The PaleozoicEra is the first of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six geologic periods :

The Silurian is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at 443.8 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, 419.2 Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out.

Trilobites are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last trilobites disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 251.9 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described.
Stenolaemata are a class of exclusively marine bryozoans. Stenolaemates originated and diversified in the Ordovician, and more than 600 species are still alive today. All extant (living) species are in the order Cyclostomatida, the third-largest order of living bryozoans.

Tabulata, commonly known as tabulate corals, are an order of extinct forms of coral. They are almost always colonial, forming colonies of individual hexagonal cells known as corallites defined by a skeleton of calcite, similar in appearance to a honeycomb. Adjacent cells are joined by small pores. Their distinguishing feature is their well-developed horizontal internal partitions (tabulae) within each cell, but reduced or absent vertical internal partitions. They are usually smaller than rugose corals, but vary considerably in shape, from flat to conical to spherical.

Stromatoporoidea is an extinct clade of sea sponges common in the fossil record from the Middle Ordovician to the Late Devonian. They can be characterized by their densely layered calcite skeletons lacking spicules. Stromatoporoids were among the most abundant and important reef-builders of their time, living close together in flat biostromes or elevated bioherms on soft tropical carbonate platforms.

The Oncocerida comprise a diverse group of generally small nautiloid cephalopods known from the Middle Ordovician to the Mississippian, in which the connecting rings are thin and siphuncle segments are variably expanded. At present the order consists of some 16 families, a few of which, such as the Oncoceratidae, Brevicoceratidae, and Acleistoceratidae contain a fair number of genera each while others like the Trimeroceratidae and Archiacoceratidae are represented by only two or three.

Reticulosa is an extinct order of sea sponges in the class Hexactinellida and the subclass Amphidiscophora. Reticulosans were diverse in shape and size, similar to their modern relatives, the amphidiscosidans. Some were smooth and attached to a surface at a flat point, others were polyhedral or ornamented with nodes, many were covered in bristles, and a few were even suspended above the seabed by a rope-like anchor of braided glass spicules.
Helen Margaret Duncan was a geologist and paleontologist with the United States Geological Survey from 1945 to 1971, where she worked in the Paleontology and Stratigraphy Branch. Duncan was considered one of the strongest women in the Cincinnati geology department; her contributions to the Lipalian Research Foundation and the Pick and Hammer shows were additional work of her time. Duncan paved the path for many geology scholars to follow with her discoveries on fossil records and her studies in paleontology and stratigraphy.

Ray Smith Bassler was an American geologist and paleontologist.

Holopea is an extinct genus of fossil sea snails, Paleozoic gastropod mollusks in the family Holopeidae.
Paleontology in Tennessee refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Tennessee. During the early part of the Paleozoic era, Tennessee was covered by a warm, shallow sea. This sea was home to brachiopods, bryozoans, cephalopods, corals, and trilobites. Tennessee is one of the best sources of Early Devonian fossils in North America. During the mid-to-late Carboniferous, the state became a swampy environment, home to a rich variety of plants including ferns and scale trees. A gap in the local rock record spans from the Permian through the Jurassic. During the Cretaceous, the western part of the state was submerged by seawater. The local waters were home to more fossil gastropods than are known from anywhere else in the world. Mosasaurs and sea turtles also inhabited these waters. On land the state was home to dinosaurs. Western Tennessee was still under the sea during the early part of the Cenozoic. Terrestrial portions of the state were swampy. Climate cooled until the Ice Age, when the state was home to Camelops, horses, mammoths, mastodons, and giant ground sloths. The local Yuchi people told myths of giant lizard monsters that may have been inspired by fossils either local or encountered elsewhere. In 1920, after local fossils became a subject of formal scientific study, a significant discovery of a variety of Pleistocene creatures was made near Nashville. The Cretaceous bivalve Pterotrigonia thoracica is the Tennessee state fossil.

Paleontology in Oklahoma refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Oklahoma. Oklahoma has a rich fossil record spanning all three eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Oklahoma is the best source of Pennsylvanian fossils in the United States due to having an exceptionally complete geologic record of the epoch. From the Cambrian to the Devonian, all of Oklahoma was covered by a sea that would come to be home to creatures like brachiopods, bryozoans, graptolites and trilobites. During the Carboniferous, an expanse of coastal deltaic swamps formed in areas of the state where early tetrapods would leave behind footprints that would later fossilize. The sea withdrew altogether during the Permian period. Oklahoma was home a variety of insects as well as early amphibians and reptiles. Oklahoma stayed dry for most of the Mesozoic. During the Late Triassic, carnivorous dinosaurs left behind footprints that would later fossilize. During the Cretaceous, however, the state was mostly covered by the Western Interior Seaway, which was home to huge ammonites and other marine invertebrates. During the Cenozoic, Oklahoma became home to creatures like bison, camels, creodonts, and horses. During the Ice Age, the state was home to mammoths and mastodons. Local Native Americans are known to have used fossils for medicinal purposes. The Jurassic dinosaur Saurophaganax maximus is the Oklahoma state fossil.
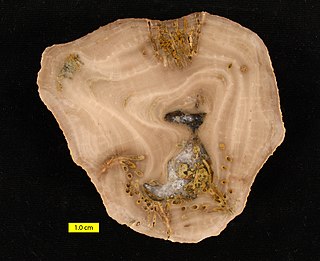
Amplexopora is a genus of bryozoans of the family Amplexoporidae, known in the rock record from the Ordovician to the Permian periods. Species belonging to this genus were stationary epifaunal suspension feeders. Their colonies showed a very great variety in shapes.

Adelophthalmidae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Adelophthalmidae is the only family classified as part of the superfamily Adelophthalmoidea, which in turn is classified within the infraorder Diploperculata in the suborder Eurypterina.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2015.
Tabulipora is an extinct genus of bryozoan belonging to the order Trepostomida. It has been found in beds of Permian age in North America, Spitzbergen, South America, and Asia. Specimens typically form cylindrical branching colonies.
Homotrypa is an extinct genus of bryozoans from the Ordovician and Silurian periods, known from fossils found in the United States. Its colonies are branch-like and have small monticules made of groups of three or four larger zooecia slightly protruding out from the main surface of the colony. In cross section, the zooecia are erect in axis and gently curve toward the surface of the colony.
Labechiida is an extinct order of stromatoporoid sponges. They lived from the Early Ordovician to the Late Devonian, though a few putative fossils have been reported from younger sediments. Labechiids were the first order of stromatoporoids to appear and were probably ancestral to all other orders in the main Paleozoic radiation.












