Related Research Articles

Olive oil is a liquid fat obtained by pressing whole olives, the fruit of Olea europaea, a traditional tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin, and extracting the oil.

Soul food is an ethnic cuisine originating in the Southern United States historically pertaining to African-Americans. It originated from the cuisines of enslaved Africans trafficked to the North American colonies through the Atlantic slave trade during the Antebellum period and is closely associated with the cuisine of the American South. The expression "soul food" originated in the mid-1960s, when "soul" was a common word used to describe African-American culture. Soul food uses cooking techniques and ingredients from West African, Central African, Western European, and Indigenous cuisine of the Americas. Soul food came from the blending of what African Americans ate in their native countries in Africa and what was available to them as slaves. The cuisine had its share of negativity initially. Soul food was initially seen as low class food, and Northern African Americans looked down on their Black Southern counterparts who preferred soul food. The term evolved from being the diet of a slave in the South to being a primary pride in the African American community in the North such as New York City.

Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp of the fruit of the oil palms. The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel. Palm oil accounted for about 36% of global oils produced from oil crops in 2014. Palm oils are easier to stabilize and maintain quality of flavor and consistency in ultra-processed foods, so are frequently favored by food manufacturers. On average globally, humans consumed 7.7 kg (17 lb) of palm oil per person in 2015. Demand has also increased for other uses, such as cosmetics and biofuels, creating more demand on the supply encouraging the growth of palm oil plantations in tropical countries.

Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of fruits. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are mixtures of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed oils, or fats from seeds. Olive oil, palm oil, and rice bran oil are examples of fats from other parts of fruits. In common usage, vegetable oil may refer exclusively to vegetable fats which are liquid at room temperature. Vegetable oils are usually edible.

Coconut oil is an edible oil derived from the kernels, meat, and milk of the coconut palm fruit. Coconut oil is a white solid fat below around 25 °C (77 °F), and a clear thin liquid oil in warmer climates. Unrefined varieties have a distinct coconut aroma. Coconut oil is used as a food oil, and in industrial applications for cosmetics and detergent production. The oil is rich in medium-chain fatty acids.

The Maya are an ethnolinguistic group of indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica. The ancient Maya civilization was formed by members of this group, and today's Maya are generally descended from people who lived within that historical region. Today they inhabit southern Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, Nicaragua, and Honduras. "Maya" is a modern collective term for the peoples of the region; however, the term was not historically used by the indigenous populations themselves. There was no common sense of identity or political unity among the distinct populations, societies and ethnic groups because they each had their own particular traditions, cultures and historical identity.

The Maya Mountains are a mountain range located in Belize and eastern Guatemala, in Central America.
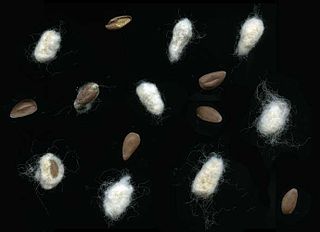
Cottonseed oil is cooking oil from the seeds of cotton plants of various species, mainly Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium herbaceum, that are grown for cotton fiber, animal feed, and oil.

Heart of palm is a vegetable harvested from the inner core and growing bud of certain palm trees, most notably the coconut, juçara, açaí palm, palmetto, and peach palm. Harvesting of many uncultivated or wild single-stemmed palms results in palm tree death. However, other palm species are clonal or multi-stemmed plants, and moderate harvesting will not kill the entire clonal palm. Heart of palm may be eaten on its own, and often it is eaten in a salad.

Recado rojo or achiote paste is a popular blend of spices. It is now strongly associated with Mexican and Belizean cuisines, especially of Yucatán and Oaxaca. The spice mixture usually includes annatto, oregano, cumin, clove, cinnamon, black pepper, allspice, garlic, and salt. The annatto seeds dye the mixture red, and impart a distinctive red-orange color to the food.
Lauric acid, systematically dodecanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid with a 12-carbon atom chain, thus having many properties of medium-chain fatty acids. It is a bright white, powdery solid with a faint odor of bay oil or soap. The salts and esters of lauric acid are known as laurates.
Palm kernel oil is an edible plant oil derived from the kernel of the oil palm tree Elaeis guineensis. It is related to other two edible oils: palm oil, extracted from the fruit pulp of the oil palm, and coconut oil, extracted from the kernel of the coconut.

Perilla oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from perilla seeds. Having a distinct nutty aroma and taste, the oil pressed from the toasted perilla seeds is used as a flavor enhancer, condiment, and cooking oil in Korean cuisine. The oil pressed from untoasted perilla seeds is used for non-culinary purposes.

Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, and small parts of Honduras, Nicaragua and Costa Rica. As a cultural area, Mesoamerica is defined by a mosaic of cultural traits developed and shared by its indigenous cultures.
The flora of Belize is highly diverse by regional standards, given the country's small geographical extent. Situated on the Caribbean coast of northern Central America the flora and vegetation have been intimately intertwined with Belize's history. The nation itself grew out of British timber extraction activities from the 17th century onwards, at first for logwood and later for mahogany, fondly called "red gold" because of its high cost and was much sought after by European aristocracy. Central America generally is thought to have gained much of it characteristic flora during the "Great American interchange" during which time South American elements migrated north after the geological closure of the isthmus of Panama. Few Amazonian elements penetrate as far north as Belize and in species composition the forests of Belize are most similar to the forests of the Petén (Guatemala) and the Yucatán (Mexico).

The Maya civilization was a Mesoamerican civilization that existed from antiquity to the early modern period. It is known by its ancient temples and glyphs (script). The Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. The civilization is also noted for its art, architecture, mathematics, calendar, and astronomical system.

Fried chicken, also known as Southern fried chicken, is a dish consisting of chicken pieces that have been coated with seasoned flour or batter and pan-fried, deep fried, pressure fried, or air fried. The breading adds a crisp coating or crust to the exterior of the chicken while retaining juices in the meat. Broiler chickens are most commonly used.

Attalea cohune, commonly known as the cohune palm, is a species of palm tree native to Mexico and parts of Central America.

Cooking oil is a plant or animal liquid fat used in frying, baking, and other types of cooking. Oil allows higher cooking temperatures than water, making cooking faster and more flavorful, while likewise distributing heat, reducing burning and uneven cooking. It sometimes imparts its own flavor. Cooking oil is also used in food preparation and flavoring not involving heat, such as salad dressings and bread dips.
References
- ↑ Dweck, Anthony (2011). Formulating Natural Cosmetics (PDF). Allured Pub Corp. ISBN 978-1-932633-75-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-12-26. Retrieved 2011-12-14.
- ↑ Axtell, B.L. (1992). "Cohune palm". Minor Oil Crops . from research by R.M. Fairman. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. ISBN 92-5-103128-2. OCLC 26187175 . Retrieved 2007-01-01.
- ↑ Cohune oil at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- ↑ Gann, Thomas W.F. (1918). The Maya Indians of Southern Yucatan and Northern British Honduras (PDF online facsimile of original, digitized [2008] by the Internet Archive). Smithsonian Institution Bureau of American Ethnology Bulletin no. 64. Washington DC: Government Printing Office. pp. 17, 31, 130–131. OCLC 424421.
- ↑ Schlesinger, Victoria (2001). Animals and Plants of the Ancient Maya: A Guide. Juan C. Chab-Medina (illus.), foreword by Carlos Galindo-Leal. Austin: University of Texas Press. pp. 116–119. ISBN 0-292-77759-0. OCLC 46937482.