
Conceptual economy is a term describing the contribution of creativity, innovation, and design skills to economic competitiveness, especially in the global context.

Conceptual economy is a term describing the contribution of creativity, innovation, and design skills to economic competitiveness, especially in the global context.
Alan Greenspan, former chairman of the Federal Reserve Board, recognized the role of conceptual output as early as 1997 in a speech at the University of Connecticut when he said "The growth of the conceptual component of output has brought with it accelerating demands for workers who are equipped not simply with technical know-how, but with the ability to create, analyze, and transform information and to interact effectively with others." [1] By 2004, he had developed his views on the topic, referring to reductions in manufacturing in the United States, outsourcing to India and China, excess of supply and the global marketplace, all leading to the increasing conceptualization of economic output. [2]

In his book A Whole New Mind, Daniel H. Pink explains how the economy is now moving from the information age to the conceptual age. He describes how abundance (over-supply), Asia (outsourcing) and automation contribute to the need for business to concentrate on cognitive or creative assets such as design, storytelling, teamwork, empathy, play and meaning. He bases his approach on brain functions explaining how qualities dependent on the left hemisphere of the brain (logic, knowledge) now need to be complemented by those associated with right-brained processes (intuition and creative thinking).
Other contributors to our understanding of the conceptual economy include Tom Friedman who describes the opportunities of globalization in his book The World Is Flat . He emphasizes the importance of the internet and personal computers for communications and software sharing across the globe. This explains how American companies are able to outsource a substantial portion of their business to India and China with no disruptions for the customer.
Tom Kelley is also a key player in the field, both as general manager of IDEO, a highly successful design and innovation company, and the author of two widely acclaimed books: The Art of Innovation, highlighting the importance of brainstorming and teamwork in product creation; and The Ten Faces of Innovation , explaining the role of assets such as empathy, storytelling, individual experiences and stimulating work environments in fostering creative ideas.
The key steps behind the conceptual economy fall into the following categories:
Until quite recently, our understanding of the economy was based on the premise that the way forward would depend on traditional values and qualifications such as those for accountants, lawyers, engineers, mathematicians or computer programmers. With the new opportunities resulting from globalization and the internet, the accepted forms of success are losing ground to scenarios drawing on innovative ideas. Here there is an increasing need for artists, designers and creative authors to contribute not only to product design but also to business management and strategic planning.
Areas deserving particular attention are related to three key developments:
For the past 15 or 20 years, the Western economies (Europe, North America) have experienced a situation of fully dependable supply of basic goods, including round-the-year abundance of agricultural produce, with the result that a significant proportion of households have begun to look for more than just the basic necessities. Families now look for goods which extend beyond the basic norm such as organic foods or sophisticated digital television sets, mobile phones and cars with four-wheel drive, cruise control or integrated navigation systems.
Given the low costs of labour in developing countries such as China, India and the Philippines, American and European companies are now outsourcing or offshoring an ever-increasing proportion of their production, manufacturing or service tasks to foreign countries. As a result, job opportunities in the West are slowly moving away from routine tasks such as accounting, telephone support services, computer programming and electronic component manufacturing. The efficiency of outsourcing has also been improving as the internet continues to provide increasingly reliable and ever faster global communications links.
In industry too, the development of robotics and automated manufacturing facilities means that opportunities for traditional jobs in industries such as automobile manufacturing and food processing are also diminishing. Ever higher levels of qualification are now required to contribute to operations that are largely computerized. [3]

Partly a result of the above factors, a wide range of new facilities and opportunities has begun to emerge. These include:
Virtually every area of industry can benefit from developments of this kind both to improve the products themselves and to offer better marketing opportunities and after-sales services. As a result, these factors are seen as major contributors to increased productivity and economic growth.
Drivers behind the conceptual economy, can be categorised into the following areas: [4]
Educational institutions need to place more emphasis on creativity and the arts rather than on traditional qualifications in the areas of engineering and management. In particular, more attention needs to be devoted to basic literacy, analytical and critical thinking, synthesis and quantitative skills: [5]
Until now, information technology has had considerable impact on the economy. Increasingly, success will depend on how to make use of the knowledge and information that has emerged. Here qualities such as intuition, creativity and game-based approaches will become ever more important.
Prosperity and competitiveness in the 21st century will depend on an understanding of diverse national cultures and how to draw on their ideas in order to assist the innovation process. Here too, there will be a need for more extensive teamwork, creativity and leading-edge thinking, all in the context of the global economy.
In business theory, disruptive innovation is innovation that creates a new market and value network or enters at the bottom of an existing market and eventually displaces established market-leading firms, products, and alliances. The concept was developed by the American academic Clayton Christensen and his collaborators beginning in 1995, and has been called the most influential business idea of the early 21st century. Lingfei Wu, Dashun Wang, and James A. Evans generalized this term to identify disruptive science and technological advances from more than 65 million papers, patents and software products that span the period 1954–2014. Their work was featured as the cover of the February 2019 issue of Nature and was selected as the Altmetric 100 most-discussed work in 2019.

A business model describes how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value, in economic, social, cultural or other contexts. The process of business model construction and modification is also called business model innovation and forms a part of business strategy.

Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity realizing or redistributing value". Others have different definitions; a common element in the definitions is a focus on newness, improvement, and spread of ideas or technologies.

