
Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic disorder in which a person's cells have only one X chromosome or are partially missing an X chromosome. Most people have two sex chromosomes. The chromosomal abnormality is often present in just some cells, in which case it is known as Turner syndrome with mosaicism. 45,X0 with mosaicism can occur in males or females, but Turner syndrome without mosaicism only occurs in females. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hairline at the back of the neck, short stature, and swollen hands and feet are seen at birth. Typically, those affected do not develop menstrual periods or breasts without hormone treatment and are unable to have children without reproductive technology. Heart defects, diabetes, and hypothyroidism occur in the disorder more frequently than average. Most people with Turner syndrome have normal intelligence; however, many have problems with spatial visualization that may be needed in order to learn mathematics. Vision and hearing problems also occur more often than average.
Menarche is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fertility.
Amenorrhea is the absence of a menstrual period in a female who has reached reproductive age. Physiological states of amenorrhoea are seen, most commonly, during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding). Outside the reproductive years, there is absence of menses during childhood and after menopause.

Growth hormone deficiency (GHD), or human growth hormone deficiency, is a medical condition resulting from not enough growth hormone (GH). Generally the most noticeable symptom is that an individual attains a short height. Newborns may also present low blood sugar or a small penis size. In adults there may be decreased muscle mass, high cholesterol levels, or poor bone density.
In medicine, precocious puberty is puberty occurring at an unusually early age. In most cases, the process is normal in every aspect except the unusually early age and simply represents a variation of normal development. There is early development of secondary sex characters and gametogenesis also starts earlier. Precocious puberty is of two types: true precocious puberty and pseudoprecocious puberty. In a minority of children with precocious puberty, the early development is triggered by a disease such as a tumor or injury of the brain.
Delayed puberty is when a person lacks or has incomplete development of specific sexual characteristics past the usual age of onset of puberty. The person may have no physical or hormonal signs that puberty has begun. In the United States, girls are considered to have delayed puberty if they lack breast development by age 13 or have not started menstruating by age 15. Boys are considered to have delayed puberty if they lack enlargement of the testicles by age 14. Delayed puberty affects about 2% of adolescents.
Pubarche refers to the first appearance of pubic hair at puberty and it also marks the beginning of puberty. It is one of the physical changes of puberty and can occur independently of complete puberty. The early stage of sexual maturation, also known as adrenarche, is marked by characteristics including the development of pubic hair, axillary hair, adult apocrine body odor, acne, and increased oiliness of hair and skin. The Encyclopedia of Child and Adolescent Health corresponds SMR2 with pubarche, defining it as the development of pubic hair that occurs at a mean age of 11.6 years in females and 12.6 years in males. It further describes that pubarche's physical manifestation is vellus hair over the labia or the base of the penis. See Table 1 for the entirety of the sexual maturity rating description.
Gonadarche refers to the earliest gonadal changes of puberty. In response to pituitary gonadotropins, the ovaries in females and the testes in males begin to grow and increase the production of the sex steroids, especially estradiol and testosterone. The ovary and testis have receptors, follicle cells and leydig cells, respectively, where gonadotropins bind to stimulate the maturation of the gonads and secretion of estrogen and testosterone. Certain disorders can result in changes to timing or nature of these processes.

