Related Research Articles
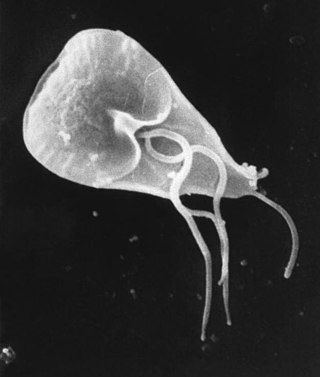
Giardia is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing the disease giardiasis. Their life cycle alternates between a swimming trophozoite and an infective, resistant cyst. Giardia were first seen by the Dutch microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1681. The genus is named after French zoologist Alfred Mathieu Giard.

Giardia duodenalis, also known as Giardia intestinalis and Giardia lamblia, is a flagellated parasitic protozoan microorganism of the genus Giardia that colonizes the small intestine, causing a diarrheal condition known as giardiasis. The parasite attaches to the intestinal epithelium by a ventral disc, and reproduces via binary fission. G. duodenalis is a non-invasive parasite, that does not spread to other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, but remains confined to the lumen of the small intestine. The parasite exists in two forms; trophozoites and cysts. The microorganism can undergo encystation, transforming into a dormant cyst that enables it to survive outside of its host. Giardia trophozoites are anaerobic, and absorb their nutrients from the intestinal lumen. If the organism is stained, its characteristic pattern resembles the familiar "smiley face" symbol.

Entamoeba histolytica is an anaerobic parasitic amoebozoan, part of the genus Entamoeba. Predominantly infecting humans and other primates causing amoebiasis, E. histolytica is estimated to infect about 35-50 million people worldwide. E. histolytica infection is estimated to kill more than 55,000 people each year. Previously, it was thought that 10% of the world population was infected, but these figures predate the recognition that at least 90% of these ball infections were due to a second species, E. dispar. Mammals such as dogs and cats can become infected transiently, but are not thought to contribute significantly to transmission.

Cysticercosis is a tissue infection caused by the young form of the pork tapeworm. People may have few or no symptoms for years. In some cases, particularly in Asia, solid lumps of between one and two centimetres may develop under the skin. After months or years these lumps can become painful and swollen and then resolve. A specific form called neurocysticercosis, which affects the brain, can cause neurological symptoms. In developing countries this is one of the most common causes of seizures.

Praziquantel (PZQ), sold under the brandname Biltricide among others, is a medication used to treat a number of types of parasitic worm infections in mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish. In humans specifically, it is used to treat schistosomiasis, clonorchiasis, opisthorchiasis, tapeworm infections, cysticercosis, echinococcosis, paragonimiasis, fasciolopsiasis, and fasciolosis. It should not be used for worm infections of the eye. It is taken by mouth.
Hymenolepiasis is infestation by one of two species of tapeworm: Hymenolepis nana or H. diminuta. Alternative names are dwarf tapeworm infection and rat tapeworm infection. The disease is a type of helminthiasis which is classified as a neglected tropical disease.
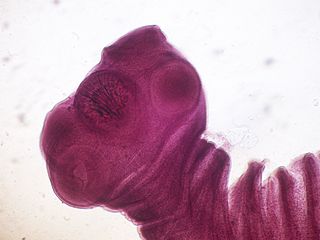
Taenia solium, the pork tapeworm, belongs to the cyclophyllid cestode family Taeniidae. It is found throughout the world and is most common in countries where pork is eaten. It is a tapeworm that uses humans as its definitive host and pigs as the intermediate or secondary hosts. It is transmitted to pigs through human feces that contain the parasite eggs and contaminate their fodder. Pigs ingest the eggs, which develop into larvae, then into oncospheres, and ultimately into infective tapeworm cysts, called cysticerci. Humans acquire the cysts through consumption of uncooked or under-cooked pork and the cysts grow into adult worms in the small intestine.

Echinococcus is a genus within Cestoda, a parasitic class of the platyhelminthes phylum. Human echinococcosis is an infectious disease caused by the following species: E. granulosus, E. multilocularis, E. vogeli or E. oligarthrus.

Echinococcus granulosus, also called the hydatid worm or dog tapeworm, is a cyclophyllid cestode that dwells in the small intestine of canids as an adult, but which has important intermediate hosts such as livestock and humans, where it causes cystic echinococcosis, also known as hydatid disease. The adult tapeworm ranges in length from 3 mm to 6 mm and has three proglottids ("segments") when intact—an immature proglottid, mature proglottid and a gravid proglottid. The average number of eggs per gravid proglottid is 823. Like all cyclophyllideans, E. granulosus has four suckers on its scolex ("head"), and E. granulosus also has a rostellum with hooks. Several strains of E. granulosus have been identified, and all but two are noted to be infective in humans.
The Hymenolepididae are family of cyclophyllid tapeworms. Their characteristic feature is the small number of testes. The unilateral genital pores and large external seminal vesicle allow for easy recognition. Most species are small, transparent, and easy to study. The family contains over 90 genera with over 900 species, having as their definitive host birds or mammals. Most reside in the intestines of their definitive hosts. The majority of species with known lifecycles have arthropods as intermediate hosts.
Dwarf tapeworm is a cosmopolitan species though most common in temperate zones, and is one of the most common cestodes infecting humans, especially children.

