Related Research Articles

Johannesburg, colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, or "The City of Gold", is the largest city in South Africa, classified as a megacity, and is one of the 100 largest urban areas in the world. According to Demographia, the Johannesburg–Pretoria urban area is the 26th-largest in the world in terms of population, with 14,167,000 inhabitants. It is the provincial capital and largest city of Gauteng, which is the wealthiest province in South Africa. Johannesburg is the seat of the Constitutional Court, the highest court in South Africa. Most of the major South African companies and banks have their head offices in Johannesburg. The city is located in the mineral-rich Witwatersrand range of hills and is the centre of large-scale gold and diamond trade.

Gauteng is one of the nine provinces of South Africa. The name in Sotho-Tswana languages means 'place of gold'.

The effects of climate change impact the physical environment, ecosystems and human societies. The environmental effects of climate change are broad and far-reaching. They affect the water cycle, oceans, sea and land ice (glaciers), sea level, as well as weather and climate extreme events. The changes in climate are not uniform across the Earth. In particular, most land areas have warmed faster than most ocean areas, and the Arctic is warming faster than most other regions. The regional changes vary: at high latitudes it is the average temperature that is increasing, while for the oceans and tropics it is in particular the rainfall and the water cycle where changes are observed. The magnitude of future impacts of climate change can be reduced by climate change mitigation and adaptation.

Climate change adaptation is the process of adjusting to current or expected effects of climate change. For humans, adaptation aims to moderate or avoid harm, and exploit opportunities; for natural systems, humans may intervene to help adjustment. Adaptation actions can be either incremental or transformative. The need for adaptation varies from place to place, depending on the risk to human or ecological systems. Adaptation actions can be grouped into four categories: Infrastructural and technological; institutional; behavioural and cultural; and nature-based options.

Climate change in South Asia is having significant impacts already which are expected to intensify as global temperatures rise due to climate change. The South Asia region consists of the eight countries Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, the Maldives and Sri Lanka. In the 2017 edition of Germanwatch's Climate Risk Index, Bangladesh and Pakistan ranked sixth and seventh respectively as the countries most affected by climate change in the period from 1996 to 2015, while India ranked fourth among the list of countries most affected by climate change in 2015. South Asia is one of the most vulnerable regions globally to a number of direct and indirect effects of climate change, including sea level rise, cyclonic activity, and changes in ambient temperature and precipitation patterns. Ongoing sea level rise has already submerged several low-lying islands in the Sundarbans region, displacing thousands of people.

The IPCC Fourth Assessment Report (AR4) is a report on climate change created with the help of a large number of contributors, both scientists and governmental representatives. There has been considerable political controversy over a small number of errors found in the report, and there have been calls for review of the process used to formulate the report. The overwhelming majority view of scientists with expertise in climate change is that errors, when found, are corrected, and the issues as identified do not undermine the conclusions of the report that the climate system is warming in response to increased levels of greenhouse gases, largely due to human activities.
The Burtoni Award was created in 2003 by a group of leading experts and policy makers in the field of climate change. It is named for the Canadian science pioneer Ian Burton. Its purpose is to recognize outstanding contributions to the science of adaptation to climate change. The award is named after the first recipient of the award, Ian Burton, an emeritus professor at the University of Toronto and a pioneer in the field of adaptation to climate change and extreme events and disasters. Ian has contributed to three assessment reports of the IPCC and the recent Special Report on Extremes (SREX).
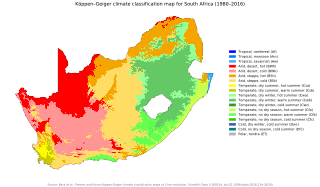
The climate of South Africa is determined by South Africa's situation between 22°S and 35°S, in the Southern Hemisphere's subtropical zone, and its location between two oceans, Atlantic and the Indian.

Saleemul Huq is a Bangladeshi-British scientist and has been the Director of the International Centre for Climate Change & Development (ICCCAD) based in Bangladesh, also Professor at Independent University, Bangladesh (IUB). He was elected one of Nature's 10 Ones in 2022.

The economic impacts of climate change vary geographically and are difficult to forecast exactly. Researchers have warned that current economic forecasts may seriously underestimate the effects of climate change, and point to the need for new models that give a more accurate picture of potential damages. Nevertheless, one 2018 study found that potential global economic gains if countries implement mitigation strategies to comply with the 2 °C target set at the Paris Agreement are in the vicinity of US$17 trillion per year up to 2100 compared to a very high emission scenario.
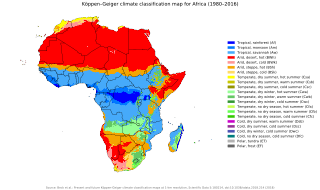
The climate of Africa is a range of climates such as the equatorial climate, the tropical wet and dry climate, the tropical monsoon climate, the semi-arid climate, the desert climate, the humid subtropical climate, and the subtropical highland climate. Temperate climates are rare across the continent except at very high elevations and along the fringes. In fact, the climate of Africa is more variable by rainfall amount than by temperatures, which are consistently high. African deserts are the sunniest and the driest parts of the continent, owing to the prevailing presence of the subtropical ridge with subsiding, hot, dry air masses. Africa holds many heat-related records: the continent has the hottest extended region year-round, the areas with the hottest summer climate, the highest sunshine duration, and more.

