
Blists Hill Victorian Town is an open-air museum built on a former industrial complex located in the Madeley area of Telford, Shropshire, England. The museum attempts to recreate the sights, sounds and smells of a Victorian Shropshire town in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It is one of ten museums operated by the Ironbridge Gorge Museum Trust.

Snailbeach District Railways was a British narrow gauge railway in Shropshire. It was built to carry lead ore from mines in the Stiperstones to Pontesbury where the ore was transshipped to the Great Western Railway's Minsterley branch line. Coal from the Pontesford coal mines travelled in the opposite direction. The line ended at Snailbeach, the location of Shropshire's largest and richest lead mine, though there had been a plan to extend it further, which would have brought it closer to more lead mines.

Dawley is a constituent town and civil parish in Telford and Wrekin in Shropshire, England. It was originally, in 1963, going to be the main centre of the 'Dawley New Town' plan before it was decided in 1968 to name the new town as 'Telford', after the engineer and road-builder Thomas Telford. Dawley now forms part of Telford which is north of the town itself.

Madeley is a constituent town and civil parish in Telford and Wrekin in Shropshire, England. The parish had a population of 17,935 at the 2001 census.

Coalport is a village in Shropshire, England. It is located on the River Severn in the Ironbridge Gorge, a mile downstream of Ironbridge. It lies predominantly on the north bank of the river; on the other side is Jackfield.

The Wolverhampton–Shrewsbury line is the railway line from Wolverhampton to Shrewsbury via Wellington; it was originally built by the Shrewsbury and Birmingham Railway. The line is double track throughout, with rarely used relief sidings at Cosford and four tracks through Wellington station.

Telford Town Park is a park and Local Nature Reserve in Telford in Shropshire. In 2015, it was voted "UK's Best Park" in the inaugural public competition organised by Fields in Trust

Jackfield is a village in Shropshire, England, lying on the south bank of River Severn in the Ironbridge Gorge, downstream from Ironbridge.
The Wellington to Craven Arms Railway was formed by a group of railway companies that eventually joined the Great Western Railway family, and connected Wellington, Shropshire and Shifnal, with Coalbrookdale, Buildwas, Much Wenlock and a junction near Craven Arms. Its objectives were dominated by the iron, colliery and limestone industries around Coalbrookdale.

Blacon railway station was located in Blacon, Cheshire, England and was part of the line between Chester Northgate and Hawarden Bridge. This line was later extended to reach Wrexham and Birkenhead.
The Wycombe Railway was a British railway between Maidenhead and Oxford that connected with the Great Western Railway at both ends; there was one branch, to Aylesbury.

The Shropshire Canal was a tub boat canal built to supply coal, ore and limestone to the industrial region of east Shropshire, England, that adjoined the River Severn at Coalbrookdale. It ran from a junction with the Donnington Wood Canal ascending the 316 yard long Wrockwardine Wood inclined plane to its summit level, it made a junction with the older Ketley Canal and at Southall Bank the Coalbrookdale (Horsehay) branch went to Brierly Hill above Coalbrookdale; the main line descended via the 600 yard long Windmill Incline and the 350 yard long Hay Inclined Plane to Coalport on the River Severn. The short section of the Shropshire Canal from the base of the Hay Inclined Plane to its junction with the River Severn is sometimes referred to as the Coalport Canal.
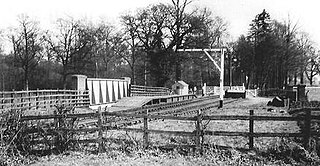
Wood Siding railway station was a halt in Bernwood Forest, Buckinghamshire, England. It opened in 1871 as a terminus of a short horse-drawn tramway built to assist the transport of goods from and around the Duke of Buckingham's extensive estates in Buckinghamshire, as well as connect the Duke's estates to the Aylesbury and Buckingham Railway at Quainton Road.

Farringdon Halt was an intermediate station on the Meon Valley line which ran from Alton to Fareham, England during the 20th century. A goods yard for loading agricultural produce was already sited there, and in 1930 a short wooden platform of one coach-length was built to serve the village. It opened on 1 May 1931, and from 1 May 1932 until 8 July 1934 was named Faringdon Platform, before reverting to the original name of Farringdon Halt.
Southfleet was a railway station on the Gravesend West Line which served the small village of Southfleet in Kent, England.

The Wolverton–Newport Pagnell line was a railway branch line in Buckinghamshire, United Kingdom running from Wolverton on the London and North Western Railway (LNWR) to Newport Pagnell. The line fully opened to passengers in 1867. An extension to Olney was planned in 1865, but this scheme was abandoned after partial construction. Earthworks along the route of the extension still exist in Bury Field, and plaques exist detailing the history of the failed project.

Chester Liverpool Road was a station on the former Chester & Connah's Quay Railway between Chester Northgate and Hawarden Bridge. It was located at the junction of Liverpool Road and Brook Lane in Chester, Cheshire, England.

Madeley Market railway station is a disused railway station in Shropshire, England.

Market Drayton railway station served the town of Market Drayton in Shropshire, England, between 1863 and 1963. It was at the junction where three railway lines met: two of them, forming the Great Western Railway route between Wellington (Shropshire) and Crewe, were met by a line from Stoke-on-Trent on the North Staffordshire Railway.

The Silkin Way is a 23km walking and cycling route through Telford starting in Bratton and finishing in Coalport. In places the path follows the former Great Western Railway and the dry canal beds of the old Shropshire Canal and goes via Telford Town Centre and the Ironbridge Gorge World Heritage Site. Along the route the Silkin Way runs close to the many natural and historical features within Telford and shows great contrasts between futuristic architecture, woodlands, and mature parkland.

















