
Proportional representation (PR) refers to any type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions among voters. The essence of such systems is that all votes cast – or almost all votes cast – contribute to the result and are effectively used to help elect someone. Under other election systems, a bare plurality or a scant majority are all that are used to elect candidates. PR systems provide balanced representation to different factions, reflecting how votes are cast.

The Alþingi, anglicised as Althingi or Althing, is the supreme national parliament of Iceland. It is the oldest surviving parliament in the world. The Althing was founded in 930 at Þingvellir, about 45 kilometres (28 mi) east of what later became the country's capital, Reykjavík. After Iceland's union with Norway in 1262, the Althing lost its legislative power, which was not restored until 1904 when Iceland gained home rule from Denmark. For 641 years, the Althing did not serve as the parliament of Iceland; ultimate power rested with the Norwegian, and subsequently the Danish throne. Even after Iceland's union with Norway in 1262, the Althing still held its sessions at Þingvellir until 1800, when it was discontinued. It was restored in 1844 by royal decree and moved to Reykjavík. The restored unicameral legislature first came together in 1845 and after 1874 operated in two chambers with an additional third chamber taking on a greater role as the decades passed until 1991 when Althing became once again unicameral. The present parliament building, the Alþingishús, was built in 1881, made of hewn Icelandic stone. The unicameral parliament has 63 members, and is elected every four years based on party-list proportional representation. The current speaker of the Althing is Birgir Ármannsson.

Elections in Sweden are held once every four years. At the highest level, all 349 members of Riksdag, the national parliament of Sweden, are elected in general elections. Elections to the 20 county councils and 290 municipal assemblies – all using almost the same electoral system – are held concurrently with the legislative elections on the second Sunday in September.
The electoral system of Australia comprises the laws and processes used for the election of members of the Australian Parliament and is governed primarily by the Commonwealth Electoral Act 1918. The system presently has a number of distinctive features including compulsory enrolment; compulsory voting; majority-preferential instant-runoff voting in single-member seats to elect the lower house, the House of Representatives; and the use of the single transferable vote proportional representation system to elect the upper house, the Senate.
An electoraldistrict, sometimes called a constituency, riding, or ward, is a geographical portion of a political unit, such as a country, state or province, city, or administrative region, created to provide the voters therein with representation in a legislature or other polity. That legislative body, the state's constitution, or a body established for that purpose determines each district's boundaries and whether each will be represented by a single member or multiple members. Generally, only voters (constituents) who reside within the district are permitted to vote in an election held there. The district representative or representatives may be elected by single-winenr first-past-the-post system, a multi-winner proportional representative system, or another voting method.

An electoral district in Canada is a geographical constituency upon which Canada's representative democracy is based. It is officially known in Canadian French as a circonscription but frequently called a comté (county). In Canadian English it is also colloquially and more commonly known as a riding or constituency.

In the United Kingdom (UK), each of the electoral areas or divisions called constituencies elects one member to the House of Commons.

Leveling seats, commonly known also as adjustment seats, are an election mechanism employed for many years by all Nordic countries in elections for their national legislatures. Germany also used national leveling seats for their parliament, the Bundestag, from 2013 through 2023. Leveling seats are seats of additional members elected to supplement the members directly elected by each constituency. The purpose of these additional seats is to ensure that each party's share of the total seats is roughly proportional to the party's overall shares of votes at the national level.
Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 12 May 2007. The Independence Party remained the largest party in the Althing, winning 25 of the 63 seats. Following the elections, a coalition government was formed by the Independence Party and the Social Democratic Alliance, with Geir Haarde continuing as Prime Minister.
Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 10 May 2003. The Independence Party remained the largest party in the Althing, winning 22 of the 63 seats. The coalition government of the Independence Party and Progressive Party remained in office, with Davíð Oddsson continuing as prime minister.
Electoral districts go by different names depending on the country and the office being elected.
Snap parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 25 April 2009, following strong pressure from the public as a result of the Icelandic financial crisis. The Social Democratic Alliance and the Left-Green Movement, which formed the outgoing coalition government under Prime Minister Jóhanna Sigurðardóttir, both made gains and formed an overall majority of seats in the Althing. The Progressive Party also made gains, and the new Citizens' Movement, formed after the January 2009 protests, won four seats. The big loser was the Independence Party, which had been in power for 18 years until January 2009; it lost nine seats as its vote share was reduced by around a third, meaning it was not the most voted-for party for the first time since 1937

Reykjavík North is one of the six multi-member constituencies of the Althing, the national legislature of Iceland. The constituency was established in 2003 when the existing Reykjavík constituency was split into two. The constituency currently elects nine of the 63 members of the Althing using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2024 parliamentary election it had 47,600 registered electors.

