomorphology of the seabed and circulation of major and local water masses, which distribute both living organisms and nutrients in complex and time-variable patterns.

A marine coastal ecosystem is a marine ecosystem which occurs where the land meets the ocean. Marine coastal ecosystems include many very different types of marine habitats, each with their own characteristics and species composition. They are characterized by high levels of biodiversity and productivity.
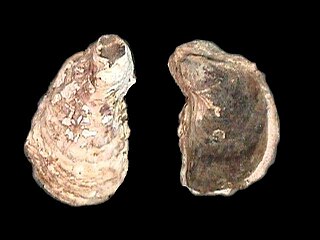
Crassostrea rhizophorae, also known as the mangrove cupped oyster, is a species of bivalve in the family Ostreidae. C. rhizophorae is one of the predominant oyster species in the South Atlantic, specifically in Central and South America. It is often found in the vast mangrove ecosystem along the coast of Brazil.
















