
A lynx is any of the four species within the medium-sized wild cat genus Lynx. The name lynx originated in Middle English via Latin from the Greek word λύγξ, derived from the Indo-European root leuk- in reference to the luminescence of its reflective eyes.

A raven is any of several larger-bodied bird species of the genus Corvus. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between "crows" and "ravens", and these appellations have been assigned to different species chiefly on the basis of their size.

Taiga, generally referred to in North America as a boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches.

Sorghum is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family (Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species, Sorghum bicolor, was originally domesticated in Africa and has since spread throughout the globe. Seventeen of the 25 species are native to Australia, with the range of some extending to Africa, Asia, Mesoamerica, and certain islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. One species is grown for grain, while many others are used as fodder plants, either cultivated in warm climates worldwide or naturalized in pasture lands. Sorghum is in the subfamily Panicoideae and the tribe Andropogoneae.

The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion. The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west.

The northern pike is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus Esox. They are typical of brackish and fresh waters of the Northern Hemisphere. They are known simply as a pike in Britain, Ireland, and most of Eastern Europe, Canada and the United States.

Larches are deciduous conifers in the genus Larix, of the family Pinaceae. Growing from 20 to 45 metres tall, they are native to much of the cooler temperate northern hemisphere, on lowlands in the north and high on mountains further south. Larches are among the dominant plants in the boreal forests of Siberia and Canada. Although they are conifers, larches are deciduous trees that lose their needles in the autumn.

Ireland is an island in the North Atlantic. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the second-largest island of the British Isles, the third-largest in Europe, and the twentieth-largest on Earth.

The pintail or northern pintail is a duck species with wide geographic distribution that breeds in the northern areas of Europe and across the Palearctic and North America. It is migratory and winters south of its breeding range to the equator. Unusually for a bird with such a large range, it has no geographical subspecies if the possibly conspecific duck Eaton's pintail is considered to be a separate species.

The northern shoveler, known simply in Britain as the shoveler, is a common and widespread duck. It breeds in northern areas of Europe and across the Palearctic and across most of North America, wintering in southern Europe, the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, Central, the Caribbean, and northern South America. It is a rare vagrant to Australia. In North America, it breeds along the southern edge of Hudson Bay and west of this body of water, and as far south as the Great Lakes west to Colorado, Nevada, and Oregon.

The northern cardinal is a bird in the genus Cardinalis; it is also known colloquially as the redbird, common cardinal, red cardinal, or just cardinal. It can be found in southeastern Canada, through the eastern United States from Maine to Minnesota to Texas, and south through Mexico, Belize, and Guatemala. It is also an introduced species in a few locations such as Bermuda and Hawaii. Its habitat includes woodlands, gardens, shrublands, and wetlands.
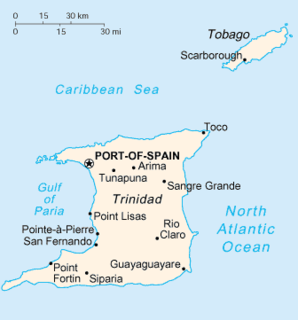
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies 11 km (6.8 mi) off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmost island in the West Indies. With an area of 4,768 km2 (1,841 sq mi), it is also the fifth largest in the West Indies.

The white rhinoceros or square-lipped rhinoceros is the largest extant species of rhinoceros. It has a wide mouth used for grazing and is the most social of all rhino species. The white rhinoceros consists of two subspecies: the southern white rhinoceros, with an estimated 19,682–21,077 wild-living animals in the year 2015, and the much rarer northern white rhinoceros. The northern subspecies has very few remaining individuals, with only two confirmed left in 2018, both in captivity. Sudan, the world's last known male northern white rhinoceros, died in Kenya on 19 March 2018.

A crow is a bird of the genus Corvus, or more broadly a synonym for all of Corvus. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of species including:

The northern giraffe, also known as three-horned giraffe, is the type species of giraffe native to North Africa.

The Holarctic realm is a biogeographic realm that comprises the majority of habitats found throughout the continents in the Northern Hemisphere. It corresponds to the floristic Boreal Kingdom. It includes both the Nearctic zoogeographical region, and Alfred Wallace's Palearctic zoogeographical region, and all of Eurasia except for the southern Arabian Peninsula.

Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of 209,331 km2 (80,823 sq mi), it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island, and the ninth-largest island in the world. The island is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The 60% smaller island of Ireland is to the west – and together these islands, along with over 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, form the British Isles archipelago.

Anteater is a common name for the four extant mammal species of the suborder Vermilingua commonly known for eating ants and termites. The individual species have other names in English and other languages. Together with the sloths, they are within the order Pilosa. The name "anteater" is also commonly applied to the unrelated aardvark, numbat, echidnas, pangolins, and some members of the Oecobiidae.

Hakea lorea, commonly known as bootlace oak or cork tree, is a species of shrub or small tree in the family Proteaceae found in central and northern Australia. It has needle-shape leaves, yellow, white or green flowers and hard corky bark.
FloraNT is a public access web-based database of the Flora of the Northern Territory. It provides authoritative scientific information on some 4300 native taxa, including descriptions, maps, images, conservation status, nomenclatural details together with names used by various aboriginal groups. Alien taxa are also recorded. Users can access fact sheets on species and some details of the specimens held in the Northern Territory Herbarium, together with keys, and some regional factsheets.


















