Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) is a technique in molecular biology for the typing of multiple loci, using DNA sequences of internal fragments of multiple housekeeping genes to characterize isolates of microbial species.

Microcins are very small bacteriocins, composed of relatively few amino acids. For this reason, they are distinct from their larger protein cousins. The classic example is microcin V, of Escherichia coli. Subtilosin A is another bacteriocin from Bacillus subtilis. The peptide has a cyclized backbone and forms three cross-links between the sulphurs of Cys13, Cys7 and Cys4 and the alpha-positions of Phe22, Thr28 and Phe31.
Chlamydia pecorum, also known as Chlamydophila pecorum is a species of Chlamydiaceae that originated from ruminants, such as cattle, sheep and goats. It has also infected koalas and swine. C. pecorum strains are serologically and pathogenically diverse.

Mycobacteroides abscessus is a species of rapidly growing, multidrug-resistant, nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) that is a common soil and water contaminant. Although M. abscessus most commonly causes chronic lung infection and skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI), it can also cause infection in almost all human organs, mostly in patients with suppressed immune systems. Amongst NTM species responsible for disease, infection caused by M. abscessus complex are more difficult to treat due to antimicrobial drug resistance.
Ralstonia pickettii is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, soil bacterium.
Ralstonia insidiosa is a Gram-negative, environmental bacterium. It has been shown to be a pathogenic in immunocompromised patients in hospital settings. This bacterium is closely related to Ralstonia pickettii.

Cronobacter sakazakii, which before 2007 was named Enterobacter sakazakii, is an opportunistic Gram-negative, rod-shaped, pathogenic bacterium that can live in very dry places, otherwise known as xerotolerance. C. sakazakii utilizes a number of genes to survive desiccation and this xerotolerance may be strain specific. The majority of C. sakazakii cases are adults but low-birth-weight preterm neonatal and older infants are at the highest risk. The pathogen is a rare cause of invasive infection in infants, with historically high case fatality rates (40–80%).
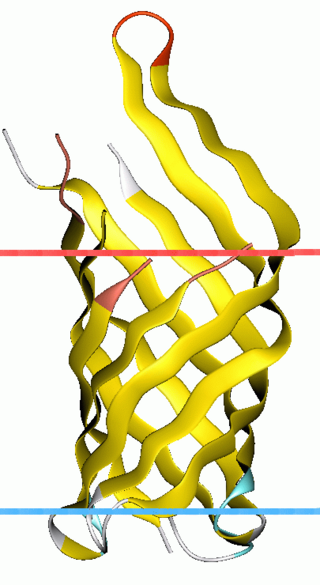
OmpA-like transmembrane domain is an evolutionarily conserved domain of bacterial outer membrane proteins. This domain consists of an eight-stranded beta barrel. OmpA is the predominant cell surface antigen in enterobacteria found in about 100,000 copies per cell. The expression of OmpA is tightly regulated by a variety of mechanisms. One mechanism by which OmpA expression is regulated in Vibrio species is by an antisense non-coding RNA called VrrA.

Cronobacter is a genus of Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, oxidase-negative, catalase-positive, rod-shaped bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Several Cronobacter species are desiccation resistant and persistent in dry products such as powdered infant formula. They are generally motile, reduce nitrate, use citrate, hydrolyze esculin and arginine, and are positive for L-ornithine decarboxylation. Acid is produced from D-glucose, D-sucrose, D-raffinose, D-melibiose, D-cellobiose, D-mannitol, D-mannose, L-rhamnose, L-arabinose, D-trehalose, galacturonate and D-maltose. Cronobacter spp. are also generally positive for acetoin production and negative for the methyl red test, indicating 2,3-butanediol rather than mixed acid fermentation. The type species of the genus Cronobacter is Cronobacter sakazakii comb. nov.
Acidovorax oryzae is a bacterium from the Comamonadaceae family which is closely related to Acidovorax citrulli. Acidovorax oryzae was reclassificated from the former name Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae. It has been shown that Acidovorax oryzae is serious pathogen fore rice.