Hymenolepis diminuta, also known as rat tapeworm, is a species of Hymenolepis tapeworm that causes hymenolepiasis. It has slightly bigger eggs and proglottids than H. nana and infects mammals using insects as intermediate hosts. The adult structure is 20 to 60 cm long and the mature proglottid is similar to that of H. nana, except it is larger.

Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels.

Eucestoda, commonly referred to as tapeworms, is the larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the class Cestoda. Larvae have six posterior hooks on the scolex (head), in contrast to the ten-hooked Cestodaria. All tapeworms are endoparasites of vertebrates, living in the digestive tract or related ducts. Examples are the pork tapeworm with a human definitive host, and pigs as the secondary host, and Moniezia expansa, the definitive hosts of which are ruminants.
Spirometra erinaceieuropaei is a parasitic tapeworm that infects domestic animals and humans. The medical term for this infection in humans and other animals is sparganosis. Morphologically, these worms are similar to other worms in the genus Spirometra. They have a long body consisting of three sections: the scolex, the neck, and the strobilia. They have a complex life cycle that consists of three hosts, and can live in varying environments and bodily tissues. Humans can contract this parasite in three main ways. Historically, humans are considered a paratenic host; however, the first case of an adult S. erinaceieuropaei infection in humans was reported in 2017. Spirometra tapeworms exist worldwide and infection is common in animals, but S. erinaceieuropaei infections are rare in humans. Treatment for infection typically includes surgical removal and anti-worm medication.

Hymenolepis is a genus of cyclophyllid tapeworms that cause hymenolepiasis. They parasitise mammals, including humans. Some notable species are:

Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of many similar units known as proglottids—essentially packages of eggs which are regularly shed into the environment to infect other organisms. Species of the other subclass, Cestodaria, are mainly fish infecting parasites.

Raillietina is a genus of tapeworms that includes helminth parasites of vertebrates, mostly of birds. The genus was named in 1920 in honour of a French veterinarian and helminthologist, Louis-Joseph Alcide Railliet. Of the 37 species recorded under the genus, Raillietina demerariensis, R. asiatica, and R. formsana are the only species reported from humans, while the rest are found in birds. R. echinobothrida, R. tetragona, and R. cesticillus are the most important species in terms of prevalence and pathogenicity among wild and domestic birds.

Raillietina echinobothrida is a parasitic tapeworm belonging to the class Cestoda. It is the most prevalent and pathogenic helminth parasite in birds, particularly in domestic fowl, Gallus domesticus Linnaeus, 1758. It requires two hosts, birds and ants, for completion of its life cycle. It is a hermaphrodite worm having both the male and female reproductive organs in its body. The parasite is responsible for 'nodular tapeworm disease' in poultry.

Hymenolepis microstoma, also known as the rodent tapeworm, is an intestinal dwelling parasite. Adult worms live in the bile duct and small intestines of mice and rats, and larvae metamorphose in the haemocoel of beetles. It belongs to the genus Hymenolepis; tapeworms that cause hymenolepiasis. H. microstoma is prevalent in rodents worldwide, but rarely infects humans.
References
- ↑ Sulima, Anna; Savijoki, Kirsi; Bień, Justyna; Näreaho, Anu; Sałamatin, Rusłan; Conn, David Bruce; Młocicki, Daniel (2018-01-15). "Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Hymenolepis diminuta Cysticercoid and Adult Stages". Frontiers in Microbiology. 8: 2672. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02672 . ISSN 1664-302X. PMC 5775281 . PMID 29379475.
- ↑ Sulima, Anna; Bień, Justyna; Savijoki, Kirsi; Näreaho, Anu; Sałamatin, Rusłan; Conn, David Bruce; Młocicki, Daniel (2017-11-21). "Identification of immunogenic proteins of the cysticercoid of Hymenolepis diminuta". Parasites & Vectors. 10 (1): 577. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2519-4 . ISSN 1756-3305. PMC 5697066 . PMID 29157281.
- ↑ Upton, Steve J.; Campos, Juan (24 September 1999). "Biology 625 Animal Parasitology Topic #12: Developmental biology of cestodes". K-State Parasitology Laboratory. Kansas State University. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- ↑ National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID), Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria (5 June 2024). "Hymenolepiasis". DPDx - Laboratory Identification of Parasites of Public Health Concern. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 5 December 2024.