Related Research Articles

Sodium ascorbate is one of a number of mineral salts of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). The molecular formula of this chemical compound is C6H7NaO6. As the sodium salt of ascorbic acid, it is known as a mineral ascorbate. It has not been demonstrated to be more bioavailable than any other form of vitamin C supplement.
Carbohydrate dehydrogenases are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the conversion from a carbohydrate to an aldehyde, lactone, or ketose.
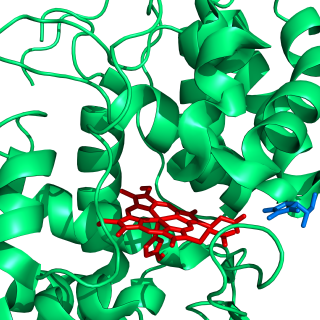
Ascorbate peroxidase (or L-ascorbate peroxidase, APX or APEX) (EC 1.11.1.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cytochrome P450 reductase is a membrane-bound enzyme required for electron transfer from NADPH to cytochrome P450 and other heme proteins including heme oxygenase in the endoplasmic reticulum of the eukaryotic cell.
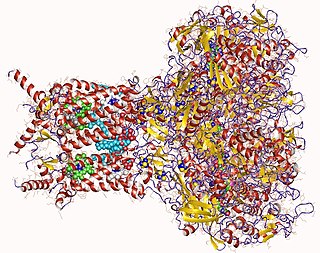
Formate dehydrogenases are a set of enzymes that catalyse the oxidation of formate to carbon dioxide, donating the electrons to a second substrate, such as NAD+ in formate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (EC 1.17.1.9) or to a cytochrome in formate:ferricytochrome-b1 oxidoreductase (EC 1.2.2.1). This family of enzymes has attracted attention as inspiration or guidance on methods for the carbon dioxide fixation, relevant to global warming.
In enzymology, a L-galactonolactone oxidase (EC 1.3.3.12) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a camphor 5-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.15.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Ecdysone 20-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.99.22) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-methylcoclaurine 3'-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.71) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pyrimidine-deoxynucleoside 1'-dioxygenase (EC 1.14.11.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pyrimidine-deoxynucleoside 2'-dioxygenase (EC 1.14.11.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a L-ascorbate oxidase (EC 1.10.3.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a glutathione dehydrogenase (ascorbate) (EC 1.8.5.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDAR) (EC 1.6.5.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cytochrome b561 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYB561 gene.
Abieta-7,13-dien-18-ol hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.109, CYP720B1, PTAO) is an enzyme with systematic name abieta-7,13-dien-18-ol,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (18-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
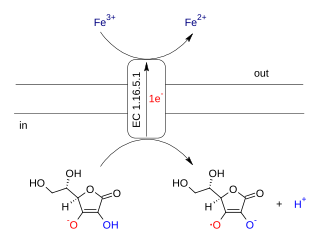
Ascorbate ferrireductase (transmembrane) (EC 1.16.5.1, cytochrome b561) is an enzyme with systematic name Fe(III):ascorbate oxidorectuctase (electron-translocating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Subrata Adak is an Indian biochemist and a senior scientist at the Indian Institute of Chemical Biology. An alumnus of Jadavpur University from where he secured a PhD, Adak is known for his studies on Leishmania, the causative pathogen of Leishmaniasis. His studies have been documented by way of a number of articles and ResearchGate, an online repository of scientific articles has listed 55 of them. Besides, he has published one monograph on Leishmania where he has also contributed chapters. The Department of Biotechnology of the Government of India awarded him the National Bioscience Award for Career Development, one of the highest Indian science awards, for his contributions to biosciences, in 2012.
References
- ↑ Cytochrome b561, Uniprot
- ↑ Lu P, Ma D, Yan C, Gong X, Du M, Shi Y (February 2014). "Structure and mechanism of a eukaryotic transmembrane ascorbate-dependent oxidoreductase". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 111 (5): 1813–8. Bibcode:2014PNAS..111.1813L. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323931111 . PMC 3918761 . PMID 24449903.