Lactobacillus johnsonii is a species in the genus Lactobacillus identified in 1980 by John L. Johnson, an American microbiologist and his associates. Its type strain is ATCC 33200. It is part of the healthy vaginal microbiota and has been identified as having probiotic properties. The L. johnsonii strain La1 was one of the first cultures to be proposed as a probiotic dairy supplement in 1995 at the Nestlé Research Center, Lausanne. Although yeast and bacteria have been used in dairy products for fermenting purposes for centuries, the investigation and choice of a microorganism as a fermenting agent based on its health benefits was novel at the time. Today the probiotic culture is used in the LC1 yogurt products by Nestlé.
Cronobacter dublinensis is a bacterium. Its name pertains to Dublin, the origin of the type strain. The type strain is originally from a milk powder manufacturing facility. C. dublinensis sp. nov. is dulcitol negative and methyl-α-D-glucopyranoside positive and generally positive for indole production.
Cronobacter muytjensii is a bacterium. It is named after Harry Muytjens. Its type strain is ATCC 51329T. It is indole, dulcitol, and malonate positive but palatinose and methyl-α-D-glucopyranoside negative.
Brucella pinnipedialis is a species of bacteria. It causes infections and related diseases primarily in pinnipeds and cetaceans.
Arcobacter halophilus is a species of obligate halophilic bacteria. It is Gram-negative, and its type strain is LA31BT(=ATCC BAA-1022T =CIP 108450T).
Cronobacter malonaticus, formerly considered a subspecies of Cronobacter sakazakii, is a bacterium. Its type strain is CDC 1058-77T.
Rickettsia asiatica is a tick-borne pathogenic species borne by Ixodes ovatus. The type strain of Rickettsia asiatica sp. nov. is IO-1T.
Enterobacter cowanii is a Gram-negative, motile, facultatively-anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium of the genus Enterobacter. The species is typically associated with natural environments and is found in soil, water, and sewage. E. cowanii is associated with plant pathogens that exhibit symptoms of severe defoliation and plant death. This species, originally referred to as NIH Group 42, was first proposed in 2000 as a potential member of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The name of this species honors S. T. Cowan, an English bacteriologist, for his significant contributions to the field of bacterial taxonomy.
Actinotignum schaalii is a bacterium first isolated from human blood cultures. Its type strain is CCUG 27420. It is a Gram-positive, facultative anaerobic coccoid rod, considered a human pathogen.

Phytobacter is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria emerging from the grouping of isolates previously assigned to various genera of the family Enterobacteriaceae. This genus was first established on the basis of nitrogen fixing isolates from wild rice in China, but also includes a number of isolates obtained during a 2013 multi-state sepsis outbreak in Brazil and, retrospectively, several clinical strains isolated in the 1970s in the United States that are still available in culture collections, which originally were grouped into Brenner's Biotype XII of the Erwinia herbicola-Enterobacter agglomerans-Complex (EEC). Standard biochemical evaluation panels are lacking Phytobacter spp. from their database, thus often leading to misidentifications with other Enterobacterales species, especially Pantoea agglomerans. Clinical isolates of the species have been identified as an important source of extended-spectrum β-lactamase and carbapenem-resistance genes, which are usually mediated by genetic mobile elements. Strong protection of co-infecting sensitive bacteria has also been reported. Bacteria belonging to this genus are not pigmented, chemoorganotrophic and able to fix nitrogen. They are lactose fermenting, cytochrome-oxidase negative and catalase positive. Glucose is fermented with the production of gas. Colonies growing on MacConkey agar (MAC) are circular, convex and smooth with non-entire margins and a usually elevated center. Three species are currently validly included in the genus Phytobacter, which is still included within the Kosakonia clade in the lately reviewed family of Enterobacteriaceae. The incorporation of a fourth species, Phytobacter massiliensis, has recently been proposed via the unification of the genera Metakosakonia and Phytobacter.





