Related Research Articles

The larynx, commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word 'larynx' comes from the Ancient Greek word lárunx ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ

The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing.
Gender-affirming surgery is a surgical procedure, or series of procedures, that alters a person's physical appearance and sexual characteristics to resemble those associated with their identified gender. The phrase is most often associated with transgender health care and intersex medical interventions, however many such treatments are also pursued by cisgender and non-intersex individuals. It is also known as sex reassignment surgery, gender confirmation surgery, and several other names.

Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequently performed in critically injured, ill, or anesthetized patients to facilitate ventilation of the lungs, including mechanical ventilation, and to prevent the possibility of asphyxiation or airway obstruction.
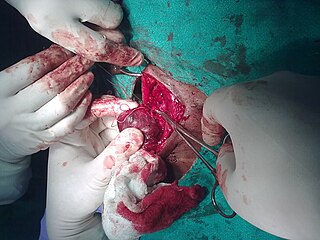
A thyroidectomy is an operation that involves the surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. In general surgery, endocrine or head and neck surgeons often perform a thyroidectomy when a patient has thyroid cancer or some other condition of the thyroid gland or goiter. Other indications for surgery include cosmetic, or symptomatic obstruction. Thyroidectomy is a common surgical procedure that has several potential complications or sequelae including: temporary or permanent change in voice, temporary or permanently low calcium, need for lifelong thyroid hormone replacement, bleeding, infection, and the remote possibility of airway obstruction due to bilateral vocal cord paralysis. Complications are uncommon when the procedure is performed by an experienced surgeon.
Facial feminization surgery (FFS) is a set of reconstructive surgical procedures that alter typically male facial features to bring them closer in shape and size to typical female facial features. FFS can include various bony and soft tissue procedures such as brow lift, rhinoplasty, cheek implantation, and lip augmentation.
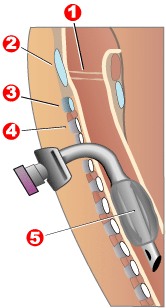
Tracheotomy, or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The resulting stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway or as a site for a tracheal tube or tracheostomy tube to be inserted; this tube allows a person to breathe without the use of the nose or mouth.

The Adam's apple or laryngeal prominence is the protrusion in the human neck formed by the angle of the thyroid cartilage surrounding the larynx, typically visible in men, less frequently in women. The prominence of the Adam's apple increases as a secondary male sex characteristic in puberty.
Gender-affirming surgery for male-to-female transgender women or transfeminine non-binary people describes a variety of surgical procedures that alter the body to provide physical traits more comfortable and affirming to an individual's gender identity and overall functioning.

Laryngectomy is the removal of the larynx and separation of the airway from the mouth, nose and esophagus. In a total laryngectomy, the entire larynx is removed. In a partial laryngectomy, only a portion of the larynx is removed. Following the procedure, the person breathes through an opening in the neck known as a stoma. This procedure is usually performed by an ENT surgeon in cases of laryngeal cancer. Many cases of laryngeal cancer are treated with more conservative methods. A laryngectomy is performed when these treatments fail to conserve the larynx or when the cancer has progressed such that normal functioning would be prevented. Laryngectomies are also performed on individuals with other types of head and neck cancer. Less invasive partial laryngectomies, including tracheal shaves and Feminization Laryngoplasty may also be performed on transgender women and other female or non-binary identified individuals to feminize the larynx and/or voice. Post-laryngectomy rehabilitation includes voice restoration, oral feeding and more recently, smell and taste rehabilitation. An individual's quality of life can be affected post-surgery.
"Voice therapy" or "voice training" refers to any non-surgical technique used to improve or modify the human voice. Because voice is a social cue to a person's sex and gender, transgender people may frequently undertake voice training or therapy as a part of gender transitioning in order to make their voices sound more typical of their gender, and therefore increase their likelihood of being perceived as that gender. Having voice and speech characteristics align with one's gender identity is often important to transgender individuals, whether their goal be feminization, neutralization or masculinization. Voice therapy can be seen as an act of gender- and identity-affirming care, in order to reduce gender dysphoria and gender incongruence, improve the self-reported wellbeing and health of transgender people, and alleviate concerns over an individual being recognized as transgender.

