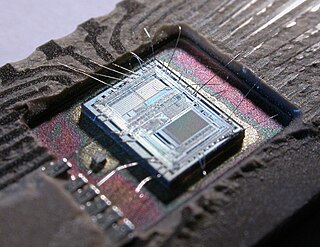
A microcontroller or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of NOR flash, OTP ROM, or ferroelectric RAM is also often included on the chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general-purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips.
The Portable Operating System Interface is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines both the system and user-level application programming interfaces (APIs), along with command line shells and utility interfaces, for software compatibility (portability) with variants of Unix and other operating systems. POSIX is also a trademark of the IEEE. POSIX is intended to be used by both application and system developers.

QNX is a commercial Unix-like real-time operating system, aimed primarily at the embedded systems market.

Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that conventionally have been implemented in analog hardware are instead implemented by means of software on a computer or embedded system. While the concept of SDR is not new, the rapidly evolving capabilities of digital electronics render practical many processes which were once only theoretically possible.
pSOS is a real-time operating system (RTOS), created in about 1982 by Alfred Chao, and developed and marketed for the first part of its life by his company Software Components Group (SCG). In the 1980s, pSOS rapidly became the RTOS of choice for all embedded systems based on the Motorola 68000 series family architecture, because it was written in 68000 assembly language and was highly optimised from the start. It was also modularised, with early support for OS-aware debugging, plug-in device drivers, Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) stacks, language libraries, and disk subsystems. Later came source code level debugging, multiprocessing support, and further computer networking extensions.

The Motorola DSP56000 is a family of digital signal processor (DSP) chips produced by Motorola Semiconductor starting in 1986 with later models are still being produced in the 2020s. The 56k series was intended mainly for embedded systems doing signal processing, but was also quite popular for a time in a number of computers, including the NeXT, Atari Falcon030 and SGI Indigo workstations all using the 56001. Upgraded 56k versions are still used today in audio equipment, radar systems, communications devices and various other embedded DSP applications. The 56000 was also used as the basis for the updated 96000, which was not commercially successful.

A system on a chip or system-on-chip is an integrated circuit that integrates most or all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include on-chip central processing unit (CPU), memory interfaces, input/output devices and interfaces, and secondary storage interfaces, often alongside other components such as radio modems and a graphics processing unit (GPU) – all on a single substrate or microchip. SoCs may contain digital and also analog, mixed-signal and often radio frequency signal processing functions.

A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit chips. They are widely used in audio signal processing, telecommunications, digital image processing, radar, sonar and speech recognition systems, and in common consumer electronic devices such as mobile phones, disk drives and high-definition television (HDTV) products.
RTLinux is a hard realtime real-time operating system (RTOS) microkernel that runs the entire Linux operating system as a fully preemptive process. The hard real-time property makes it possible to control robots, data acquisition systems, manufacturing plants, and other time-sensitive instruments and machines from RTLinux applications. The design was patented. Despite the similar name, it is not related to the Real-Time Linux project of the Linux Foundation.
Nucleus RTOS is a real-time operating system (RTOS) produced by the Embedded Software Division of Mentor Graphics, a Siemens Business, supporting 32- and 64-bit embedded system platforms. The operating system (OS) is designed for real-time embedded systems for medical, industrial, consumer, aerospace, and Internet of things (IoT) uses. Nucleus was released first in 1993. The latest version is 3.x, and includes features such as power management, process model, 64-bit support, safety certification, and support for heterogeneous computing multi-core system on a chip (SOCs) processors.

The Blackfin is a family of 16-/32-bit microprocessors developed, manufactured and marketed by Analog Devices. The processors have built-in, fixed-point digital signal processor (DSP) functionality performed by 16-bit multiply–accumulates (MACs), accompanied on-chip by a microcontroller. It was designed for a unified low-power processor architecture that can run operating systems while simultaneously handling complex numeric tasks such as real-time H.264 video encoding.
Nios II is a 32-bit embedded processor architecture designed specifically for the Altera family of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) integrated circuits. Nios II incorporates many enhancements over the original Nios architecture, making it more suitable for a wider range of embedded computing applications, from digital signal processing (DSP) to system-control.

FreeRTOS is a real-time operating system kernel for embedded devices that has been ported to 35 microcontroller platforms. It is distributed under the MIT License.

TMS320 is a blanket name for a series of digital signal processors (DSPs) from Texas Instruments. It was introduced on April 8, 1983, through the TMS32010 processor, which was then the fastest DSP on the market.

A multi-core processor is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit with two or more separate processing units, called cores, each of which reads and executes program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions but the single processor can run instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs that support multithreading or other parallel computing techniques. Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single integrated circuit die or onto multiple dies in a single chip package. The microprocessors currently used in almost all personal computers are multi-core.

Real-Time Executive for Multiprocessor Systems (RTEMS), formerly Real-Time Executive for Missile Systems, and then Real-Time Executive for Military Systems, is a real-time operating system (RTOS) designed for embedded systems. It is free and open-source software.

The Texas Instruments DaVinci is a family of system on a chip processors that are primarily used in embedded video and vision applications. Many processors in the family combine a DSP core based on the TMS320 C6000 VLIW DSP family and an ARM CPU core into a single system on chip. By using both a general-purpose processor and a DSP, the control and media portions can both be executed by separate processors.
TI-RTOS is an embedded tools ecosystem created and offered by Texas Instruments (TI) for use across a range of their embedded system processors. It includes a real-time operating system (RTOS) component named TI-RTOS Kernel, networking connectivity stacks, power management, file systems, instrumentation, and inter-processor communications like DSP/BIOS Link. It is free and open-source software, released under a BSD license.

OpenComRTOS is a commercial network-centric, formally developed real-time operating system (RTOS), aimed mainly at the embedded system market.












