
The Balfour Declaration was a public statement issued by the British Government in 1917 during the First World War announcing its support for the establishment of a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine, then an Ottoman region with a small minority Jewish population. The declaration was contained in a letter dated 2 November 1917 from the United Kingdom's Foreign Secretary Arthur Balfour to Lord Rothschild, a leader of the British Jewish community, for transmission to the Zionist Federation of Great Britain and Ireland. The text of the declaration was published in the press on 9 November 1917.

Zionism is a nationalist movement that emerged in Europe in the late 19th century aiming for the establishment of a homeland for the Jewish people, particularly in Palestine, a region roughly corresponding to the Land of Israel in Jewish tradition. Following the establishment of the State of Israel, Zionism became an ideology that supports the development and protection of Israel as a Jewish state. It has also been described as Israel's national or state ideology.
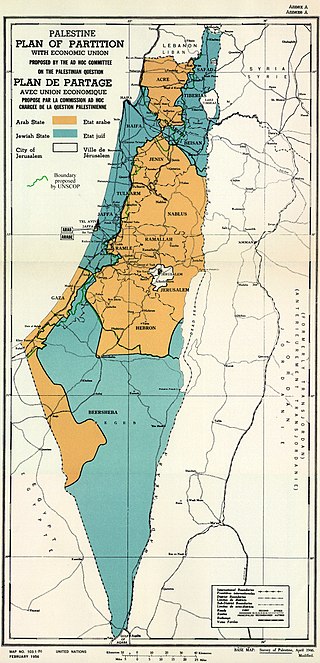
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations, which recommended a partition of Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. On 29 November 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted the Plan as Resolution 181 (II). The resolution recommended the creation of independent Arab and Jewish States linked economically and a Special International Regime for the city of Jerusalem and its surroundings.

A homeland for the Jewish people is an idea rooted in Jewish history, religion, and culture. The Jewish aspiration to return to Zion, generally associated with divine redemption, has suffused Jewish religious thought since the destruction of the First Temple and the Babylonian exile.

Christian Zionism is a political and religious ideology that, in a Christian context, espouses the return of the Jewish people to the Holy Land. Likewise, it holds that the founding of the State of Israel in 1948 was in accordance with biblical prophecies transmitted through the Old Testament: that the re-establishment of Jewish sovereignty in the Levant—the eschatological "Gathering of Israel"—is a prerequisite for the Second Coming of Jesus Christ. The term began to be used in the mid-20th century, in place of Christian restorationism, as proponents of the ideology rallied behind Zionists in support of a Jewish national homeland.
Soviet anti-Zionism is an anti-Zionist and pro-Arab doctrine promulgated in the Soviet Union during the Cold War. While the Soviet Union initially pursued a pro-Zionist policy after World War II due to its perception that the Jewish state would be socialist and pro-Soviet, its outlook on the Arab–Israeli conflict changed as Israel began to develop a close relationship with the United States and aligned itself with the Western Bloc. Anti-Israel Soviet propaganda intensified after Israel's sweeping victory in the 1967 Arab–Israeli War, and it was officially sponsored by the agitation and propaganda media of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union as well as by the KGB. Among other charges, it alleged that Zionism was a form of racism. The Soviets framed their anti-Zionist propaganda in the guise of a study of modern Zionism, dubbed Zionology. The Soviet anti-Israel policy included the regulated denial of permission for Jews in the Soviet Union to emigrate, primarily to Israel, but also to any other country.

Kermit "Kim" Roosevelt Jr. was an American intelligence officer who served in the Office of Strategic Services during and following World War II. A grandson of Theodore Roosevelt, the 26th President of the United States, Roosevelt went on to establish American Friends of the Middle East and then played a lead role in the CIA's efforts to overthrow Mohammad Mosaddegh, the democratically elected Majlis-appointed prime minister of Iran, in August 1953.

Nahum Goldmann was a leading Zionist. He was a founder of the World Jewish Congress and its president from 1951 to 1978, and was also president of the World Zionist Organization from 1956 to 1968.

Virginia Crocheron Gildersleeve was an American academic, the long-time dean of Barnard College, co-founder of the International Federation of University Women, and the only woman delegated by United States to the April 1945 San Francisco United Nations Conference on International Organization, which negotiated the charter for and creation of the United Nations.

