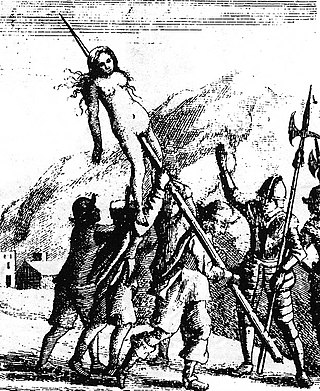Painting
Following the publication of Thomas Carlyle's Oliver Cromwell's letters and speeches, with elucidations (1845), Cromwell had been regularly portrayed in a heroic light in British art. His actions with regard to the Vaudois had been illustrated several times. Charles Rowley commissioned Brown to create the picture.
I commissioned him to paint for me the fine picture now at Manchester, "Cromwell, Protector of the Vaudois." I wanted a picture of John Milton, and the result is this masterpiece: Cromwell, Milton, and Andrew Marvell, who was then secretary to the blind poet. [3]
Brown's painting differs from earlier versions of the scene because of its highly dynamic composition designed to stress the relationship between Cromwell as a man of action and Milton as a powerful intellectual force, with Marvell energetically poised to execute their combined wills. In this respect the painting is a development of the central theme of Brown's earlier painting Work , but in this case emphasises the work of a "power elite" rather than ordinary manual labour. Cromwell's pose, splayed across the desk, is a development of earlier imagery in which Cromwell had been depicted as a rough or unceremonious figure. [4] His contained energy is emphasised by the precariously balanced desk, supported on a curved base with small stabilising feet. Milton's gesture is similarly transitory, finger raised, while the cropped, half-obscured figure of Marvell holds his pen ready waiting.

Ford Madox Brown was a British painter of moral and historical subjects, notable for his distinctively graphic and often Hogarthian version of the Pre-Raphaelite style. Arguably, his most notable painting was Work (1852–1865). Brown spent the latter years of his life painting the twelve works known as The Manchester Murals, depicting Mancunian history, for Manchester Town Hall.

Oliver Cromwell was an English statesman, politician, and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in the history of the British Isles. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially as a senior commander in the Parliamentarian army and latterly as a politician. A leading advocate of the execution of Charles I in January 1649, which led to the establishment of The Protectorate, he ruled as Lord Protector from December 1653 until his death in September 1658. Cromwell remains a controversial figure due to his use of the army to acquire political power, and the brutality of his 1649 campaign in Ireland.

Andrew Marvell was an English metaphysical poet, satirist and politician who sat in the House of Commons at various times between 1659 and 1678. During the Commonwealth period he was a colleague and friend of John Milton. His poems range from the love-song "To His Coy Mistress", to evocations of an aristocratic country house and garden in "Upon Appleton House" and "The Garden", the political address "An Horatian Ode upon Cromwell's Return from Ireland", and the later personal and political satires "Flecknoe" and "The Character of Holland".

Charles Emmanuel II ; 20 June 1634 – 12 June 1675) was Duke of Savoy and ruler of the Savoyard states from 4 October 1638 until his death in 1675 and under regency of his mother Christine of France until 1648. He was also Marquis of Saluzzo, Count of Aosta, Geneva, Moriana and Nice, as well as claimant king of Cyprus, Jerusalem and Armenia. At his death in 1675, his second wife Marie Jeanne Baptiste of Savoy-Nemours acted as regent for their nine-year-old son.

The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood was a group of English painters, poets, and art critics, founded in 1848 by William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, William Michael Rossetti, James Collinson, Frederic George Stephens and Thomas Woolner who formed a seven-member "Brotherhood" partly modelled on the Nazarene movement. The Brotherhood was only ever a loose association and their principles were shared by other artists of the time, including Ford Madox Brown, Arthur Hughes and Marie Spartali Stillman. Later followers of the principles of the Brotherhood included Edward Burne-Jones, William Morris and John William Waterhouse.
Events from the year 1877 in art.

