Related Research Articles

Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensation, vision, hearing, and speaking. Often, babies with cerebral palsy do not roll over, sit, crawl or walk as early as other children of their age. Other symptoms include seizures and problems with thinking or reasoning, which each occur in about one-third of people with CP. While symptoms may get more noticeable over the first few years of life, underlying problems do not worsen over time.
Speech disorders or speech impairments are a type of communication disorder in which normal speech is disrupted. This can mean stuttering, lisps, etc. Someone who is unable to speak due to a speech disorder is considered mute. Speech skills are vital to social relationships and learning, and delays or disorders that relate to developing these skills can impact individuals function. For many children and adolescents, this can present as issues with academics. Speech disorders affect roughly 11.5% of the US population, and 5% of the primary school population. Speech is a complex process that requires precise timing, nerve and muscle control, and as a result is susceptible to impairments. A person who has a stroke, an accident or birth defect may have speech and language problems.

The Moro reflex is an infantile reflex that develops between 28 and 32 weeks of gestation and disappears at 3–6 months of age. It is a response to a sudden loss of support and involves three distinct components:
- spreading out the arms (abduction)
- pulling the arms in (adduction)
- crying (usually)
Worster-Drought syndrome is a form of congenital suprabulbar paresis that occurs in some children with cerebral palsy. It is caused by inadequate development of the corticobulbar tracts and causes problems with the mouth and tongue including impaired swallowing. A similar syndrome in adults is called anterior opercular syndrome.
The Bobath concept is an approach to neurological rehabilitation that is applied in patient assessment and treatment. The goal of applying the Bobath concept is to promote motor learning for efficient motor control in various environments, thereby improving participation and function. This is done through specific patient handling skills to guide patients through the initiation and completing of intended tasks. This approach to neurological rehabilitation is multidisciplinary, primarily involving physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and speech and language therapists. In the United States, the Bobath concept is also known as 'neuro-developmental treatment' (NDT).
bibic is a small charitable organization based in the United Kingdom that supports children, young people and their families deal with a number of different conditions. The charity was founded by the late Keith Pennock who had a daughter with a learning disability. The work was derived from Glenn Doman's The Institutes for The Achievement of Human Potential (IAHP) in Philadelphia, USA.

Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) is a form of white-matter brain injury, characterized by the necrosis of white matter near the lateral ventricles. It can affect newborns and fetuses; premature infants are at the greatest risk of neonatal encephalopathy which may lead to this condition. Affected individuals generally exhibit motor control problems or other developmental delays, and they often develop cerebral palsy or epilepsy later in life. The white matter in preterm born children is particularly vulnerable during the third trimester of pregnancy when white matter developing takes place and the myelination process starts around 30 weeks of gestational age.
Hypertonia is a term sometimes used synonymously with spasticity and rigidity in the literature surrounding damage to the central nervous system, namely upper motor neuron lesions. Impaired ability of damaged motor neurons to regulate descending pathways gives rise to disordered spinal reflexes, increased excitability of muscle spindles, and decreased synaptic inhibition. These consequences result in abnormally increased muscle tone of symptomatic muscles. Some authors suggest that the current definition for spasticity, the velocity-dependent over-activity of the stretch reflex, is not sufficient as it fails to take into account patients exhibiting increased muscle tone in the absence of stretch reflex over-activity. They instead suggest that "reversible hypertonia" is more appropriate and represents a treatable condition that is responsive to various therapy modalities like drug and/or physical therapy.

Developmental coordination disorder (DCD), also known as developmental motor coordination disorder, developmental dyspraxia or simply dyspraxia from the word 'praxis' meaning to do or act, is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impaired coordination of physical movements as a result of brain messages not being accurately transmitted to the body. Deficits in fine or gross motor skills movements interfere with activities of daily living. It is often described as disorder in skill acquisition, where the learning and execution of coordinated motor skills is substantially below that expected given the individual's chronological age. Difficulties may present as clumsiness, slowness and inaccuracy of performance of motor skills. It is also often accompanied by difficulty with organisation and/or problems with attention, working memory and time management.
The William Little Foundation is a London-based charity operating internationally.

Over time, the approach to cerebral palsy management has shifted away from narrow attempts to fix individual physical problems – such as spasticity in a particular limb – to making such treatments part of a larger goal of maximizing the person's independence and community engagement. Much of childhood therapy is aimed at improving gait and walking. Approximately 60% of people with CP are able to walk independently or with aids at adulthood. However, the evidence base for the effectiveness of intervention programs reflecting the philosophy of independence has not yet caught up: effective interventions for body structures and functions have a strong evidence base, but evidence is lacking for effective interventions targeted toward participation, environment, or personal factors. There is also no good evidence to show that an intervention that is effective at the body-specific level will result in an improvement at the activity level, or vice versa. Although such cross-over benefit might happen, not enough high-quality studies have been done to demonstrate it.
Dyskinetic cerebral palsy (DCP) is a subtype of cerebral palsy (CP) and is characterized by impaired muscle tone regulation, coordination and movement control. Dystonia and choreoathetosis are the two most dominant movement disorders in patients with DCP.
The Gross Motor Function Classification System or GMFCS is a 5 level clinical classification system that describes the gross motor function of people with cerebral palsy on the basis of self-initiated movement abilities. Particular emphasis in creating and maintaining the GMFCS scale rests on evaluating sitting, walking, and wheeled mobility. Distinctions between levels are based on functional abilities; the need for walkers, crutches, wheelchairs, or canes / walking sticks; and to a much lesser extent, the actual quality of movement.

