
London Stock Exchange (LSE) is a stock exchange in the City of London, England, United Kingdom. As of August 2023, the total market value of all companies trading on the LSE stood at $3.18 trillion. Its current premises are situated in Paternoster Square close to St Paul's Cathedral in the City of London. Since 2007, it has been part of the London Stock Exchange Group. The LSE is the most-valued stock exchange in Europe as of 2023. According to the 2020 Office for National Statistics report, approximately 12% of UK-resident individuals reported having investments in stocks and shares. According to the 2020 Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) report, approximately 15% of UK adults reported having investments in stocks and shares.

The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) is a global derivatives marketplace based in Chicago and located at 20 S. Wacker Drive. The CME was founded in 1898 as the Chicago Butter and Egg Board, an agricultural commodities exchange. For most of its history, the exchange was in the then common form of a non-profit organization, owned by members of the exchange. The Merc demutualized in November 2000, went public in December 2002, and merged with the Chicago Board of Trade in July 2007 to become a designated contract market of the CME Group Inc., which operates both markets. The chairman and chief executive officer of CME Group is Terrence A. Duffy, Bryan Durkin is president. On August 18, 2008, shareholders approved a merger with the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) and COMEX. CME, CBOT, NYMEX, and COMEX are now markets owned by CME Group. After the merger, the value of the CME quadrupled in a two-year span, with a market cap of over $25 billion.
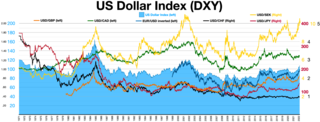
The foreign exchange market is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all aspects of buying, selling and exchanging currencies at current or determined prices. In terms of trading volume, it is by far the largest market in the world, followed by the credit market.
A foreign exchange spot transaction, also known as FX spot, is an agreement between two parties to buy one currency against selling another currency at an agreed price for settlement on the spot date. The exchange rate at which the transaction is done is called the spot exchange rate. As of 2010, the average daily turnover of global FX spot transactions reached nearly US$1.5 trillion, counting 37.4% of all foreign exchange transactions. FX spot transactions increased by 38% to US$2.0 trillion from April 2010 to April 2013.
An electronic communication network (ECN) is a type of computerized forum or network that facilitates the trading of financial products outside traditional stock exchanges. An ECN is generally an electronic system that widely disseminates orders entered by market makers to third parties and permits the orders to be executed against in whole or in part. The primary products that are traded on ECNs are stocks and currencies. ECNs are generally passive computer-driven networks that internally match limit orders and charge a very small per share transaction fee.
Algorithmic trading is a method of executing orders using automated pre-programmed trading instructions accounting for variables such as time, price, and volume. This type of trading attempts to leverage the speed and computational resources of computers relative to human traders. In the twenty-first century, algorithmic trading has been gaining traction with both retail and institutional traders. A study in 2019 showed that around 92% of trading in the Forex market was performed by trading algorithms rather than humans.

The Nigerian Stock Exchange (NSE), now Nigerian Exchange Group, is a Nigerian stock exchange founded in 1961 in Lagos. As of November 2019, it has a total of 161 listed companies, with 8 domestic companies on the premium board, 144 companies on the mainboard, and 4 on the Alternative Securities Market (ASeM) board. In the Fixed Income market, the NSE has 84 FGN bonds, 21 state bonds, 27 corporate bonds, 1 supranational bond, and 53 memorandum listings.
Electronic Broking Services (EBS) is a wholesale electronic trading platform used to trade on the foreign exchange market (FX) with market-making banks. It was originally created as a partnership by large banks and then became part of CME Group.

