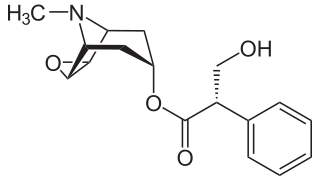
Scopolamine, also known as hyoscine, or Devil's Breath, is a natural or synthetically produced tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic drug that is formally used as a medication for treating motion sickness and postoperative nausea and vomiting. It is also sometimes used before surgery to decrease saliva. When used by injection, effects begin after about 20 minutes and last for up to 8 hours. It may also be used orally and as a transdermal patch.
A parasympathomimetic drug, sometimes called a cholinomimetic drug or cholinergic receptor stimulating agent, is a substance that stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS). These chemicals are also called cholinergic drugs because acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter used by the PSNS. Chemicals in this family can act either directly by stimulating the nicotinic or muscarinic receptors, or indirectly by inhibiting cholinesterase, promoting acetylcholine release, or other mechanisms. Common uses of parasympathomimetics include glaucoma, sjögren syndrome and underactive bladder.

Noscapine is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, of the phthalideisoquinoline structural subgroup, which has been isolated from numerous species of the family Papaveraceae. It lacks significant hypnotic, euphoric, or analgesic effects affording it with very low addictive potential. This agent is primarily used for its antitussive (cough-suppressing) effects.

Argemone mexicana is a species of poppy found in Mexico and now widely naturalized in many parts of the world. An extremely hardy pioneer plant, it is tolerant of drought and poor soil, often being the only cover on new road cuttings or verges. It has bright yellow latex. It is poisonous to grazing animals, and it is rarely eaten, but it has been used medicinally by many peoples, including those in its native area, as well as the Natives of the western US, parts of Mexico and many parts of India. In India, during the colorful festival Holika Dahan, adults and children worship by offering flowers, and this species is in its maximum flowering phase during March when the Holi festival is celebrated. It is also referred to as "kateli ka phool” in India.

Huperzine A is a naturally occurring sesquiterpene alkaloid compound found in the firmoss Huperzia serrata and in varying quantities in other food Huperzia species, including H. elmeri, H. carinat, and H. aqualupian. Huperzine A has been investigated as a treatment for neurological conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, but a meta-analysis of those studies concluded that they were of poor methodological quality and the findings should be interpreted with caution. Huperzine A inhibits the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. It is commonly available over the counter as a nutrient supplement, and is marketed as a cognitive enhancer for improving memory and concentration.

A muscarinic agonist is an agent that activates the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. The muscarinic receptor has different subtypes, labelled M1-M5, allowing for further differentiation.

Cevimeline (trade name Evoxac) is a synthetic analog of the natural alkaloid muscarine with a particular agonistic effect on M1 and M3 receptors. It is used in the treatment of dry mouth and Sjögren's syndrome.

Tetrandrine, a bis-benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, is a calcium channel blocker. It is isolated from the plant Stephania tetrandra, and other Chinese and Japanese herbs.

Tropacocaine is a cocaine-related alkaloid and a contaminant of street cocaine.

Pleiocarpa mutica is a plant in the family Apocynaceae.
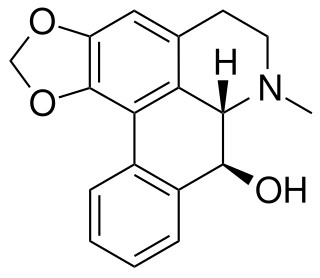
Oliveroline is an anti-cholinergic aporphine alkaloid.
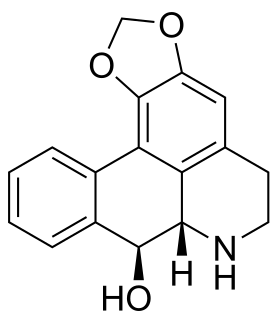
Noroliveroline is an anticholinergic alkaloid.
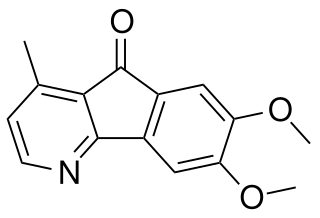
Polyfothine is an anticholinergic alkaloid.

Eburnamenine is an anticholinergic alkaloid.
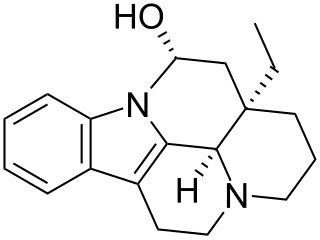
Eburnamine is an indole alkaloid in the aspidosperma group. It has anticholinergic activity.
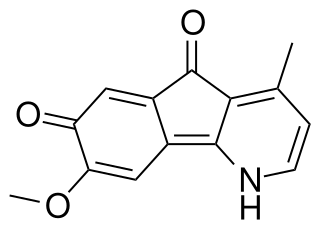
Isooncodine is an anticholinergic alkaloid. It was first synthesized in 1989 because it is an isomer of oncodine, an azafluorenone alkaloid derived from Meiogyne monosperma. It was first derived from the leaves of Polyalthia longifolia.
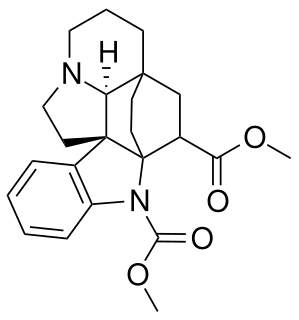
Pleiocarpine is an anticholinergic alkaloid.

Pleiocarpamine is a natural anticholinergic alkaloid.
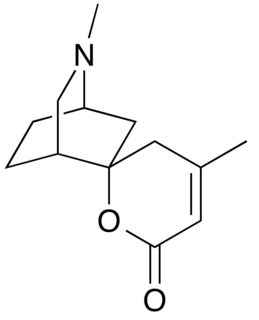
Dioscorine is an alkaloid toxin isolated from the tubers of tropical yam on several continents. It has been used as a monkey poison in some African countries, and as an arrow poison to aid in hunting in several parts of Asia. It was first isolated from Dioscorea hirsute by Boorsma in 1894 and obtained in a crystalline form by Schutte in 1897, and has since been found in other Dioscorea species. Dioscorine is a neurotoxin that acts by blocking the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Dioscorine is generally isolated in tandem with other alkaloids such as dioscin but is usually the most potent toxin in the mixture. It is a convulsant, producing symptoms similar to picrotoxin, with which it shares a similar mechanism of action.
Dewan Singh Bhakuni is an Indian natural product chemist, stereochemist and a former director general-grade scientist of the Central Drug Research Institute. He is known for his researches on the biogenesis of alkaloids and is an elected fellow of the Indian Academy of Sciences, the National Academy of Sciences, India and the Indian National Science Academy. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards, in 1975, for his contributions to chemical sciences.


















