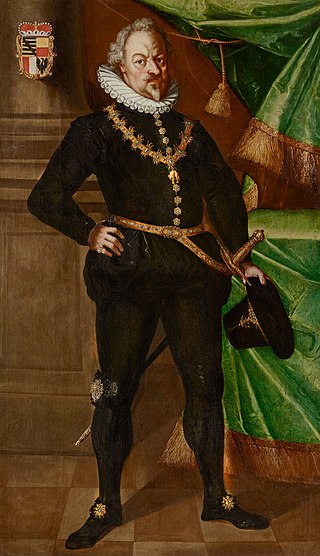The House of Ascania was a dynasty of German rulers. It is also known as the House of Anhalt, which refers to its longest-held possession, Anhalt.

Liechtenstein is a principality governed under a semi-constitutional monarchy. It has a form of mixed constitution in which political power is shared by the monarch and a democratically elected parliament. There is a two-party system and a form of representative democracy in which the prime minister and head of government is responsible to parliament. However the Prince of Liechtenstein is head of state and exercises considerable political powers.

Political identity came to the territory now occupied by the Principality of Liechtenstein in 814, with the formation of the subcountry of Lower Rhætia. Liechtenstein's borders have remained unchanged since 1434, when the Rhine established the border between the Holy Roman Empire and the Swiss cantons.

Vaduz is the capital of Liechtenstein and also the seat of the national parliament. The city, which is located along the Rhine River, has 5,696 residents. The most prominent landmark of Vaduz is Vaduz Castle, perched atop a steep hill overlooking the city. It is home to the reigning prince of Liechtenstein and the Liechtenstein princely family. The city's distinctive architecture is also displayed in landmarks such as the Cathedral of St. Florin, Government House, City Hall, the National Art Gallery, as well as the National Museum. Although Vaduz is the best-known town in the principality internationally, it is not the largest; neighbouring Schaan has a larger population.
Fürst is a German word for a ruler as well as a princely title. Fürsten were, starting in the Middle Ages, members of the highest nobility who ruled over states of the Holy Roman Empire and later its former territories, below the ruling Kaiser (emperor) or König (king).

The national emblem of Belarus features a ribbon in the colors of the national flag, a silhouette of Belarus, wheat ears and a red star. It is sometimes referred to as the coat of arms of Belarus, although in heraldic terms this is inaccurate as the emblem does not respect the rules of conventional heraldry. The emblem is an allusion to one that was used by the Byelorussian SSR, designed by Ivan Dubasov in 1950, with the biggest change being a replacement of the Communist hammer and sickle with a silhouette of Belarus. The Belarusian name is Dziaržaŭny hierb Respubliki Biełaruś, and the name in Russian is Gosudarstvennyĭ gerb Respubliki Belarusʹ.

The flag of Haiti is the national flag of the Republic of Haiti. It is a bicolour flag featuring two horizontal bands coloured blue and red, emblazoned by a white rectangular panel bearing the coat of arms of Haiti. The coat of arms depicts a trophy of weapons atop a green hill and a royal palm symbolizing independence. The palm is topped by the Cap of Liberty. The motto L'Union fait la Force appears on a white ribbon below the arrangement.

Johann II, nicknamed the Good, was Prince of Liechtenstein from 12 November 1858 until his death in 1929.

Franz Joseph II was the reigning Prince of Liechtenstein from 25 July 1938 until his death in November 1989.
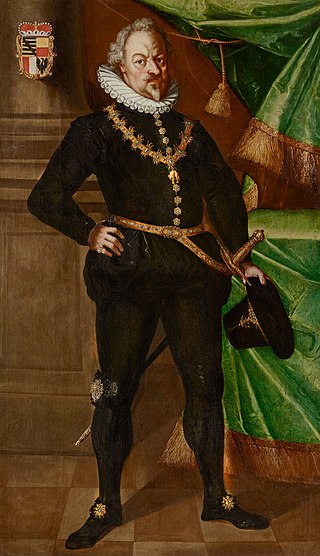
Karl I, was the first member of the Liechtenstein family to become a Monarch of Liechtenstein, thus he was the founder of the Princely Family of Liechtenstein.

Sophie, Hereditary Princess of Liechtenstein, Countess of Rietberg was born a member of the House of Wittelsbach, with the courtesy title of Duchess in Bavaria, and second in line for the Jacobite succession. She is married to Alois, Hereditary Prince and Regent of Liechtenstein.

Gamprin is a municipality of Liechtenstein, on the Rhine on the border with the municipality of Sennwald, in Switzerland. It had 1,690 inhabitants in 2019. The municipality contains the village of Bendern and scattered hamlets and the Liechtenstein Institute and LGT Group.

Prince Constantin of Liechtenstein, known professionally as Constantin Liechtenstein, was a member of the Princely House of Liechtenstein, and a businessman. He was the third son of Prince Hans-Adam II and his wife, Countess Marie Kinsky of Wchinitz and Tettau. He was the chief executive officer of the LGT Group from 2020 to 2023.
Prince Maximilian of Liechtenstein, Count of Rietberg, known professionally as Max von Liechtenstein, is a Liechtensteiner prince and businessman. He is the second son of Hans-Adam II, Prince of Liechtenstein and his wife, Countess Marie Kinsky of Wchinitz and Tettau.
Princess Angela of Liechtenstein, Countess of Rietberg is a Panamanian-American fashion designer and member of the Liechtenstein princely family. Born in Panama and raised in the United States, Angela became the first woman of primarily African descent to marry into a reigning European dynasty. She married Prince Maximilian of Liechtenstein in January 2000 and the couple has a son, Prince Alfons, who is sixth in the line of succession to the Liechtensteiner throne.

Countess Georgina von Wilczek was Princess of Liechtenstein from 1943 to 1989 as the wife of Prince Franz Joseph II. She was the mother of Prince Hans-Adam II and was widely known as Gina.
Liechtenstein heraldry is the form of heraldic art found in the country of Liechtenstein. It does not have a heraldic body of its own, relying on primarily German influences through the ruling house. It follows the German-Nordic tradition.

The monarchy of Liechtenstein is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of Liechtenstein. The current monarch is Prince Hans-Adam II. The House of Liechtenstein, after which the sovereign principality was named in 1719, hails from Liechtenstein Castle in Lower Austria, which the family possessed from at least 1140 to the thirteenth century, and from 1807 onward. It is the only remaining European monarchy that practises strict agnatic primogeniture.

The flag of Tuscany is the official flag of the region of Tuscany, Italy. The flag depicts a silver Pegasus rampant on a white field between two horizontal red bands. The flag first appeared as a gonfalon on 20 May 1975 along with accompanying text Regione Toscana above the Pegasus. It was officially adopted as the flag of Tuscany on 3 February 1995.

The coat of arms of Lower Silesia, and simultaneously of Silesia, shows a black eagle with silver crescent with cross in the middle on its chest on a golden background. It has been assumed in the tradition that the coat of arms and colors of Lower Silesia are simultaneously used as symbols of Silesia as a whole.