Climate change in Bangladesh is a critical issue as the country is one of the most vulnerable to the effects of climate change. In the 2020 edition of Germanwatch's Climate Risk Index, it ranked seventh in the list of countries most affected by climate calamities during the period 1999–2018. Bangladesh's vulnerability to climate change impacts is due to a combination of geographical factors, such as its flat, low-lying, and delta-exposed topography, and socio-economic factors, including its high population density, levels of poverty, and dependence on agriculture.

Climate change in Africa is an increasingly serious threat in Africa which is among the most vulnerable continents to the effects of climate change. Some sources even classify Africa as "the most vulnerable continent on Earth". This vulnerability is driven by a range of factors that include weak adaptive capacity, high dependence on ecosystem goods for livelihoods, and less developed agricultural production systems. The risks of climate change on agricultural production, food security, water resources and ecosystem services will likely have increasingly severe consequences on lives and sustainable development prospects in Africa. With high confidence, it was projected by the IPCC in 2007 that in many African countries and regions, agricultural production and food security would probably be severely compromised by climate change and climate variability. Managing this risk requires an integration of mitigation and adaptation strategies in the management of ecosystem goods and services, and the agriculture production systems in Africa.
Diana Liverman is a retired Regents Professor of Geography and Development and past Director of the University of Arizona School of Geography, Development and Environment in the College of Social and Behavioral Sciences in Tucson, Arizona.

The contributions of women in climate change have received increasing attention in the early 21st century. Feedback from women and the issues faced by women have been described as "imperative" by the United Nations and "critical" by the Population Reference Bureau. A report by the World Health Organization concluded that incorporating gender-based analysis would "provide more effective climate change mitigation and adaptation."
Sally Archibald is a South African scientist and Associate Professor at the University of Witwatersrand. Her research primarily focuses on savanna ecosystems within the context of global climate change as well as the exploration of fire ecology and earth-system feedbacks. Archibald was the recipient of the 2012 Mercer Award for her co-authorship of the paper "Tree cover in sub-Saharan Africa: Rainfall and fire constrain forest and savanna as alternative stable states".

Climate change vulnerability is defined as the "propensity or predisposition to be adversely affected" by climate change. It can apply to humans but also to natural systems (ecosystems). Human and ecosystem vulnerability are interdependent. Climate change vulnerability encompasses "a variety of concepts and elements, including sensitivity or susceptibility to harm and lack of capacity to cope and adapt". Vulnerability is a component of climate risk. Vulnerability differs within communities and across societies, regions and countries, and can change over time. Approximately 3.3 to 3.6 billion people live in contexts that are highly vulnerable to climate change in 2021.
Balgis Osman-Elasha is a Sudanese climate scientist who studies the effects of climate change in Africa and promotes sustainable development and climate change adaptations. She was a lead writer on the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report that garnered the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change a Nobel Peace Prize, and she was named a 2008 United Nations Environment Programme Champion of the Earth.
Lindsay Bremner is a South African scholar and architect, and is currently Professor of Architecture at the University of Westminster, in the United Kingdom. She has authored several books and her work has won several awards, including the Jane Jacobs Prize in 2011. Bremner's research studies oceans, design, and climate change.
Frances Gamble (1949–1997) was a South African climatologist and speleologist. Her work on cave conservation was extensive and pioneering. She evaluated cave ecosystems and conservation policies which were necessary to protect them. Gamble was one of the founders of the Cave Research Organisation of South Africa, which aimed at improving the scientific and professional development of speleology in South Africa. She was president of the Environmental Education Association of South Africa from 1986 to 1989 and of the South African Geographical Society from 1989 to 1991. At a time when Apartheid limited collaboration for South African researchers, she built networks internationally to facilitate research.
References
- 1 2 "Prof. Coleen Vogel". WIOMSA. Retrieved 2022-12-15.
- ↑ South African researcher takes top climate change award Archived May 27, 2012, at the Wayback Machine National Climate Change Adaptation Research Facility, 30 June 2010
- ↑ "Richard Klein recognized for 'outstanding contributions' to adaptation science". SEI. Retrieved 2022-12-15.
- ↑ Mbiyozo, Francois Engelbrecht, Alize le Roux, Coleen Vogel and Aimee-Noel (2022-05-12). "ISS TODAY: Poor climate adaptation, outdated infrastructure served as catalysts for KZN floods". Daily Maverick. Retrieved 2022-12-15.
- ↑ "Climate change: Universities should lead research effort". University World News. Retrieved 2022-12-15.
- ↑ "Coleen Vogel ─ Minding the Gap: Creating Coalitions for Sustainable Change | Watson Institute". Watson Institute for International and Public Affairs. Retrieved 2022-12-15.