Politics in Estonia takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister of Estonia is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Legislative power is vested in the Estonian parliament. Executive power is exercised by the government, which is led by the prime minister. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. Estonia is a member of the United Nations, the European Union, and NATO.

Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state.
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well as the means by which a mayor is elected or otherwise mandated. Depending on the system chosen, a mayor may be the chief executive officer of the municipal government, may simply chair a multi-member governing body with little or no independent power, or may play a solely ceremonial role. A mayor's duties and responsibilities may be to appoint and oversee municipal managers and employees, provide basic governmental services to constituents, and execute the laws and ordinances passed by a municipal governing body. Options for selection of a mayor include direct election by the public, or selection by an elected governing council or board.

The municipalities of Sweden are its lower-level local government entities. There are 290 municipalities which are responsible for a large proportion of local services, including schools, emergency services and physical planning.
Region Skåne is the region of Skåne County in Sweden. Region Skåne was formed on 1 January 1999 by the amalgamation of the county councils of Malmöhus County and Kristianstad County and some of the tasks handled by Malmö Municipality.
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.
The Council of Rotuma is a municipal body on the island of Rotuma, a Fijian dependency. Owing to the unique character of Rotuma, the powers of this council are greater than those of other municipal bodies in Fiji and in some ways it approximates a legislative body, though it is in every way subordinate to the Parliament of Fiji.

The Legislative Council of Fiji was the colonial precursor to the present-day Parliament, which came into existence when Fiji became independent on 10 October 1970.

The government of Florida is established and operated according to the Constitution of Florida and is composed of three branches of government: the executive branch consisting of the governor of Florida and the other elected and appointed constitutional officers; the legislative branch, the Florida Legislature, consisting of the Senate and House; and the judicial branch consisting of the Supreme Court of Florida and lower courts. The state also allows direct participation of the electorate by initiative, referendum, and ratification.
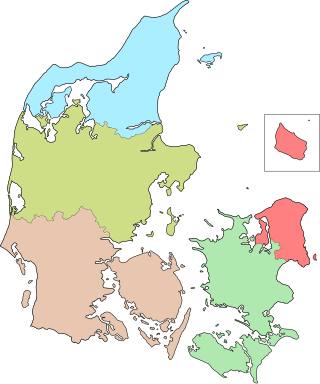
The five Regions of Denmark were created as administrative entities at a level above the municipalities and below the central government in the public sector as part of the 2007 Danish Municipal Reform, when the 13 counties (amter) were abolished. At the same time, the number of municipalities (kommuner) was cut from 270 to 98. The reform was approved and made into a law by the lawmakers in the Folketing 26 June 2005 with elections to the 98 municipalities and 5 regions being held Tuesday 15 November 2005.
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural council, village council, or board of aldermen.

Bent Høie is a Norwegian politician from the Conservative Party who has served as county governor of Rogaland since 2021. He previously served as Minister of Health and Care Services from 2013 to 2021, and a member of the Storting from Rogaland from 2000 to 2021.

The county governor is a Norwegian government agency that represents the central government administration in every county in Norway. Responsible for a number of supervision and management duties, the governor is the representative of the king and the government of Norway in each county, functioning as the connection between the state and the municipalities. The county governor is subordinate to the Ministry of Local Government and Modernisation but also to the other ministries in their respective duties.
The government of Nevada comprises three branches of government: the executive branch consisting of the governor of Nevada and the governor's cabinet along with the other elected constitutional officers; the legislative branch consisting of the Nevada Legislature which includes the Assembly and the Senate; and the judicial branch consisting of the Supreme Court of Nevada and lower courts.
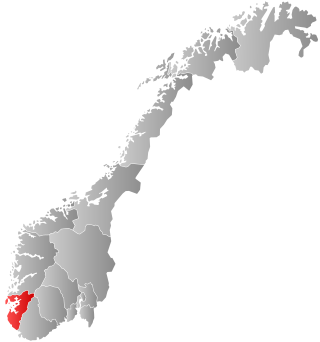
Rogaland County Municipality is the democratically elected regional governing administration of Rogaland county, Norway. The responsibilities of the county municipality include the running of 29 upper secondary schools as well as managing the county roadways, public transport, dental care, cultural affairs, and cultural heritage. The county municipality also coordinates regional planning and economic development. The Rogfast is a major road project that is being financed by the county municipality. The administration is located in the city of Stavanger.
The Oklahoma State Department of Health (OSDH) is a department of the government of Oklahoma under the supervision of the Oklahoma Secretary of Health. The department is responsible for protecting the health of all Oklahomans and providing other essential human services. The OSDH serves as the primary public health protection agency in the state.

The Bangkok Metropolitan Administration (BMA) is the local government of Bangkok, which includes the capital of the Kingdom of Thailand. The government is composed of two branches: the executive and the legislative. The administration's roles are to formulate and implement policies to manage Bangkok. Its purview includes transport services, urban planning, waste management, housing, roads and highways, security services, and the environment.
Norway's elongated shape, its numerous internal geographical barriers and the often widely dispersed and separated settlements are all factors that have strongly influenced the structure of the country's administrative subdivisions. This structure has varied over time and is subject to continuous review. In 2017, the government decided to abolish some of the counties and to merge them with other counties to form larger ones, reducing the number of counties from 19 to 11, which was implemented on 1 January 2020. Following protests, the new government decided to abolish three of the new counties in 2022, and re-establish seven of the old ones. Taking effect on 1 January 2024 there are fifteen counties in Norway.

Aust-Agder County Municipality was the regional governing administration of the old Aust-Agder county in Norway. The county municipality was established on 1 January 1976 when the law was changed to allow elected county councils in Norway. The county municipality was dissolved on 1 January 2020, when Aust-Agder was merged with the neighboring Vest-Agder county, creating the new Agder county which is led by the Agder County Municipality.
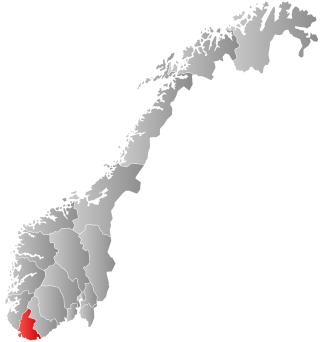
Vest-Agder County Municipality was the regional governing administration of the old Vest-Agder county in Norway. The county municipality was established on 1 January 1976 when the law was changed to allow elected county councils in Norway. The county municipality was dissolved on 1 January 2020, when Vest-Agder was merged with the neighboring Aust-Agder county, creating the new Agder county which is led by the Agder County Municipality.