Creativity is a phenomenon whereby something new and valuable is formed. The created item may be intangible or a physical object.
In business and engineering, new product development (NPD) covers the complete process of bringing a new product to market, renewing an existing product or introducing a product in a new market. A central aspect of NPD is product design, along with various business considerations. New product development is described broadly as the transformation of a market opportunity into a product available for sale. The products developed by an organisation provide the means for it to generate income. For many technology-intensive firms their approach is based on exploiting technological innovation in a rapidly changing market.
The knowledge economy is an economic system in which the production of goods and services is based principally on knowledge-intensive activities that contribute to advancement in technical and scientific innovation. The key element of value is the greater dependence on human capital and intellectual property for the source of the innovative ideas, information and practices. Organisations are required to capitalise this "knowledge" into their production to stimulate and deepen the business development process. There is less reliance on physical input and natural resources. A knowledge-based economy relies on the crucial role of intangible assets within the organisations' settings in facilitating modern economic growth.
IDEO is a design and consulting firm with offices in the U.S., England, Germany, Japan, and China. It was founded in Palo Alto, California, in 1991. The company's 700 staff uses a design thinking approach to design products, services, environments, and digital experiences.
Offshoring is the relocation of a business process from one country to another—typically an operational process, such as manufacturing, or supporting processes, such as accounting. Usually this refers to a company business, although state governments may also employ offshoring. More recently, technical and administrative services have been offshored.
The creative industries refers to a range of economic activities which are concerned with the generation or exploitation of knowledge and information. They may variously also be referred to as the cultural industries or the creative economy, and most recently they have been denominated as the Orange Economy in Latin America and the Caribbean.

A strategic partnership is a relationship between two commercial enterprises, usually formalized by one or more business contracts. A strategic partnership will usually fall short of a legal partnership entity, agency, or corporate affiliate relationship. Strategic partnerships can take on various forms from shake hand agreements, contractual cooperation's all the way to equity alliances, either the formation of a joint venture or cross-holdings in each other.
Design thinking refers to the set of cognitive, strategic and practical procedures used by designers in the process of designing, and to the body of knowledge that has been developed about how people reason when engaging with design problems.

Computational creativity is a multidisciplinary endeavour that is located at the intersection of the fields of artificial intelligence, cognitive psychology, philosophy, and the arts.
Strategic design is the application of future-oriented design principles in order to increase an organization's innovative and competitive qualities. Its foundations lie in the analysis of external and internal trends and data, which enables design decisions to be made on the basis of facts rather than aesthetics or intuition. The discipline is mostly practiced by design agencies or by internal development departments.
Innovation economics is new and growing field of economic theory and applied and experimental economics that emphasizes innovation and entrepreneurship. It comprises both the application of any type of innovations, especially technological, but not only, into economic use, in classical economics this is the application of customer new technology into economic use; but also it could refer to the field of innovation and experimental economics that refers the new economic science developments that may be considered innovative. In his 1942 book Capitalism, Socialism and Democracy, economist Joseph Schumpeter introduced the notion of an innovation economy. He argued that evolving institutions, entrepreneurs and technological changes were at the heart of economic growth. However, it is only in recent years that "innovation economy," grounded in Schumpeter's ideas, has become a mainstream concept".
Innovation management is a combination of the management of innovation processes, and change management. It refers to product, business process, marketing and organizational innovation. Innovation management is the subject of ISO 56000 series standards being developed by ISO TC 279.
The Offshoring Research Network is an international network of researchers and practitioners studying organizations in their transition to globalizing their business functions, processes and administrative services. The ORN conducts annual surveys tracking global sourcing strategies, drivers, concrete implementations and plans across all business functions and processes.
The Design Society is an international non-governmental, non-profit organisation with a focus on engineering design. The Design Society is a charitable body, registered in Scotland under the Office of the Scottish Charity Regulator, number SC 031694. The Design Society's flagship event is the biennial International Conference in Engineering Design (ICED).
A creative economy is based on people's use of their creative imagination to increase an idea's value. John Howkins developed the concept in 2001 to describe economic systems where value is based on novel imaginative qualities rather than the traditional resources of land, labour and capital.: Compared to creative industries, which are limited to specific sectors, the term is used to describe creativity throughout a whole economy.
Functional diversity encapsulates the cognitive resource diversity theory, which is the idea that diversity of cognitive resources promotes creativity and innovation, problem solving capacity, and organizational flexibility. Functionally diverse teams “consist of individuals with a variety of educational and training backgrounds working together." This differs from social diversity, which in accordance with the similarity attraction (homophily) paradigm, is the idea that individuals who are more similar together are able to work together more effectively. There is a degree of ambiguity in academic literature in the definition of functional and social diversity due to many studies in this matter either focusing on one or the other or mashing up the different characteristics.Psychologists, economists, sociologists have conducted numerous studies on diversity within groups to examine the effects on group performance. There are debates about benefits and costs of working in a functionally diverse groups. Milliken and Martins (1996) concluded that “diversity appears to be a double-edged sword”.
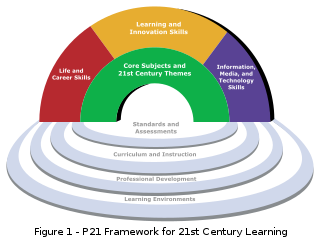
21st century skills comprise skills, abilities, and learning dispositions that have been identified as being required for success in 21st century society and workplaces by educators, business leaders, academics, and governmental agencies. This is part of a growing international movement focusing on the skills required for students to master in preparation for success in a rapidly changing, digital society. Many of these skills are also associated with deeper learning, which is based on mastering skills such as analytic reasoning, complex problem solving, and teamwork. These skills differ from traditional academic skills in that they are not primarily content knowledge-based.