Athetoid cerebral palsy, or dyskinetic cerebral palsy, is a type of cerebral palsy primarily associated with damage, like other forms of CP, to the basal ganglia in the form of lesions that occur during brain development due to bilirubin encephalopathy and hypoxic–ischemic brain injury. Unlike spastic or ataxic cerebral palsies, ADCP is characterized by both hypertonia and hypotonia, due to the affected individual's inability to control muscle tone. Clinical diagnosis of ADCP typically occurs within 18 months of birth and is primarily based upon motor function and neuroimaging techniques. While there are no cures for ADCP, some drug therapies as well as speech, occupational therapy, and physical therapy have shown capacity for treating the symptoms.
Pamela Evans is a British author who is also trained as a medical doctor and a published academic.
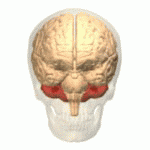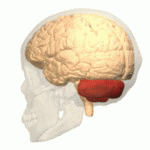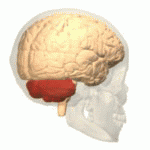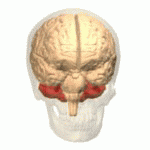
Ataxic cerebral palsy is clinically in approximately 5–10% of all cases of cerebral palsy, making it the least frequent form of cerebral palsy diagnosed. Ataxic cerebral palsy is caused by damage to cerebellar structures, differentiating it from the other two forms of cerebral palsy, which are spastic cerebral palsy and dyskinetic cerebral palsy.

Spastic cerebral palsy is the type of cerebral palsy characterized by spasticity or high muscle tone often resulting in stiff, jerky movements. Cases of spastic CP are further classified according to the part or parts of the body that are most affected. Such classifications include spastic diplegia, spastic hemiplegia, spastic quadriplegia, and in cases of single limb involvement, spastic monoplegia.

Cerebral folate deficiency is a condition in which concentrations of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate are low in the brain as measured in the cerebral spinal fluid despite being normal in the blood. Symptoms typically appear at about 5 to 24 months of age. Without treatment there may be poor muscle tone, trouble with coordination, trouble talking, and seizures.
The Manual Ability Classification System (MACS) is a medical classification system used to describe how children aged from 4 to 18 years old with cerebral palsy use their hands with objects during activities of daily living, with a focus on the use of both hands together. Like the Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS), there are five levels - level I being the least impaired, only finding difficulty in tasks needing speed and accuracy, and level V being the most impaired, not being able to handle objects and having severely limited abilities for even simple actions.

Diane Louise Damiano is an American biomedical scientist and physical therapist specializing in physical medicine and rehabilitation approaches in children with cerebral palsy. She is chief of the functional and applied biomechanics section at the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center. Damiano has served as president of the Clinical Gait and Movement Analysis Society and the American Academy for Cerebral Palsy and Developmental Medicine.
References
- ↑ HIDECKER, MARY JO COOLEY; PANETH, NIGEL; ROSENBAUM, PETER L; KENT, RAYMOND D; LILLIE, JANET; EULENBERG, JOHN B; CHESTER JR, KEN; JOHNSON, BRENDA; MICHALSEN, LAUREN; EVATT, MORGAN; TAYLOR, KARA (August 2011). "Developing and validating the Communication Function Classification System for individuals with cerebral palsy". Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 53 (8): 704–710. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2011.03996.x. PMC 3130799 . PMID 21707596.
- ↑ Morris, C; Bartlett, D (January 2004). "Gross Motor Function Classification System: impact and utility". Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 46 (1): 60–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2004.tb00436.x . PMID 14974650.
- ↑ Palisano, R; Rosenbaum, P; Walter, S; Russell, D; Wood, E; Galuppi, B (April 1997). "Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy". Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 39 (4): 214–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1997.tb07414.x . PMID 9183258.
- ↑ Palisano, RJ; Rosenbaum, P; Bartlett, D; Livingston, MH (October 2008). "Content validity of the expanded and revised Gross Motor Function Classification System". Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 50 (10): 744–50. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.03089.x. PMID 18834387. S2CID 45875650.
- ↑ Eliasson, AC; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L; Rösblad, B; Beckung, E; Arner, M; Ohrvall, AM; Rosenbaum, P (July 2006). "The Manual Ability Classification System (MACS) for children with cerebral palsy: scale development and evidence of validity and reliability". Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 48 (7): 549–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2006.tb01313.x . PMID 16780622.