
Alder is the common name of a genus of flowering plants, Alnus, belonging to the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few species extending into Central America, as well as the northern and southern Andes.

A melon is any of various plants of the family Cucurbitaceae with sweet, edible, and fleshy fruit. The word "melon" can refer to either the plant or specifically to the fruit. Botanically, a melon is a kind of berry, specifically a "pepo". The word melon derives from Latin melopepo, which is the latinization of the Greek μηλοπέπων (mēlopepōn), meaning "melon", itself a compound of μῆλον (mēlon), "apple, treefruit " and πέπων (pepōn), amongst others "a kind of gourd or melon". Many different cultivars have been produced, particularly of cantaloupes.

The hobo spider is a member of the genus of spiders known colloquially as funnel web spiders, but not to be confused with the Australian funnel-web spider. Individuals construct a funnel-shaped structure of silk sheeting and lie in wait at the small end of the funnel for prey insects to blunder onto their webs. Hobo spiders sometimes build their webs in or around human habitations. The hobo spider lays its eggs in September and they hatch during late spring. After the male hobo spider mates it dies.

The Agelenidae are a large family of spiders in the suborder Araneomorphae. Well-known examples include the common "grass spiders" of the genus Agelenopsis. Nearly all Agelenidae are harmless to humans, but the bite of the hobo spider may be medically significant, and some evidence suggests it might cause necrotic lesions. However, the matter remains subject to debate. The most widely accepted common name for members of the family is funnel weaver.

Marah fabacea, the California manroot, bigroot or regionally as space pods, is the most common of the manroot species native to California. Its range throughout the state subsumes nearly the entire ranges of all the other California native manroots species and intergrades. Hybrids between California manroot and other species of Marah are common.

Limonium is a genus of 120 flowering plant species. Members are also known as sea-lavender, statice, caspia or marsh-rosemary. Despite their common names, species are not related to the lavenders or to rosemary. They are instead in Plumbaginaceae, the plumbago or leadwort family. The generic name is from the Latin līmōnion, used by Pliny for a wild plant and is ultimately derived from the Ancient Greek leimon.

Carl Johann Maximovich was a Russian botanist. Maximovich spent most of his life studying the flora of the countries he had visited in the Far East, and naming many new species. He worked at the Saint Petersburg Botanical Gardens from 1852 as curator of the herbarium collection, becoming Director in 1869.

The field vole or short-tailed vole is a grey-brown vole, around 10 cm in length, with a short tail. It is one of the most common mammals in Europe, with a range extending from the Atlantic coast to Lake Baikal. These voles are found in moist grassy habitats, such as woodland, marsh or on river banks. Although they make shallow burrows, they usually build nests above ground. They are an important food source for owls and some other predators and their population size tends to peak and trough cyclically. Field voles breed prolifically, mainly in summer, but often all year round, even under snow. Females produce up to seven litters a year, each averaging from four to six young which are weaned after about fourteen days. The field vole is both widespread and common and is listed as being of "Least Concern" by the IUCN.
Circaeasteraceae is a family of two species of herbaceous plants native to China and the Himalayas.

Mentha arvensis, the corn mint, field mint, or wild mint, is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae. It has a circumboreal distribution, being native to the temperate regions of Europe and western and central Asia, east to the Himalaya and eastern Siberia, and North America. Mentha canadensis, the related species, is also included in Mentha arvensis by some authors as two varieties, M. arvensis var. glabrata Fernald and M. arvensis var. piperascens Malinv. ex L. H. Bailey.

Kingdonia uniflora is a species of perennial herbs native to China. The plants have one leaf and a short (100 mm) flower stalk with a small (8 mm) flower.
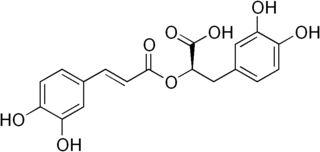
Rosmarinic acid is a chemical compound found in a variety of plants. It was found to exhibit photoprotective effect against ultraviolet C (UVC) damage when examined in vitro.

Gomphrena agrestis is a plant native to Cerrado vegetation in Brazil. This plant is cited in Flora Brasiliensis by Carl Friedrich Philipp von Martius.

Agoseris is a small genus of annual or perennial herbs in the Asteraceae or sunflower family described as a genus in 1817.

Fritillaria agrestis is a species of fritillary known by the common name stinkbells. It is endemic to California, where it is found in scattered populations from Mendocino County and Butte County to Ventura County. It grows in heavy soils, particularly clay. It is not common.

Cucumis melo, also known as melon, is a species of Cucumis that has been developed into many cultivated varieties. The fruit is a pepo. The flesh is either sweet or bland, with or without a musky aroma, and the rind can be smooth, ribbed, wrinkled, or netted. In North America, the sweet-flesh varieties are often collectively called muskmelon, including the musky netted-rind varieties and the inodorous smooth-rind varieties, and cantaloupe usually means the former type. However, muskmelon in a narrow sense only refers to the musky netted-rind type, while the true cantaloupe is the European type with ribbed and often warty rind that is seldom grown in North America.

The flora of China is diverse. More than 30,000 plant species are native to China, representing nearly one-eighth of the world's total plant species, including thousands found nowhere else on Earth.

Anthoceros agrestis, commonly called field hornwort, is a bryophyte of the genus Anthoceros. It has complicated taxonomies.
Helianthus agrestis is a species of sunflower known by the common name southeastern sunflower. It is one of 150 sunflower species in the genus Helianthus. It is found only in the states of Florida and Georgia in the southeastern United States. This plant is native to Florida. It grows in wet soil in marshes and pine flatwoods at elevations less than 50 meters elevation.
A. agrestis may refer to:

