The Germ, thoughts towards nature in art and literature (1850) was a periodical established by the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood to disseminate their ideas. The magazine was edited by William Michael Rossetti. The Germ was renamed Art and Poetry, being Thoughts towards Nature, conducted principally by Artists for its last two issues. It was not a success, only surviving for four issues between January and April 1850.

The Last of England is an 1855 oil-on-panel painting by Ford Madox Brown depicting two emigrants leaving England to start a new life in Australia with their baby. The painting has an oval format and is in the Birmingham Museum and Art Gallery.

Work (1852–1865) is a painting by Ford Madox Brown that is generally considered to be his most important achievement. It exists in two versions. The painting attempts to portray, both literally and analytically, the totality of the Victorian social system and the transition from a rural to an urban economy. Brown began the painting in 1852 and completed it in 1865, when he set up a special exhibition to show it along with several of his other works. He wrote a detailed catalogue explaining the significance of the picture.

Cromwell on his Farm (1874) is a painting by Ford Madox Brown which depicts Oliver Cromwell observing a bonfire on his farm and thinking of a passage in the Book of Psalms: "Lord, how long wilt thou hide thyself - forever? And shall thy wrath burn like fire?". The words are inscribed on the painting's frame along with a quotation from one of Cromwell's speeches, in which he describes his life before entering into politics: "living neither in any considerable height, nor yet in obscurity, I did endeavour to discharge the duty of an honest man."

The Manchester Murals are a series of twelve paintings by Ford Madox Brown in the Great Hall of Manchester Town Hall and are based on the history of Manchester. Following the success of Brown's painting Work he was commissioned to paint six murals for its Great Hall. Another six murals were to be completed by Frederic Shields who later withdrew, leaving Brown to complete all twelve works. The murals were begun in 1879, towards the end of Brown's career, but were not completed until 1893, the year he died. During this period he moved from London to Manchester with his family, first living in Crumpsall and then Victoria Park.

Take Your Son, Sir! (1851–56) is an unfinished painting by Ford Madox Brown which depicts a woman showing her newborn son to its father. She is offering her baby towards the viewer of the painting, who is implicitly equated with the father - seen in the mirror behind, opening his arms to receive the baby. The mirror also forms a halo behind the mother's head, and the pattern on the wallpaper suggests the starry heavens. Brown's principal influence was Jan van Eyck's painting the Arnolfini Marriage Portrait, recently acquired by the National Gallery. The mirror resembles the circular mirror in van Eyck's painting, which reflects an image of the artist looking at the couple in the image.
Nathaniel Ingelo was an English clergyman, writer and musician, best known for the allegorical romance Bentivolio and Urania.

Isaac Sailmaker was an etcher and marine painter of the Baroque period, who had a long career in England. He was referred to in contemporary books and journals as "the father of British sea painting", but was eclipsed by his contemporaries, the Dutch marine painters Willem van de Velde the Elder and his son Willem van de Velde the Younger, who for a period dominated the London market. Sailmaker was commissioned by the English Lord Protector, Oliver Cromwell, to paint the English fleet at Fort-Mardyck.
Nationality words link to articles with information on the nation's poetry or literature.

Lucy Madox Brown Rossetti was a British artist, author, and model associated with the Pre-Raphaelites. She was married to the writer and art critic William Michael Rossetti.

Catherine Madox Brown Hueffer, also known as Cathy, the first child of Ford Madox Brown and Emma Hill, was an artist and model associated with the Pre-Raphaelites and married to the writer Francis Hueffer.
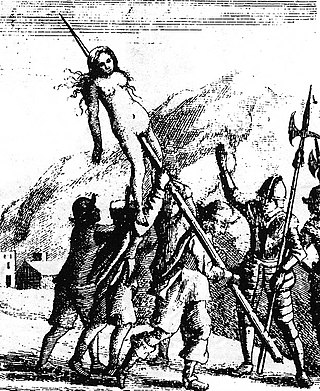
The Piedmontese Easter was a series of massacres on Waldensians by Savoyard troops in the Duchy of Savoy in 1655.

The Pretty Baa-Lambs is an oil-on-panel painting executed in 1851 by the English Pre-Raphaelite artist Ford Madox Brown and part of the collection of Birmingham Museums and Art Gallery.