Related Research Articles

Debian, also known as Debian GNU/Linux, is a Linux distribution composed of free and open-source software and proprietary software developed by the community-supported Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock on August 16, 1993. The first version of Debian (0.01) was released on September 15, 1993, and its first stable version (1.1) was released on June 17, 1996. The Debian Stable branch is the most popular edition for personal computers and servers. Debian is also the basis for many other distributions that have different purposes, like Proxmox for servers, Ubuntu or Linux Mint for desktops, Kali for penetration testing or Pardus and Astra for government use.

A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that includes the Linux kernel and often a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to powerful supercomputers.
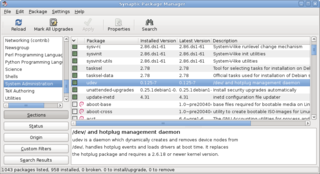
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner.

Advanced package tool, or APT, is a free-software user interface that works with core libraries to handle the installation and removal of software on Debian, and Debian-based Linux distributions. APT simplifies the process of managing software on Unix-like computer systems by automating the retrieval, configuration and installation of software packages, either from precompiled files or by compiling source code.
dpkg is the software at the base of the package management system in the free operating system Debian and its numerous derivatives. dpkg is used to install, remove, and provide information about .deb packages.
deb is the format, as well as filename extension of the software package format for the Debian Linux distribution and its derivatives.
Computer operating systems based on the Linux kernel are used in embedded systems such as consumer electronics, in-vehicle infotainment (IVI), networking equipment, machine control, industrial automation, navigation equipment, spacecraft flight software, and medical instruments in general.

The Linksys WRT54G Wi-Fi series is a series of Wi-Fi–capable residential gateways marketed by Linksys, a subsidiary of Cisco, from 2003 until acquired by Belkin in 2013. A residential gateway connects a local area network to a wide area network.
Wajig is a simplified wrapper to Debian's package management system dpkg/APT. Wajig provides the functionality of apt-get, dpkg, dpkg-deb, apt-cache and other tools. These tools launch as a subprocess. Wajig also provides extra functionality beyond that of the stock apt and dpkg tools. For example, the command wajig sizes provides a listing of all installed packages and the amount of disk space they require, from smallest to largest.
The NSLU2 is a network-attached storage (NAS) device made by Linksys introduced in 2004 and discontinued in 2008. It makes USB flash memory and hard disks accessible over a network using the SMB protocol. It was superseded mainly by the NAS200 and in another sense by the WRT600N and WRT300N/350N which both combine a Wi-Fi router with a storage link.
Squashfs is a compressed read-only file system for Linux. Squashfs compresses files, inodes and directories, and supports block sizes from 4 KiB up to 1 MiB for greater compression. Several compression algorithms are supported. Squashfs is also the name of free software, licensed under the GPL, for accessing Squashfs filesystems.

X-Wrt is a set of packages and patches to provide a web interface for the Linux distribution OpenWrt. It is based on haserl and has nothing to do with the X Window System. It allows web based management of an OpenWrt device. It was originally created as a package for OpenWrt White Russian. At present it can be found in the OpenWrt trunk as the webif package. Some newer features such as dual-band support may not be present. On 31 October 2013, the X-Wrt homepage moved to Google Code.

The SheevaPlug is a "plug computer" designed to allow standard computing features in as small a space as possible. It was a small embedded Linux ARM computer without a display which can be considered an early predecessor to the subsequent Raspberry Pi.
OpenWrt is an open-source project for embedded operating systems based on Linux, primarily used on embedded devices to route network traffic. The main components are Linux, util-linux, musl, and BusyBox. All components have been optimized to be small enough to fit into the limited storage and memory available in home routers.
A delta update is a software update that requires the user to download only those parts of the software's code that are new, or have been changed from their previous state, in contrast to having to download the entire program. The use of delta updates can save significant amounts of time and computing bandwidth. The name "delta" derives from the mathematical science use of the Greek letter delta, Δ or δ to denote change.
DNOS or Dell Networking Operating System is a network operating system running on switches from Dell Networking. It is derived from either the PowerConnect OS or Force10 OS/FTOS and will be made available for the 10G and faster Dell Networking S-series switches, the Z-series 40G core switches and DNOS6 is available for the N-series switches.

Buildroot is a set of Makefiles and patches that simplifies and automates the process of building a complete and bootable Linux environment for an embedded system, while using cross-compilation to allow building for multiple target platforms on a single Linux-based development system. Buildroot can automatically build the required cross-compilation toolchain, create a root file system, compile a Linux kernel image, and generate a boot loader for the targeted embedded system, or it can perform any independent combination of these steps. For example, an already installed cross-compilation toolchain can be used independently, while Buildroot only creates the root file system.

Endian Firewall is an open-source router, firewall and gateway security Linux distribution developed by the South Tyrolean company Endian. The product is available as either free software, commercial software with guaranteed support services, or as a hardware appliance.
References
- ↑ "Milestone Angel 2.0-1". 2010-09-26. Archived from the original on 2011-08-14. Retrieved 2011-05-30.
- ↑ "Debian Installer 6.0 Release Candidate 1". 2009-02-01. Retrieved 2011-05-30.