Bone age is the degree of a person's skeletal development. In children, bone age serves as a measure of physiological maturity and aids in the diagnosis of growth abnormalities, endocrine disorders, and other medical conditions. As a person grows from fetal life through childhood, puberty, and finishes growth as a young adult, the bones of the skeleton change in size and shape. These changes can be seen by x-ray and other imaging techniques. A comparison between the appearance of a patient's bones to a standard set of bone images known to be representative of the average bone shape and size for a given age can be used to assign a "bone age" to the patient.
Idiopathic short stature (ISS) refers to extreme short stature that does not have a diagnostic explanation after an ordinary growth evaluation. The term has been in use since at least 1975 without a precise percentile or statistical definition of "extreme".
Pediatric endocrinology is a medical subspecialty dealing with disorders of the endocrine glands, such as variations of physical growth and sexual development in childhood, diabetes and many more.
Short stature refers to a height of a human which is below typical. Whether a person is considered short depends on the context. Because of the lack of preciseness, there is often disagreement about the degree of shortness that should be called short. Dwarfism is the condition of being very short, often caused by a medical condition. In a medical context, short stature is typically defined as an adult height that is more than two standard deviations below a population’s mean for age and sex, which corresponds to the shortest 2.3% of individuals in that population.
The short-stature homeobox gene (SHOX), also known as short-stature-homeobox-containing gene, is a gene located on both the X and Y chromosomes, which is associated with short stature in humans if mutated or present in only one copy (haploinsufficiency).

A growth chart is used by pediatricians and other health care providers to follow a child's growth over time. Growth charts have been constructed by observing the growth of large numbers of healthy children over time. The height, weight, and head circumference of a child can be compared to the expected parameters of children of the same age and sex to determine whether the child is growing appropriately. Growth charts can also be used to predict the expected adult height and weight of a child because, in general, children maintain a fairly constant growth curve. When a child deviates from his or her previously established growth curve, investigation into the cause is generally warranted. Parameters used to analyze growth charts include weight velocity, height velocity, and whether someone's growth chart crosses percentiles. For instance, endocrine disorders can be associated with a decrease in height velocity and preserved weight velocity while normal growth variants are associated with a decrease in height and weight velocity that are proportional to each other. It's important to note that other parameters are more commonly used such as waist circumference for assessing obesity and skin fold difference for assessing malnutrition. Growth charts can also be compiled with a portion of the population deemed to have been raised in more or less ideal environments, such as nutrition that conforms to pediatric guidelines, and no maternal smoking. Charts from these sources end up with slightly taller but thinner averages.
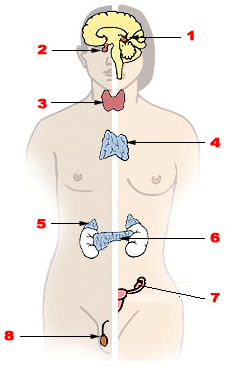
Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology.

Laron syndrome (LS), also known as growth hormone insensitivity or growth hormone receptor deficiency (GHRD), is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by a lack of insulin-like growth factor 1 production in response to growth hormone. It is usually caused by inherited growth hormone receptor (GHR) mutations.
Glycogenic hepatopathy(also known as Mauriac syndrome ) is a rare complication of type 1 diabetes characterized by extreme liver enlargement due to glycogen deposition, along with growth failure and delayed puberty. It occurs in some children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes irrespective of their glycemic control.
Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism (HH), also known as primary or peripheral/gonadal hypogonadism or primary gonadal failure, is a condition which is characterized by hypogonadism which is due to an impaired response of the gonads to the gonadotropins, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), and in turn a lack of sex steroid production. As compensation and the lack of negative feedback, gonadotropin levels are elevated. Individuals with HH have an intact and functioning hypothalamus and pituitary glands so they are still able to produce FSH and LH. HH may present as either congenital or acquired, but the majority of cases are of the former nature. HH can be treated with hormone replacement therapy.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) insensitivity also known as Isolated gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)deficiency (IGD) is a rare autosomal recessive genetic and endocrine syndrome which is characterized by inactivating mutations of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (GnRHR) and thus an insensitivity of the receptor to gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), resulting in a partial or complete loss of the ability of the gonads to synthesize the sex hormones. The condition manifests itself as isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH), presenting with symptoms such as delayed, reduced, or absent puberty, low or complete lack of libido, and infertility, and is the predominant cause of IHH when it does not present alongside anosmia.

Early childhood development is the period of rapid physical, psychological and social growth and change that begins before birth and extends into early childhood. While early childhood is not well defined, one source asserts that the early years begin in utero and last until 3 years of age.





