Related Research Articles

The Guinean Armed Forces are the armed forces of Guinea. They are responsible for the territorial security of Guinea's border and the defence of the country against external attack and aggression.

Lansana Conté was a Guinean politician and military official who served as the second president of Guinea, from 3 April 1984 until his death on 22 December 2008. Conté came to power in the 1984 Guinean coup d'état.

Amadou Toumani Touré was a Malian politician. He supervised Mali's first multiparty elections as chairman of the transitional government (1991–1992), and later became the second democratically elected President of Mali (2002–2012).

Cellou Dalein Diallo is a Guinean economist and politician who was Prime Minister of Guinea from 2004 to 2006. Previously he held a succession of ministerial posts in the government from 1996 to 2004. Currently he is President of the Union of Democratic Forces of Guinea (UFDG), an opposition party. He was a candidate in the 2020 Guinean presidential election but lost to incumbent Alpha Condé.

Ali Bongo Ondimba, also known as Ali Bongo and Ali Ben Bongo, is a Gabonese former politician who was the third president of Gabon from 2009 to 2023. He is a member of the Gabonese Democratic Party. He is the son of Omar Bongo, who was president of Gabon from 1967 until his death in 2009. During his father's presidency, he was Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1989 to 1991, represented Bongoville as a deputy in the National Assembly from 1991 to 1999, and was the Minister of Defense from 1999 to 2009. After his father's death, he won the 2009 Gabonese presidential election. He was reelected in 2016, in elections marred by numerous irregularities, arrests, human rights violations, and post-election protests and violence.

Alpha Condé is a Guinean politician who served as the fourth president of Guinea from 2010 to 2021.

Sidya Touré is a Guinean politician. He was Prime Minister of Guinea from 1996 to 1999 and is currently the President of the Union of Republican Forces (UFR), an opposition party.

El Hajj Aboubacar Somparé was a Guinean politician who was President of the National Assembly of Guinea from 2002 to 2008. He was previously Guinea's Ambassador to France from 1978 to 1984 and was Secretary-General of the Unity and Progress Party (PUP) from 1995 to 2002.
Ahmed Tidiane Souaré is a Guinean political figure who was the Prime Minister of Guinea from May 2008 to December 2008, when he was replaced by Kabine Komara following a military coup d'état.

The 2008 Guinean coup d'état occurred in Guinea on 23 December 2008, shortly after the death of long-time President Lansana Conté. A junta called the National Council for Democracy and Development, headed by Captain Moussa Dadis Camara, seized power and announced that it planned to rule the country for two years prior to a new presidential election. Camara did indeed step down after Alpha Condé was elected in the 2010 election.

Captain Moussa Dadis Camara, now called Moïse Dadis Camara, is an ex-officer of the Guinean army who served as the President of Guinea from 23 December 2008 to 15 January 2010. He was the leader of the National Council for Democracy and Development, which seized power in a military coup d'état on 23 December 2008 shortly after the death of long-time president Lansana Conté.

The National Council for Democracy and Development was the ruling junta of Guinea from 2008 to 2010.
The 2009 Guinean protests were an opposition rally in Conakry, Guinea on Monday, 28 September 2009, with about 50,000 participants protesting against the junta government that came to power after the Guinean coup d'état of December 2008. The protest march was fueled by the indication of junta leader Captain Moussa Dadis Camara breaking his pledge to not run in the next presidential vote due in January 2010. The government had already banned any form of protests until 2 October, and when the demonstrators gathered in a large stadium, the security forces opened fire at them. At least 157 demonstrators were killed, 1,253 injured and 30, including Cellou Dalein Diallo, the leader of the opposition Union of Democratic Forces of Guinea (UDFG), were arrested and taken away in lorries.
Jean-Marie Doré was a Guinean politician who was the prime minister of Guinea from January 2010 until December 2010. Doré, who was the president of the Union for the Progress of Guinea (UPG), was an opposition leader for years before being chosen to head a transitional government that was in place during the preparation and conduct of the 2010 presidential election.

The Mali War is an ongoing, armed conflict that started in January 2012 between the northern and southern parts of Mali in Africa. On 16 January 2012, several insurgent groups began fighting a campaign against the Malian government for independence or greater autonomy for northern Mali, which they called Azawad. The National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad (MNLA), an organization fighting to make this area of Mali an independent homeland for the Tuareg people, had taken control of the region by April 2012.

Gilbert Diendéré is a Burkinabé military officer and the Chairman of the National Council for Democracy, the military junta that briefly seized power in Burkina Faso in the September 2015 coup d'état. He was a long-time aide to President Blaise Compaoré, serving as commander of the Regiment of Presidential Security (RSP) during Compaoré's rule. He was appointed as chairman of the junta on 17 September 2015.

General Évariste Ndayishimiye is a Burundian politician, who has served as President of Burundi since 18 June 2020. He became involved in the rebel National Council for the Defense of Democracy – Forces for the Defense of Democracy during the Burundian Civil War and rose up the ranks of its militia. At the end of the conflict, he entered the Burundian Army and held a number of political offices under the auspices of President Pierre Nkurunziza. Nkurunziza endorsed Ndayishimiye as his successor ahead of the 2020 elections which he won with a large majority.

Mamady Doumbouya is a Guinean military officer serving as the interim president of Guinea since 1 October 2021. Doumbouya led a coup d'état on 5 September 2021 that overthrew the previous president, Alpha Condé. He is a member of the Guinean Special Forces Group and a former French legionnaire. On the day of the coup, Doumbouya issued a broadcast on state television declaring that his faction had dissolved the government and constitution. On 1 October 2021, Doumbouya was sworn in as interim president.
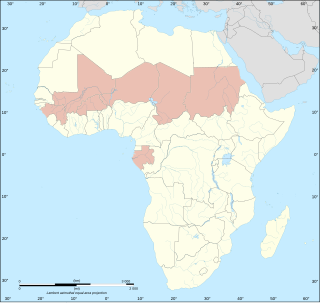
The Coup Belt is a modern geopolitical concept and neologism which emerged during the 2020s to describe the region of West Africa, Central Africa and the Sahel, a region with a high prevalence of coup d'états.
On 4 November 2023, armed men raided the Maison Centrale de Conakry prison and broke out former President of Guinea Moussa Dadis Camara and three other officials. The raid killed nine people and injured six others.
References
- 1 2 "Guinea stadium massacre: Minister Claude Pivi charged". BBC. 28 June 2013. Retrieved 19 May 2015.
- ↑ "Africanews | Commando operation in Guinea: reward offered for the capture of the last fugitive". Africanews. 2023-11-09. Retrieved 2023-11-20.
- ↑ "Guinea junta purges security services after ex-dictator's jailbreak". Monitor. 2023-11-06. Retrieved 2023-11-20.
- ↑ "En Guinée, les autorités offrent une récompense pour la capture de Claude Pivi, dernier évadé toujours en fuite" [In Guinea, authorities offer a reward for the capture of Claude Pivi, the last escapee still on the run] (in French). LeMonde. 9 November 2023. Retrieved 10 November 2023.