Combinatorial chemistry comprises chemical synthetic methods that make it possible to prepare a large number of compounds in a single process. These compound libraries can be made as mixtures, sets of individual compounds or chemical structures generated by computer software. Combinatorial chemistry can be used for the synthesis of small molecules and for peptides.

A cloning vector is a small piece of DNA that can be stably maintained in an organism, and into which a foreign DNA fragment can be inserted for cloning purposes. The cloning vector may be DNA taken from a virus, the cell of a higher organism, or it may be the plasmid of a bacterium. The vector contains features that allow for the convenient insertion of a DNA fragment into the vector or its removal from the vector, for example through the presence of restriction sites. The vector and the foreign DNA may be treated with a restriction enzyme that cuts the DNA, and DNA fragments thus generated contain either blunt ends or overhangs known as sticky ends, and vector DNA and foreign DNA with compatible ends can then be joined by molecular ligation. After a DNA fragment has been cloned into a cloning vector, it may be further subcloned into another vector designed for more specific use.

Molecular genetics is a sub-field of biology that addresses how differences in the structures or expression of DNA molecules manifests as variation among organisms. Molecular genetics often applies an "investigative approach" to determine the structure and/or function of genes in an organism's genome using genetic screens. The field of study is based on the merging of several sub-fields in biology: classical Mendelian inheritance, cellular biology, molecular biology, biochemistry, and biotechnology. Researchers search for mutations in a gene or induce mutations in a gene to link a gene sequence to a specific phenotype. Molecular genetics is a powerful methodology for linking mutations to genetic conditions that may aid the search for treatments/cures for various genetics diseases.

In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered.

In molecular biology, biochips are engineered substrates that can host large numbers of simultaneous biochemical reactions. One of the goals of biochip technology is to efficiently screen large numbers of biological analytes, with potential applications ranging from disease diagnosis to detection of bioterrorism agents. For example, digital microfluidic biochips are under investigation for applications in biomedical fields. In a digital microfluidic biochip, a group of (adjacent) cells in the microfluidic array can be configured to work as storage, functional operations, as well as for transporting fluid droplets dynamically.

Phage display is a laboratory technique for the study of protein–protein, protein–peptide, and protein–DNA interactions that uses bacteriophages to connect proteins with the genetic information that encodes them. In this technique, a gene encoding a protein of interest is inserted into a phage coat protein gene, causing the phage to "display" the protein on its outside while containing the gene for the protein on its inside, resulting in a connection between genotype and phenotype. These displaying phages can then be screened against other proteins, peptides or DNA sequences, in order to detect interaction between the displayed protein and those other molecules. In this way, large libraries of proteins can be screened and amplified in a process called in vitro selection, which is analogous to natural selection.
Chemical biology is a scientific discipline between the fields of chemistry and biology. The discipline involves the application of chemical techniques, analysis, and often small molecules produced through synthetic chemistry, to the study and manipulation of biological systems. In contrast to biochemistry, which involves the study of the chemistry of biomolecules and regulation of biochemical pathways within and between cells, chemical biology deals with chemistry applied to biology.

Two-hybrid screening is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions (PPIs) and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.
Bacterial display is a protein engineering technique used for in vitro protein evolution. Libraries of polypeptides displayed on the surface of bacteria can be screened using flow cytometry or iterative selection procedures (biopanning). This protein engineering technique allows us to link the function of a protein with the gene that encodes it. Bacterial display can be used to find target proteins with desired properties and can be used to make affinity ligands which are cell-specific. This system can be used in many applications including the creation of novel vaccines, the identification of enzyme substrates and finding the affinity of a ligand for its target protein.

Directed evolution (DE) is a method used in protein engineering that mimics the process of natural selection to steer proteins or nucleic acids toward a user-defined goal. It consists of subjecting a gene to iterative rounds of mutagenesis, selection and amplification. It can be performed in vivo, or in vitro. Directed evolution is used both for protein engineering as an alternative to rationally designing modified proteins, as well as for experimental evolution studies of fundamental evolutionary principles in a controlled, laboratory environment.
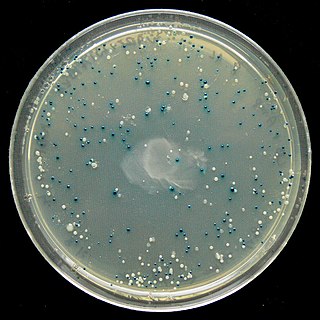
The blue–white screen is a screening technique that allows for the rapid and convenient detection of recombinant bacteria in vector-based molecular cloning experiments. This method of screening is usually performed using a suitable bacterial strain, but other organisms such as yeast may also be used. DNA of transformation is ligated into a vector. The vector is then inserted into a competent host cell viable for transformation, which are then grown in the presence of X-gal. Cells transformed with vectors containing recombinant DNA will produce white colonies; cells transformed with non-recombinant plasmids grow into blue colonies.

