
In finance, a bond is a type of security under which the issuer (debtor) owes the holder (creditor) a debt, and is obliged – depending on the terms – to provide cash flow to the creditor. The timing and the amount of cash flow provided varies, depending on the economic value that is emphasized upon, thus giving rise to different types of bonds. The interest is usually payable at fixed intervals: semiannual, annual, and less often at other periods. Thus, a bond is a form of loan or IOU. Bonds provide the borrower with external funds to finance long-term investments or, in the case of government bonds, to finance current expenditure.

A printed circuit board is a medium used to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers: each of the conductive layers is designed with an artwork pattern of traces, planes and other features etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto and/or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate. Electrical components may be fixed to conductive pads on the outer layers in the shape designed to accept the component's terminals, generally by means of soldering, to both electrically connect and mechanically fasten them to it. Another manufacturing process adds vias: plated-through holes that allow interconnections between layers.

A government bond or sovereign bond is a form of bond issued by a government to support public spending. It generally includes a commitment to pay periodic interest, called coupon payments, and to repay the face value on the maturity date.

The M1 Garand or M1 rifle is a semi-automatic rifle that was the service rifle of the U.S. Army during World War II and the Korean War.
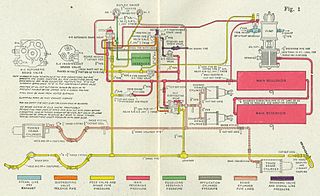
A railway air brake is a railway brake power braking system with compressed air as the operating medium. Modern trains rely upon a fail-safe air brake system that is based upon a design patented by George Westinghouse on April 13, 1869. The Westinghouse Air Brake Company was subsequently organized to manufacture and sell Westinghouse's invention. In various forms, it has been nearly universally adopted.
A perpetuity is an annuity that has no end, or a stream of cash payments that continues forever. There are few actual perpetuities in existence. For example, the United Kingdom (UK) government issued them in the past; these were known as consols and were all finally redeemed in 2015.

In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure.

In marketing, a coupon is a ticket or document that can be redeemed for a financial discount or rebate when purchasing a product.
In the United Kingdom, the football pools, often referred to as "the pools", is a betting pool based on predicting the outcome of association football matches taking place in the coming week. The pools are typically cheap to enter, and may encourage gamblers to enter several bets.

A collateralized mortgage obligation (CMO) is a type of complex debt security that repackages and directs the payments of principal and interest from a collateral pool to different types and maturities of securities, thereby meeting investor needs.

The karbovanets or karbovanet, also known as kupon or coupon, has been a distinct unit of currency in Ukraine during three separate periods of the 20th century. It is also a predecessor currency of today's Ukrainian hryvnia.
Gilt-edged securities are bonds issued by the UK Government. The term is of British origin, and then referred to the debt securities issued by the Bank of England on behalf of His Majesty's Treasury, whose paper certificates had a gilt edge. Hence, they are known as gilt-edged securities, or gilts for short.
The National Bank of Ukraine has issued four banknote series since 1996. All banknotes in denominations of ₴1, ₴2, ₴5, ₴10, ₴20, ₴50, ₴100, ₴200, ₴500 and ₴1,000 issued after 2003 are considered legal tender. All of them depict an important person in Ukraine's history on the obverse and a landmark place on the reverse. The lowest four denominations are no longer issued in banknotes and are intended to be gradually substituted by coins, though they remain common. There have been four commemorative banknote issues.
Corrosion monitoring is the use of a corrator or set of methods and equipment to provide offline or online information about corrosion rate expressed in mpy. - for better care and to take or improve preventive measures to combat and protect against corrosion. In this article, the difference between corrosion monitoring and corrosion protection, its difference with corrosion inspection and also the relationship between them, as well as online corrosion monitoring methods, equipment used and applications of each of them, are presented.
Stencil printing is the process of depositing solder paste on the printed wiring boards (PWBs) to establish electrical connections. It is immediately followed by the component placement stage. The equipment and materials used in this stage are a stencil, solder paste, and a printer.
A coupon or test coupon is a printed circuit board (PCB) used to test the quality of a printed wiring board (PWB) fabrication process. Test coupons are fabricated on the same panel as the PWBs, typically at the edges. Coupons are then inspected to ensure proper layer alignment, electrical connectivity, and cross sectioned to inspect internal structures. Coupons can be designed custom for a PWB or selected from a vendor library.
Electrofusion welding is a form of resistive implant welding used to join pipes. A fitting with implanted metal coils is placed around two ends of pipes to be joined, and current is passed through the coils. Resistive heating of the coils melts small amounts of the pipe and fitting, and upon solidification, a joint is formed. It is most commonly used to join polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) pipes. Electrofusion welding is the most common welding technique for joining PE pipes. Because of the consistency of the electrofusion welding process in creating strong joints, it is commonly employed for the construction and repair of gas-carrying pipelines. The development of the joint strength is affected by several process parameters, and a consistent joining procedure is necessary for the creation of strong joints.

Fatigue testing is a specialised form of mechanical testing that is performed by applying cyclic loading to a coupon or structure. These tests are used either to generate fatigue life and crack growth data, identify critical locations or demonstrate the safety of a structure that may be susceptible to fatigue. Fatigue tests are used on a range of components from coupons through to full size test articles such as automobiles and aircraft.









