
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name petroleum covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil and petroleum products that consist of refined crude oil. A fossil fuel, petroleum is formed when large quantities of dead organisms, mostly zooplankton and algae, are buried underneath sedimentary rock and subjected to both prolonged heat and pressure.

Peak oil is the moment at which extraction of petroleum reaches a rate greater than that at any time in the past and starts to permanently decrease. It is related to the distinct concept of oil depletion; while global petroleum reserves are finite, the limiting factor is not whether the oil exists but whether it can be extracted economically at a given price. A secular decline in oil extraction could be caused both by depletion of accessible reserves and by reductions in demand that reduce the price relative to the cost of extraction, as might be induced to reduce carbon emissions.

The Bakken Formation is a rock unit from the Late Devonian to Early Mississippian age occupying about 200,000 square miles (520,000 km2) of the subsurface of the Williston Basin, underlying parts of Montana, North Dakota, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. The formation was initially described by geologist J. W. Nordquist in 1953. The formation is entirely in the subsurface, and has no surface outcrop. It is named after Henry O. Bakken (1901–1982), a farmer in Tioga, North Dakota, who owned the land where the formation was initially discovered while drilling for oil.

The Monterey Formation is an extensive Miocene oil-rich geological sedimentary formation in California, with outcrops of the formation in parts of the California Coast Ranges, Peninsular Ranges, and on some of California's off-shore islands. The type locality is near the city of Monterey, California. The Monterey Formation is the major source-rock for 37 to 38 billion barrels of oil in conventional traps such as sandstones. This is most of California's known oil resources. The Monterey has been extensively investigated and mapped for petroleum potential, and is of major importance for understanding the complex geological history of California. Its rocks are mostly highly siliceous strata that vary greatly in composition, stratigraphy, and tectono-stratigraphic history.

Petroleum in the United States has been a major industry since shortly after the oil discovery in the Oil Creek area of Titusville, Pennsylvania in 1859. The industry includes exploration, production, processing (refining), transportation, and marketing of natural gas and petroleum products. In 2018, the U.S. became the worlds largest crude oil producer, producing 15% of global crude oil, surpassing Russia and Saudi Arabia. The leading oil-producing area in the United States in 2019 was Texas, followed by the offshore federal zone of the Gulf of Mexico, North Dakota and New Mexico. In 2020, the top five U.S. oil producing states were Texas (43%), North Dakota (10.4%), New Mexico (9.2%), Oklahoma (4.1%), and Colorado (4.0%).

Within the petroleum industry, proven oil reserves in the United States were 43.8 billion barrels of crude oil as of the end of 2018, excluding the Strategic Petroleum Reserve. The 2018 reserves represent the largest US proven reserves since 1972. The Energy Information Administration estimates US undiscovered, technically recoverable oil resources to be an additional 198 billion barrels.
Morocco's energy policy is set independently by two agencies of the government: the Office of Hydrocarbons and Mining (ONHYM) which sets domestic oil policy, and the Office National de l'Electricité (ONE), which sets policy with regard to electricity. The two major weaknesses of the energy policy of Morocco are the lack of coordination between these two agencies and the lack of development of domestic energy sources.
Although production rates were small as of 2013, the volume of technically recoverable shale gas in China has been estimated to be 1,115 trillion cubic feet, the largest of any country in the world. As of 2013, China is one of only three countries to produce shale gas in commercial quantities.

Tight oil is light crude oil contained in petroleum-bearing formations of low permeability, often shale or tight sandstone. Economic production from tight oil formations requires the same hydraulic fracturing and often uses the same horizontal well technology used in the production of shale gas. While sometimes called "shale oil", tight oil should not be confused with oil shale or shale oil. Therefore, the International Energy Agency recommends using the term "light tight oil" for oil produced from shales or other very low permeability formations, while the World Energy Resources 2013 report by the World Energy Council uses the terms "tight oil" and "shale-hosted oil".
Shale gas is natural gas produced from shale, a type of sedimentary rock. Shale gas has become an increasingly important source of natural gas in the United States over the past decade, and interest has spread to potential gas shales in Canada, Europe, Asia, and Australia. One analyst expects shale gas to supply as much as half the natural gas production in North America by 2020.

The Vaca Muerta Formation, commonly known as Vaca Muerta, is a geologic formation of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous age, located in the Neuquén Basin in northern Patagonia, Argentina. It is well known as the host rock for major deposits of shale oil and shale gas.
The Los Molles Formation is a geologic formation of Early to Middle Jurassic age, located at northern and central part of Neuquén Basin at Mendoza Shelf in Argentina. It is overlain by the Niyeu–Lajas Formation.
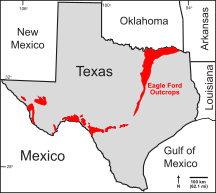
The Eagle Ford Group is a sedimentary rock formation deposited during the Cenomanian and Turonian ages of the Late Cretaceous over much of the modern-day state of Texas. The Eagle Ford is predominantly composed of organic matter-rich fossiliferous marine shales and marls with interbedded thin limestones. It derives its name from outcrops on the banks of the West Fork of the Trinity River near the old community of Eagle Ford, which is now a neighborhood within the city of Dallas. The Eagle Ford outcrop belt trends from the Oklahoma-Texas border southward to San Antonio, westward to the Rio Grande, Big Bend National Park, and the Quitman Mountains of West Texas. It also occurs in the subsurface of East Texas and South Texas, where it is the source rock for oil found in the Woodbine, Austin Chalk, and the Buda Limestone, and is produced unconventionally in South Texas and the "Eaglebine" play of East Texas. The Eagle Ford was one of the most actively drilled targets for unconventional oil and gas in the United States in 2010, but its output had dropped sharply by 2015. By the summer of 2016, Eagle Ford spending had dropped by two-thirds from $30 billion in 2014 to $10 billion, according to an analysis from the research firm Wood Mackenzie. This strike has been the hardest hit of any oil fields in the world. The spending was, however, expected to increase to $11.6 billion in 2017. A full recovery is not expected any time soon.

Natural gas was the United States' largest source of energy production in 2016, representing 33 percent of all energy produced in the country. Natural gas has been the largest source of electrical generation in the United States since July 2015.

The East-West Pipeline, also known as the Petroline, is a 746 miles (1,201 km)-long 48 inches (120 cm) pipeline that runs from the Abqaiq oil field in the Eastern Province across the width of the Arabian Peninsula to the Red Sea. It was built during the Iran-Iraq war. The line was converted to carry natural gas, but was converted back to carry crude oil. The pipeline is actually twinned pipes, and as of 2018 had a capacity of 5 million bbl/d.

On 8 March 2020, Saudi Arabia initiated a price war on oil with Russia, facilitating a 65% quarterly fall in the price of oil. In the first few weeks of March, US oil prices fell by 34%, crude oil fell by 26%, and Brent oil fell by 24%. The price war was triggered by a break-up in dialogue between the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and Russia over proposed oil-production cuts in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. Russia walked out of the agreement, leading to the fall of the OPEC+ alliance. Oil prices had already fallen 30% since the start of the year due to a drop in demand. The price war is one of the major causes and effects of the ensuing global stock-market crash.