mRNA display is a display technique used for in vitro protein, and/or peptide evolution to create molecules that can bind to a desired target. The process results in translated peptides or proteins that are associated with their mRNA progenitor via a puromycin linkage. The complex then binds to an immobilized target in a selection step. The mRNA-protein fusions that bind well are then reverse transcribed to cDNA and their sequence amplified via a polymerase chain reaction. The result is a nucleotide sequence that encodes a peptide with high affinity for the molecule of interest.

Transcription regulator protein BACH1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BACH1 gene.
High throughput biology is the use of automation equipment with classical cell biology techniques to address biological questions that are otherwise unattainable using conventional methods. It may incorporate techniques from optics, chemistry, biology or image analysis to permit rapid, highly parallel research into how cells function, interact with each other and how pathogens exploit them in disease.
Richard A. Houghten is a heterocyclic organic chemist and founder of the journal Peptide Research, which was later merged with the International Journal of Peptide and Protein Research, to become the Journal of Peptide Research. His work mainly concerns peptide activity and pharmacology. He is the founder and president of the Torrey Pines Institute for Molecular Studies (TPIMS), a biomedical research institute. Houghten pioneered the "tea-bag" approach of producing peptides for pharmacological work.
Morten Peter Meldal is a Danish chemist and Nobel laureate. He is a professor of chemistry at the University of Copenhagen in Copenhagen, Denmark. He is best known for developing the CuAAC-click reaction, concurrently with but independent of Valery V. Fokin and K. Barry Sharpless.
DNA-encoded chemical libraries (DECL) is a technology for the synthesis and screening on an unprecedented scale of collections of small molecule compounds. DECL is used in medicinal chemistry to bridge the fields of combinatorial chemistry and molecular biology. The aim of DECL technology is to accelerate the drug discovery process and in particular early phase discovery activities such as target validation and hit identification.
Synthetic antibodies are affinity reagents generated entirely in vitro, thus completely eliminating animals from the production process. Synthetic antibodies include recombinant antibodies, nucleic acid aptamers and non-immunoglobulin protein scaffolds. As a consequence of their in vitro manufacturing method the antigen recognition site of synthetic antibodies can be engineered to any desired target and may extend beyond the typical immune repertoire offered by natural antibodies. Synthetic antibodies are being developed for use in research, diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Synthetic antibodies can be used in all applications where traditional monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies are used and offer many inherent advantages over animal-derived antibodies, including comparatively low production costs, reagent reproducibility and increased affinity, specificity and stability across a range of experimental conditions.
Split-intein circular ligation of peptides and proteins (SICLOPPS) is a biotechnology technique that permits the creation of cyclic peptides. These peptides are produced by ribosomal protein synthesis, followed by an intein-like event that splices the protein into a loop. By contrast with the nonribosomal peptide synthetases that produces some cyclic peptides like gramicidin S, SICLOPPS offers the advantage that the peptides' structure can be encoded by DNA in a simple manner according to the genetic code, but for this reason it imposes limitations on the types of amino acids incorporated that are comparable to those that apply to ordinary proteins. As implemented there is also some constraint on the peptide sequence of the cyclic sequence; for example, libraries may use the sequence SGXX..XXPL to increase the efficiency of circularization of the peptide. SICLOPPS is frequently used with a library of randomized DNA sequence that permits the simultaneous production and screening of large numbers of constructs at once, followed by the recovery of the DNA sequences responsible for the activity of the clone of interest.
Creative Biolabs, Inc. is a life-science company which produces and supplies biotech products and services for early drug discovery and development, including various phage display libraries such as pre-made libraries, phage display services, antibody sequencing, and antibody humanization. Customers include pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, government agencies, clinical research organizations and biotechnology companies.










