
A dictator is a political leader who possesses absolute power. A dictatorship is a state ruled by one dictator or by a polity. The word originated as the title of a Roman dictator elected by the Roman Senate to rule the republic in times of emergency. Like the terms "tyrant" and "autocrat", dictator came to be used almost exclusively as a non-titular term for oppressive rule. In modern usage the term dictator is generally used to describe a leader who holds or abuses an extraordinary amount of personal power.
A dictatorship is an autocratic form of government which is characterized by a leader, or a group of leaders, who hold governmental powers with few to no limitations. Politics in a dictatorship are controlled by a dictator, and they are facilitated through an inner circle of elites that includes advisers, generals, and other high-ranking officials. The dictator maintains control by influencing and appeasing the inner circle and repressing any opposition, which may include rival political parties, armed resistance, or disloyal members of the dictator's inner circle. Dictatorships can be formed by a military coup that overthrows the previous government through force or they can be formed by a self-coup in which elected leaders make their rule permanent. Dictatorships are authoritarian or totalitarian, and they can be classified as military dictatorships, one-party dictatorships, personalist dictatorships, or absolute monarchies.
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
Autocracy is a system of government in which absolute power is held by the head of state, known as an autocrat. It includes some forms of monarchy and all forms of dictatorship, while it is contrasted with democracy and feudalism. Various definitions of autocracy exist. They may restrict autocracy to cases where power is held by a single individual, or they may define autocracy in a way that includes a group of rulers who wield absolute power. The autocrat has total control over the exercise of civil liberties within the autocracy, choosing under what circumstances they may be exercised, if at all. Governments may also blend elements of autocracy and democracy, forming an anocracy. The concept of autocracy has been recognized in political philosophy since ancient times.
A military dictatorship, or a military regime, is a type of dictatorship in which power is held by one or more military officers. Military dictatorships are led by either a single military dictator, known as a strongman, or by a council of military officers known as a military junta. They are most often formed by military coups or by the empowerment of the military through a popular uprising in times of domestic unrest or instability. The military nominally seeks power to restore order or fight corruption, but the personal motivations of military officers will vary.
Führer is a German word meaning "leader" or "guide". As a political title, it is strongly associated with Adolf Hitler, the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945. Hitler officially styled himself der Führer und Reichskanzler after the death of President Paul von Hindenburg in 1934 and the subsequent merging of the offices of Reichspräsident and Reichskanzler.

The Enabling Act of 1933, officially titled Gesetz zur Behebung der Not von Volk und Reich, was a law that gave the German Cabinet – most importantly, the Chancellor – the power to make and enforce laws without the involvement of the Reichstag or Weimar President Paul von Hindenburg, leading to the rise of Nazi Germany. Critically, the Enabling Act allowed the Chancellor to bypass the system of checks and balances in the government.

Ioannis Metaxas was a Greek military officer and politician who was dictator of Greece from 1936 until his death in 1941. He governed constitutionally for the first four months of his tenure, and thereafter as the strongman leader of the 4th of August Regime following his appointment by King George II.

The president of Germany was the head of state under the Weimar Constitution, which was officially in force from 1919 to 1945, encompassing the periods of the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany.

Higinio Nicolás Morínigo Martínez was a Paraguayan military officer and politician who served as the 35th president of Paraguay from 1940 to 1948, ruling as a military dictator.
Article 48 of the constitution of the Weimar Republic of Germany (1919–1933) allowed the Reich president, under certain circumstances, to take emergency measures without the prior consent of the Reichstag. This power came to be understood to include the promulgation of emergency decrees. It was used frequently by Reich President Friedrich Ebert of the Social Democratic Party to deal with both political unrest and economic emergencies. Later, under President Paul von Hindenburg and the presidential cabinets, Article 48 was called on more and more often to bypass a politically fractured parliament and to rule without its consent. After the Nazi Party's rise to power in the early 1930s, the law allowed Chancellor Adolf Hitler, with decrees issued by Hindenburg, to create a totalitarian dictatorship by seemingly legal means.

During its independent political history, Brazil has had seven constitutions. The most recent was ratified on October 5, 1988.

Gregorio Conrado Álvarez Armelino, also known as El Goyo, was a Uruguayan Army general who served as president of Uruguay from 1981 until 1985 and was the last surviving president of the civic-military dictatorship.

The 4th of August Regime, commonly also known as the Metaxas regime, was a fascist regime under the leadership of General Ioannis Metaxas that ruled the Kingdom of Greece from 1936 to 1941.

Adolf Hitler's rise to power began in the newly established Weimar Republic in September 1919 when Hitler joined the Deutsche Arbeiterpartei. He rose to a place of prominence in the early years of the party. Being one of its most popular speakers, he was made the party leader after he threatened to otherwise leave.
The May 1958 crisis, also known as the Algiers putsch or the coup of 13 May, was a political crisis in France during the turmoil of the Algerian War of Independence (1954–1962) which led to the collapse of the Fourth Republic and its replacement by the Fifth Republic led by Charles de Gaulle who returned to power after a twelve-year absence. It started as a political uprising in Algiers on 13 May 1958 and then became a military coup d'état led by a coalition headed by Algiers deputy and reserve airborne officer Pierre Lagaillarde, French Generals Raoul Salan, Edmond Jouhaud, Jean Gracieux, and Jacques Massu, and by Admiral Philippe Auboyneau, commander of the Mediterranean fleet. The coup was supported by former Algerian Governor General Jacques Soustelle and his activist allies.
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political status quo, and reductions in democracy, separation of powers, civil liberties, and the rule of law. Political scientists have created typologies describing variations of authoritarian forms of government. Authoritarian regimes may be either autocratic or oligarchic and may be based upon the rule of a party or the military. States that have a blurred boundary between democracy and authoritarianism have some times been characterized as "hybrid democracies", "hybrid regimes" or "competitive authoritarian" states.

Various historians and other authors have carried out a comparison of Nazism and Stalinism, with particular consideration to the similarities and differences between the two ideologies and political systems, the relationship between the two regimes, and why both came to prominence simultaneously. During the 20th century, comparisons of Nazism and Stalinism were made on totalitarianism, ideology, and personality cult. Both regimes were seen in contrast to the liberal democratic Western world, emphasising the similarities between the two.

Metaxism is a Greek authoritarian, ultra-nationalist, and monarchist ideology associated with Ioannis Metaxas. It called for the regeneration of the Greek nation and the establishment of a modern, culturally homogenous Greece. Metaxism disparaged liberalism, and held individual interests to be subordinate to those of the nation, seeking to mobilize the Greek people as a disciplined mass in service to the creation of a "new Greece."
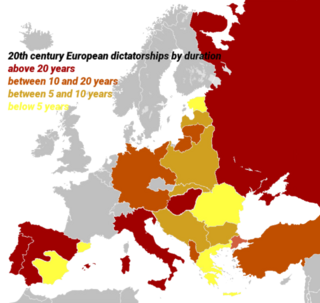
This is a list of dictatorial regimes operational in European states in the interwar period, the period between World War I and World War II.