Reykjavík South is one of the six multi-member constituencies of the Althing, the national legislature of Iceland. The constituency was established in 2003 when the existing Reykjavík constituency was split into two. The constituency currently elects nine of the 63 members of the Althing using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2024 parliamentary election it had 47,619 registered electors.

Northeast is one of the six multi-member constituencies of the Althing, the national legislature of Iceland. The constituency was established in 2003 following the re-organisation of constituencies across Iceland when the Northeastern constituency was merged with the Eastern constituency and Siglufjörður municipality from the Northwestern constituency. Northeast consists of the regions of Eastern and Northeastern. The constituency currently elects nine of the 63 members of the Althing using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2024 parliamentary election it had 31,071 registered electors.
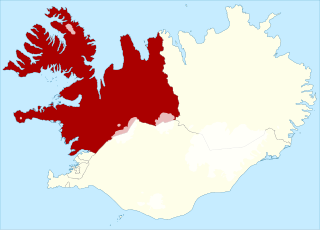
Northwest is one of the six multi-member constituencies of the Althing, the national legislature of Iceland. The constituency was established in 2003 following the re-organisation of constituencies across Iceland when the Northwestern constituency was merged with the Western and Westfjords constituencies. Northwest consists of the regions of Northwestern, Western and Westfjords. The constituency currently elects six of the 63 members of the Althing using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2024 parliamentary election it had 22,351 registered electors.
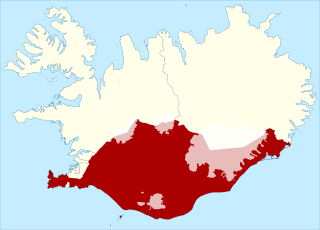
South is one of the six multi-member constituencies of the Althing, the national legislature of Iceland. The constituency was established in 2003 following the re-organisation of constituencies across Iceland when the Southern constituency was merged with municipalities of Gerðahreppur, Grindavík, Reykjanesbær, Sandgerði and Vatnsleysustrandarhreppur from the Reykjanes constituency and the municipality of Sveitarfélagið Hornafjörður from the Eastern constituency. South consists of the Southern and Southern Peninsula regions. The constituency currently elects nine of the 63 members of the Althing using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2024 parliamentary election it had 41,002 registered electors.

Southwest is one of the six multi-member constituencies of the Althing, the national legislature of Iceland. The constituency was established in 2003 following the re-organisation of constituencies across Iceland when the Reykjanes constituency was split between the new South and Southwest constituencies. Southwest is conterminous with the Capital region but excludes Reykjavík Municipality which has its own constituencies, Reykjavík North and Reykjavík South. The constituency currently elects 12 of the 63 members of the Althing using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2024 parliamentary election it had 79,087 registered electors.

Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 27 April 2013. Fifteen parties contested the elections, compared to just seven in the previous elections. The result was a victory for the two centre-right opposition parties, the Independence Party and Progressive Party, which subsequently formed a coalition government. The parties were eurosceptic and their win brought to a halt partially completed negotiations with the European Union regarding Icelandic membership.

Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 30 November 2024 to elect the 63 members of the Althing. The centre-left Social Democratic Alliance, led by Kristrún Frostadóttir, outperformed the ruling Independence Party to win the most seats, at 15. The election saw the worst performance by the Independence Party, Progressive Party, the Left-Green Movement, and the Pirate Party in each of the parties' histories, while Viðreisn, the People's Party, and the Centre Party saw their best performance in each of the parties' histories. This follows a trend of Icelanders voting against every post–2008 recession government except during the 2021 election.