Abba Hillel Silver was an American Rabbi and Zionist leader. He was a key figure in the mobilization of American support for the founding of the State of Israel, though he saw such a settlement as a means to protect Jewish heritage rather than having it serve as a main point of purpose for Jews.

The Israel lobby are individuals and groups seeking to influence the United States government to better serve Israel's interests. The largest pro-Israel lobbying group is Christians United for Israel with over seven million members. The American Israel Public Affairs Committee (AIPAC) is a leading organization within the lobby, speaking on behalf of a coalition of pro-Israel American Jewish groups.
Neo-Zionism is a right-wing, nationalistic and religious ideology that appeared in Israel following the Six-Day War in 1967 and the capture of the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Neo-Zionists consider these lands part of Israel and advocate their settlement by Israeli Jews. Some advocate the transfer of Arabs not only from these areas but also from within the Green Line.
As an organized nationalist movement, Zionism is generally considered to have been founded by Theodor Herzl in 1897. However, the history of Zionism began earlier and is intertwined with Jewish history and Judaism. The organizations of Hovevei Zion, held as the forerunners of modern Zionist ideals, were responsible for the creation of 20 Jewish towns in Palestine between 1870 and 1897.

During the British rule in Mandatory Palestine, there was civil, political and armed struggle between Palestinian Arabs and the Jewish Yishuv, beginning from the violent spillover of the Franco-Syrian War in 1920 and until the onset of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. The conflict shifted from sectarian clashes in the 1920s and early 1930s to an armed Arab Rebellion against British rule in 1936, armed Jewish Revolt primarily against the British in mid-1940s and finally open war in November 1947 between Arabs and Jews.

Anti-Zionism is opposition to Zionism. Although anti-Zionism is a heterogeneous phenomenon, all its proponents agree that the creation of the modern State of Israel, and the movement to create a sovereign Jewish state in the region of Palestine—a region partly coinciding with the biblical Land of Israel—was flawed or unjust in some way.
The American Council for Judaism (ACJ) is an organization of American Jews committed to the proposition that Jews are not a national but a religious group, adhering to the original stated principles of Reform Judaism, as articulated in the 1885 Pittsburgh Platform. In particular, it is notable for its historical opposition to Zionism. Although it has since moderated its stance on the issue, it still advocates that American Jews distance themselves from Israel politically, and does not view Israel as a universal Jewish homeland. The ACJ has also championed women's rights, including the right for women to serve as rabbis, and has supported Reform Jewish congregations and contributed to the publication of new editions of prayer books for religious services predominately in the English language for Jews in English-speaking countries.
The Azzam Pasha quotation was part of a statement made by Abdul Rahman Hassan Azzam, the Secretary-General of the Arab League from 1945 to 1952, in which he declared in 1947 that, were a war to take place with the proposed establishment of a Jewish state, it would lead to "a war of extermination and momentous massacre which will be spoken of like the Mongolian massacre and the Crusades."
Lebanese Jewish Migration to Israel included thousands of Jews, who moved to Israel, similar to how 1948 witnessed the emigration of hundreds of thousands of Jews from Arab countries. Yet, "unlike Jewish communities in many other Arab states, the Jewish communities in Lebanon grew after 1948 and it was not until the end of the civil war of 1975 that the community started to emigrate." This "Lebanese difference" derives from two components: more positive Lebanese relationships with European authorities during the French Mandate than experienced by other Arab states, leading to a more pluralistic outlook in Lebanon than its neighbors; some elements in the Maronite Christian community who were tolerant of Zionism.
This timeline of anti-Zionism chronicles the history of anti-Zionism, including events in the history of anti-Zionist thought.
Labor Zionism or socialist Zionism refers to the left-wing, socialist variation of Zionism. For many years, it was the most significant tendency among Zionists and Zionist organizations, and was seen as the Zionist sector of the historic Jewish labour movements of Eastern Europe and Central Europe, eventually developing local units in most countries with sizable Jewish populations. Unlike the "political Zionist" tendency founded by Theodor Herzl and advocated by Chaim Weizmann, Labor Zionists did not believe that a Jewish state would be created by simply appealing to the international community or to powerful nations such as the United Kingdom, Germany, or the former Ottoman Empire. Rather, they believed that a Jewish state could only be created through the efforts of the Jewish working class making aliyah to the Land of Israel and raising a country through the creation of a Labor Jewish society with rural kibbutzim and moshavim, and an urban Jewish Proletariat.











