
Senecio is a genus of flowering plants in the daisy family (Asteraceae) that includes ragworts and groundsels.

Liberty Hyde Bailey was an American horticulturist and reformer of rural life. He was cofounder of the American Society for Horticultural Science. As an energetic reformer during the Progressive Era, he was instrumental in starting agricultural extension services, the 4-H movement, the nature study movement, parcel post and rural electrification. He was considered the father of rural sociology and rural journalism.

Osteospermum, is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the Calenduleae, one of the smaller tribes of the sunflower/daisy family Asteraceae. They are known as the daisybushes or African daisies.

Senecioneae is the largest tribe of the Asteraceae, or the sunflower family, comprising over 150 genera and over 3,500 species. Almost one-third of the species in this tribe are placed in the genus Senecio. Its members exhibit probably the widest possible range of form to be found in the entire plant kingdom, and include annuals, minute creeping alpines, herbaceous and evergreen perennials, shrubs, climbers, succulents, trees, and semi-aquatic plants.

Aristaloe is a genus of evergreen flowering perennial plants in the family Asphodelaceae from Southern Africa. Its sole species is Aristaloe aristata, known as guinea-fowl aloe or lace aloe.

Gasteria is a genus of succulent plants, native to South Africa.

Brunsvigia is a genus of African flowering plants in the family Amaryllidaceae, subfamily Amaryllidoideae. It contains about 20 species native to southeastern and southern Africa from Tanzania to the Cape Provinces of South Africa.

Othonna is a genus of approximately 90 species of succulent or subsucculent perennial herbs or shrubs, with its center of diversity in the Greater Cape Floristic Region (GCFR) of South Africa but some species' ranges include southern Namibia, Angola, and Zimbabwe. The genus was established by Linnaeus in 1753 containing 14 species, however, of those original species, only four are still retained in Othonna, while the others have been transferred to different genera including Cineraria, Euryops, Hertia, Ligularia, Senecio, and Tephroseris. The genus Othonnna is known to be monophyletic. In 2012, a new genus Crassothonna B. Nord. was erected with 13 species transferred from Othonna. A complete modern taxonomic treatment of the genus is being undertaken by the Compton Herbarium and the South African National Biodiversity Institute. The first part, a revision of the Othonnna bulbosa group, was published in 2019.

Aloidendron barberae, formerly Aloe bainesii and Aloe barberae, also known as the tree aloe, is a species of succulent plant in the genus Aloidendron. It is native to South Africa northwards to Mozambique. In its native climes this slow-growing tree can reach up to 60 feet (18 m) high and 36 inches (0.91 m) in stem diameter. Aloidendron barberae is Africa's largest aloe-like plant. The tree aloe is often used as an ornamental plant. Its tubular flowers are rose pink (green-tipped); it flowers in winter and in its natural environment is pollinated by sunbirds.

Johanna Ellaphie Ward-Hilhorst was a South African botanical artist.
Crassothonna clavifolia is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is found only in Namibia. Its natural habitat is rocky areas. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Phygelius, common names Cape fuchsia or Cape figwort, is a genus of flowering plants in the family Scrophulariaceae, native to wet slopes and banks in southern Africa. They are evergreen shrubs often treated as perennials in colder climates. They bear many pendent tubular flowers over a long period in summer, in shades of white, yellow and red. The vague similarity of the blooms to fuchsias has led to the common name Cape fuchsia, though they are not closely related.

Bulbine is a genus of plants in the family Asphodelaceae and subfamily Asphodeloideae, named for the bulb-shaped tuber of many species. It was formerly placed in the Liliaceae. It is found chiefly in Southern Africa, with a few species extending into tropical Africa and a few others in Australia and Yemen.
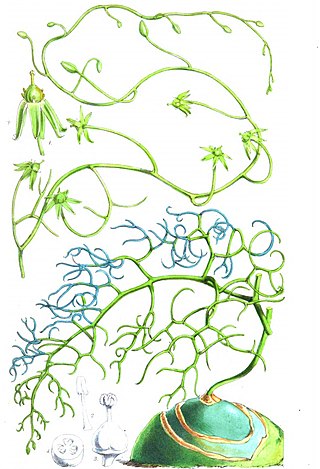
Bowiea is a genus of bulbous, perennial, succulent plants which thrive in dry and desert regions of eastern and southern Africa. It is native to a region stretching from Kenya to Cape Province. The genus contains a single species, Bowiea volubilis.

Gasteria armstrongii is a dwarf succulent plant native to South Africa, in the genus Gasteria.

Cleretum bellidiforme, commonly called Livingstone daisy, Bokbaaivygie (Afrikaans), or Buck Bay vygie, is a species of flowering plant in the family Aizoaceae, native to the Cape Peninsula in South Africa. It is a low-growing succulent annual growing to 25 cm (10 in), and cultivated for its iridescent, many-petalled, daisy-like blooms in shades of white, yellow, orange, cream, pink and crimson. In temperate areas it is popularly grown as a half-hardy annual, and lends itself to mass plantings or as edging plants in summer bedding schemes in parks and gardens. It is still widely referenced under its former names, Mesembryanthemum criniflorum and Dorotheanthus bellidiformis.

Fockea is a genus of succulent scrubs native to Africa south of the equator. They are members of the Asclepiadoideae (milkweeds), a subfamily of the dogbane family Apocynaceae. Of the six recognized species, only the two most widely distributed extend north of southern Africa, with F. multiflora reaching as far north as Tanzania and F. angustifolia reaching to southern Kenya. Fockea are known as water roots, a reference to the bulbous caudex characteristic of most species, which is also edible in at least some species.

Caputia is a small genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, native to South Africa. It may be of hybrid origin. Species in this genus were formerly considered part of the genus Senecio.
Crassothonna is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Asteraceae.

















