
Gmelina leichhardtii, the white beech, is a tree of eastern Australia. Scattered individuals or small groups of trees naturally occur from the Illawarra district of New South Wales to near Proserpine in tropical Queensland. The white beech or grey teak is a fast-growing tree, growing on volcanic and alluvial soils in areas of moderate to high rainfall. It also grows on poorer sedimentary soils in fire free areas. White beech may occasionally be seen in Australian rainforests, though their status is considered "uncommon". Unlike the Australian red cedar, the white beech has not recovered particularly well after logging in the 19th and 20th centuries.

Syzygium moorei is a rare sub tropical rainforest tree, growing on volcanic soils in the Mount Warning area of north east New South Wales and south east Queensland, Australia. Common names include coolamon, watermelon tree, durobby and robby; it is also called "rose apple" but this can refer to many species of Syzygium.

Diospyros pentamera is a common rainforest tree in the Ebony or Persimmon family (Ebenaceae) growing from near Batemans Bay in New South Wales to the Atherton Tableland in tropical Queensland, Australia. It is commonly known as the myrtle ebony, black myrtle, grey plum or grey persimmon.

Cryptocarya microneura is a rainforest tree growing at the eastern coastal parts of Australia.

Pararchidendron pruinosum is an Australian rainforest tree growing from the Shoalhaven River in New South Wales to Herberton in north Queensland. It is also found in New Guinea and Indonesia. Common names include Snow-wood, Tulip Siris and Monkey's Earrings. The habitat of the Snow-wood is tropical, sub-tropical, warm temperate, littoral and riverine rainforest. Like most legume species, it fixes atmospheric nitrogen in the soil via its symbiotic partnership with root bacteria - trading the bacteria starches in exchange for nitrogen. It can be seen growing on sand within earshot of Seven Mile Beach, New South Wales.

Cryptocarya glaucescens, commonly known as jackwood, is a rainforest tree of the laurel family growing in eastern Australia.

Endiandra sieberi, known as the corkwood is a rainforest tree growing in eastern Australia.

Emmenosperma alphitonioides, the yellow ash or bonewood, is a rainforest tree of eastern Australia. It grows from Clyde River, New South Wales near Batemans Bay, to Cape York Peninsula in at the most northerly part of Australia. It grows in many different types of rainforest, in tropical, sub tropical and warm temperate rainforests.

Symplocos stawellii, or the white hazelwood, is a rainforest tree growing in eastern Australia. It often grows along creeks in gullies, in tropical and sub-tropical rainforests. The natural distribution is from Gerringong Creek in the upper Kangaroo Valley of New South Wales to the Atherton Tableland in tropical Queensland. It also occurs in New Guinea.

Pennantia cunninghamii, known as the brown beech, is a rainforest tree of eastern Australia. The range of natural distribution is from Clyde Mountain near Batemans Bay in southern New South Wales to Atherton in tropical Queensland.

Stenocarpus salignus, known as the scrub beefwood is an Australian rainforest tree in the family Proteaceae. Found in warmer rainforests on the coast and ranges. It is often found in warm temperate rainforest on poorer sedimentary soils, or on volcanic soils above 750 metres above sea level. It was originally described by the botanist Robert Brown in 1810.

Waterhousea floribunda is a rainforest tree of eastern Australia. It grows along streams from the Williams River near Dungog to Mackay in central eastern Queensland. Known as the weeping lilli pilli, this tree is widely planted as an ornamental. Planted trees from 1827 may be seen at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Sydney. However, these trees are damaged and threatened by the roosting grey headed flying foxes. A very large tree is located at Western Park in Auckland, New Zealand.

Vitex lignum-vitae, known in Australia as yellow hollywood or "lignum-vitae", is a rainforest tree of eastern Australia. The natural range of distribution is in dry, sub-tropical or tropical rainforest from the Richmond River, New South Wales to Cape York Peninsula at the northernmost tip of Australia. It also occurs in New Guinea. Lignum vitae is Latin for "wood of life".

Macaranga tanarius is a plant found in South East Asia, Thailand, Papua New Guinea, Taiwan, and eastern Australia. It is commonly seen as a pioneer species in disturbed rainforest areas. Easily recognised for the round veiny leaves. In Australia it naturally occurs from the Richmond River, New South Wales to Cooktown in tropical Queensland.

Cryptocarya triplinervis is a rainforest tree growing in eastern Australia. Common names include the three veined laurel, three veined cryptocarya and the brown laurel.

Cryptocarya meissneriana, known as the thick-leaved laurel is a small tree growing in eastern Australia. The habitat is rainforest on the poorer sedimentary soils.
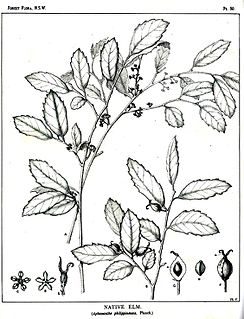
Aphananthe philippinensis is a common rainforest tree in the family Cannabaceae. In Australia it occurs from the Manning River in New South Wales to near Herberton in tropical Queensland. It was first described from the island of Luzon in the Philippines, hence the species name. The generic name of Aphananthe refers to insignificant flowers. This plant also occurs on the Solomon Islands and in Papua New Guinea

Helicia glabriflora is a species of rainforest shrubs or small trees occurring in eastern Australia. Common names include smooth or pale helicia, pale, leather or brown oak. They grow naturally in a variety of different rainforest types from the Illawarra, New South Wales to the Townsville area, Queensland. Of all the global diversity of approximately one hundred Helicia species, this one species naturally grows the furthest south, in the Minnamurra Rainforest and the Robertson area, Illawarra, New South Wales, there observed more on the relatively fertile basalt and alluvial soils.

Capparis arborea is a bush or small tree occurring in eastern Australia. The habitat is rainforest; usually riverine, littoral or the drier rainforests. Distributed from the Hunter River, New South Wales to Cape Melville in tropical Queensland. Common names include native pomegranate, wild lime, wild lemon and brush caper berry.

Endiandra compressa, the white bark, is a rainforest tree growing in eastern Australia. The habitat is rainforest growing near streams in valleys. The range of natural distribution is from the Nambucca River, New South Wales to Iron Range National Park, in north Queensland.


