A trading room gathers traders operating on financial markets. The trading room is also often called the front office. The terms "dealing room" and "trading floor" are also used, the latter being inspired from that of an open outcry stock exchange. As open outcry is gradually replaced by electronic trading, the trading room becomes the only remaining place that is emblematic of the financial market. It is also the likeliest place within the financial institution where the most recent technologies are implemented before being disseminated in its other businesses.
Direct market access (DMA) is a term used in financial markets to describe electronic trading facilities that give investors wishing to trade in financial instruments a way to interact with the order book of an exchange. Normally, trading on the order book is restricted to broker-dealers and market making firms that are members of the exchange. Using DMA, investment companies and other private traders use the information technology infrastructure of sell side firms such as investment banks and the market access that those firms possess, but control the way a trading transaction is managed themselves rather than passing the order over to the broker's own in-house traders for execution. Today, DMA is often combined with algorithmic trading giving access to many different trading strategies. Certain forms of DMA, most notably "sponsored access", have raised substantial regulatory concerns because of the possibility of a malfunction by an investor to cause widespread market disruption.

The Philippine Dealing & Exchange Corp. (PDEx) is a dealing exchange for major banks in the Philippines. The primary exchange of the country for all sectors is the Philippine Stock Exchange.

Thomson Reuters Corporation is a Canadian multinational information conglomerate. The company was founded in Toronto, Ontario, Canada and maintains its headquarters in that city's Bay Adelaide Centre.
Reuters 3000 Xtra was an electronic trading platform which was released by Reuters in 1999 and supported until the end of 2013. It was typically used by professional traders and financial analysts in trading rooms. It was superseded by the Eikon platform, first released in 2010.
The interbank market is the top-level foreign exchange market where banks exchange different currencies. The banks can either deal with one another directly, or through electronic brokering platforms. The Electronic Broking Services (EBS) and Thomson Reuters Dealing are the two competitors in the electronic brokering platform business and together connect over 1000 banks. The currencies of most developed countries have floating exchange rates. These currencies do not have fixed values but, rather, values that fluctuate relative to other currencies.

In finance, an electronic trading platform also known as an online trading platform, is a computer software program that can be used to place orders for financial products over a network with a financial intermediary. Various financial products can be traded by the trading platform, over a communication network with a financial intermediary or directly between the participants or members of the trading platform. This includes products such as stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities, derivatives and others, with a financial intermediary such as brokers, market makers, Investment banks or stock exchanges. Such platforms allow electronic trading to be carried out by users from any location and are in contrast to traditional floor trading using open outcry and telephone-based trading. Sometimes the term trading platform is also used in reference to the trading software alone.
High-frequency trading (HFT) is a type of algorithmic trading in finance characterized by high speeds, high turnover rates, and high order-to-trade ratios that leverages high-frequency financial data and electronic trading tools. While there is no single definition of HFT, among its key attributes are highly sophisticated algorithms, co-location, and very short-term investment horizons in trading securities. HFT uses proprietary trading strategies carried out by computers to move in and out of positions in seconds or fractions of a second.
MT4 ECN Bridge is a technology that allows a user to access the interbank foreign exchange market through the MetaTrader 4 (MT4) electronic trading platform. MT4 was designed to allow trading between a broker and its clients, so it did not provide for passing orders through to wholesale forex market via electronic communication networks (ECNs). In response, a number of third-party software companies developed Straight-through processing bridging software to allow the MT4 server to pass orders placed by clients directly to an ECN and feed trade confirmations back automatically.
SIX is a key financial market infrastructure company in Switzerland. The company provides services relating to securities transactions, the processing of financial information, payment transactions and is building a digital infrastructure. The company name SIX is an abbreviation and stands for Swiss Infrastructure and Exchange. SIX is globally active, with its headquarters in Zurich.
A foreign exchange aggregator or FX Aggregator is a class of systems used in Forex trading to aggregate the liquidity from several liquidity providers.

Interactive Brokers LLC (IB) is an American multinational brokerage firm. It operates the largest electronic trading platform in the United States by number of daily average revenue trades. The company brokers stocks, options, futures, EFPs, futures options, forex, bonds, funds, and some cryptocurrencies.