Toby R. Meltzer is an American plastic and reconstructive surgeon. Meltzer specializes in sex reassignment surgery male-to-female, sex reassignment surgery female-to-male, and facial feminization surgery. In the 1990s, Meltzer pioneered the neovaginal construction technique that increased the ability of the neoclitoris to feel sensations. According to his website, Meltzer performs 2-4 vaginoplasties a week, and that he has performed over 3000 male and female sexual reassignment (SRS) surgeries. Joan Roughgarden called Meltzer one of the leading surgeons in this specialized field. He practices in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Vocal cord paresis, also known as recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis or vocal fold paralysis, is an injury to one or both recurrent laryngeal nerves (RLNs), which control all intrinsic muscles of the larynx except for the cricothyroid muscle. The RLN is important for speaking, breathing and swallowing.
A laryngeal cleft or laryngotracheoesophageal cleft is a rare congenital abnormality in the posterior laryngo-tracheal wall. It occurs in approximately 1 in 10,000 to 20,000 births. It means there is a communication between the oesophagus and the trachea, which allows food or fluid to pass into the airway.
Tracheal intubation, an invasive medical procedure, is the placement of a flexible plastic catheter into the trachea. For millennia, tracheotomy was considered the most reliable method of tracheal intubation. By the late 19th century, advances in the sciences of anatomy and physiology, as well as the beginnings of an appreciation of the germ theory of disease, had reduced the morbidity and mortality of this operation to a more acceptable rate. Also in the late 19th century, advances in endoscopic instrumentation had improved to such a degree that direct laryngoscopy had finally become a viable means to secure the airway by the non-surgical orotracheal route. Nasotracheal intubation was not widely practiced until the early 20th century. The 20th century saw the transformation of the practices of tracheotomy, endoscopy and non-surgical tracheal intubation from rarely employed procedures to essential components of the practices of anesthesia, critical care medicine, emergency medicine, gastroenterology, pulmonology and surgery.
Thyroplasty is a phonosurgical technique designed to improve the voice by altering the thyroid cartilage of the larynx, which houses the vocal cords in order to change the position or the length of the vocal cords.
Arytenoid adduction is a surgical procedure used to treat vocal cord paralysis. A suture is used to emulate the action of the lateral cricoarytenoid muscle and position the paralyzed vocal cord closer to the midline. This allows the two vocal cords to meet and can improve speaking and swallowing ability for affected patients. Arytenoid adduction is often performed in conjunction with medialization thyroplasty.
Laryngotracheal reconstruction is a surgical procedure that involves expanding or removing parts of the airway to widen a narrowing within it, called laryngotracheal stenosis or subglottic stenosis.
Facial masculinization surgery (FMS) is a set of plastic surgery procedures that can transform the patient's face to exhibit typical masculine morphology. Cisgender men may elect to undergo these procedures, and in the context of transgender people, FMS is a type of facial gender confirmation surgery (FGCS), which also includes facial feminization surgery (FFS) for transgender women.

Feminization laryngoplasty is a reconstructive surgery surgical procedure that results in the increase of the pitch of a patient, making the voice sound higher and more feminine. It is a form of Open Laryngoplasty and effectively reaches its goals via a Partial Laryngectomy of the anterior portion of the larynx, thereby diminishing the size of the larynx to cisgender female proportions. It also changes the vocal weight or resonance quality of the voice by diminishing the size of the larynx. It is a type of voice feminization surgery (VFS) and an alternative to vocal therapy. Feminization laryngoplasty is performed as a treatment for both transgender women and non-binary people as part of their gender transition, and women with androphonia. The surgery can be categorized into two main steps: Incision and vocal fold modification followed by thyrohyoid elevation. Risks and complications include granuloma, dysphonia and tracheostomy. Patients are recommended to follow perioperative management such as voice rest to hasten recovery.
References
- 1 2 "FFS: Trachea shave". 2005-06-21. Archived from the original on 2005-06-21. Retrieved 2021-06-28.
- ↑ "Facial Feminization Surgery - Tracheal shave - Removing the Adam's apple". 2pass Clinic. Retrieved 2021-06-28.
- ↑ Thomas, James (2022). "Feminization Laryngoplasty - A Comprehensive Approach to Reducing the Size of the Larynx and Pharynx". Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America. NIH. 55 (4): 739–748. doi:10.1016/j.otc.2022.05.002. PMID 35750518. S2CID 249934885 . Retrieved 20 August 2023.
- 1 2 3 Wolfort, Francis G.; Parry, Richard G. (October 1975). "Laryngeal Chondroplasty for Appearance". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 56 (4): 371–374. doi:10.1097/00006534-197510000-00001. ISSN 0032-1052. PMID 1161910. S2CID 41632068.
- 1 2 3 Spiegel, Jeffrey H.; Rodriguez, Gerardo (2008-07-21). "Chondrolaryngoplasty Under General Anesthesia Using a Flexible Fiberoptic Laryngoscope and Laryngeal Mask Airway". Archives of Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery. 134 (7): 704–708. doi:10.1001/archotol.134.7.704. ISSN 0886-4470. PMID 18645118. S2CID 667521.
- ↑ Kreukels, Baudewijntje P.C.; Steensma, Thomas D.; de Vries, Annelou L.C., eds. (2013-07-01). Gender Dysphoria and Disorders of Sex Development: Progress in Care and Knowledge. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 303. ISBN 978-1-4614-7441-8.
- ↑ Therattil, Paul J.; Hazim, Nemesis Y.; Cohen, Wess A.; Keith, Jonathan D. (2019-12-01). "Esthetic reduction of the thyroid cartilage: A systematic review of chondrolaryngoplasty". JPRAS Open. 22: 27–32. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2019.07.002. ISSN 2352-5878. PMC 7061662 . PMID 32158894.
- 1 2 Cohen, Michael B.; Insalaco, Louis F.; Tonn, Christopher R.; Spiegel, Jeffrey H. (2018-10-03). "Patient Satisfaction after Aesthetic Chondrolaryngoplasty". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Global Open. 6 (10): e1877. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000001877. ISSN 2169-7574. PMC 6250475 . PMID 30534483.