
A truss is an assembly of members such as beams, connected by nodes, that creates a rigid structure.

A cantilever bridge is a bridge built using cantilevers, structures that project horizontally into space, supported on only one end. For small footbridges, the cantilevers may be simple beams; however, large cantilever bridges designed to handle road or rail traffic use trusses built from structural steel, or box girders built from prestressed concrete. The steel truss cantilever bridge was a major engineering breakthrough when first put into practice, as it can span distances of over 1,500 feet (460 m), and can be more easily constructed at difficult crossings by virtue of using little or no falsework.

A truss bridge is a bridge whose load-bearing superstructure is composed of a truss, a structure of connected elements, usually forming triangular units. The connected elements may be stressed from tension, compression, or sometimes both in response to dynamic loads. The basic types of truss bridges shown in this article have simple designs which could be easily analyzed by 19th and early 20th-century engineers. A truss bridge is economical to construct because it uses materials efficiently.

Beam bridges are the simplest structural forms for bridge spans supported by an abutment or pier at each end. No moments are transferred throughout the support, hence their structural type is known as simply supported.

A plate girder bridge is a bridge supported by two or more plate girders.

A trestle bridge is a bridge composed of a number of short spans supported by closely spaced frames. A trestle is a rigid frame used as a support, historically a tripod used to support a stool or a pair of isosceles triangles joined at their apices by a plank or beam such as the support structure for a trestle table. Each supporting frame is a bent. A trestle differs from a viaduct in that viaducts have towers that support much longer spans and typically have a higher elevation.

Robert Maillart was a Swiss civil engineer who revolutionized the use of structural reinforced concrete with such designs as the three-hinged arch and the deck-stiffened arch for bridges, and the beamless floor slab and mushroom ceiling for industrial buildings. His Salginatobel (1929–1930) and Schwandbach (1933) bridges changed the aesthetics and engineering of bridge construction dramatically and influenced decades of architects and engineers after him. In 1991 the Salginatobel Bridge was declared an International Historic Civil Engineering Landmark by the American Society of Civil Engineers.

An orthotropic bridge or orthotropic deck is typically one whose fabricated deck consists of a structural steel deck plate stiffened either longitudinally with ribs or transversely, or in both directions. This allows the fabricated deck both to directly bear vehicular loads and to contribute to the bridge structure's overall load-bearing behaviour. The orthotropic deck may be integral with or supported on a grid of deck framing members, such as transverse floor beams and longitudinal girders. All these various choices for the stiffening elements, e.g., ribs, floor beams and main girders, can be interchanged, resulting in a great variety of orthotropic panels.
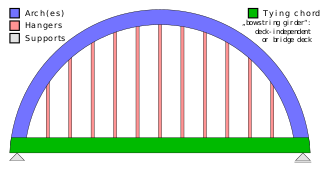
A tied-arch bridge is an arch bridge in which the outward horizontal forces of the arch(es) caused by tension at the arch ends to a foundation are countered by equal tension of its own gravity plus any element of the total deck structure such great arch(es) support. The arch(es) have strengthened chord(s) that run to a strong part of the deck structure or to independent tie-rods below the arch ends.

A girder bridge is a bridge that uses girders as the means of supporting its deck. The two most common types of modern steel girder bridges are plate and box.
This is an alphabetical list of articles pertaining specifically to structural engineering. For a broad overview of engineering, please see List of engineering topics. For biographies please see List of engineers.

A Howe truss is a truss bridge consisting of chords, verticals, and diagonals whose vertical members are in tension and whose diagonal members are in compression. The Howe truss was invented by William Howe in 1840, and was widely used as a bridge in the mid to late 1800s.

Borodinsky Bridge is a steel plate girder bridge that spans Moskva River, connecting Dorogomilovo District and Kievsky Rail Terminal with the centre of Moscow, Russia. The bridge was built in 1911–1912 as deck arch bridge by N.I. Oskolkov, M.I. Schekotov and Roman Klein. In 2001, the bridge was reconstructed, replacing arches and deck with a plate girder structure.

The Salford Quays lift bridge, also known as the Salford Quays Millennium footbridge or the Lowry bridge, is a 91.2-metre (299 ft) long vertical lift bridge spanning the Manchester Ship Canal between Salford and Trafford in Greater Manchester, England. The pedestrian bridge, which was completed in 2000, is near the terminus of the ship canal at the old Manchester Docks. It is sited beside The Lowry theatre and gallery and links Salford Quays and MediaCityUK to Trafford Wharf and the Imperial War Museum North. It has a lift of 18 metres (59 ft), allowing large watercraft to pass beneath.

In structural engineering, the open web steel joist (OWSJ) is a lightweight steel truss consisting, in the standard form, of parallel chords and a triangulated web system, proportioned to span between bearing points.

The Schierstein Bridge is 1,282-meter (4,206 ft) long, four-lane highway bridge in Germany. It carries Bundesautobahn 643 over the Rhine River between Mainz-Mombach, Rhineland-Palatinate and Wiesbaden-Schierstein, Hesse. Crossing two arms of the Rhine and the intervening island of Rettbergsaue, the bridge is made of six individual structures, including 100 m (330 ft) from prestressed concrete. It was built between 1959 and 1962.

The Godavari Arch Bridge is a bowstring-girder bridge that spans the Godavari River in Rajahmundry, India. It is the latest of the three bridges that span the Godavari river at Rajahmundry. The Havelock Bridge being the earliest, was built in 1897, and having served its full utility, was decommissioned in 1997. The second bridge known as the Godavari Bridge is a truss bridge and is India's third longest road-cum-rail bridge crossing a water body.

The Adomi Bridge is a latticed steel arch suspension bridge crossing the Volta River at Atimpoku in Ghana in West Africa. It is the first permanent bridge to span the Volta River, which drains south into the Gulf of Guinea, and is Ghana's longest suspension bridge. It provides the main road passage, just south of the Akosombo Dam, between the Eastern Region and the Volta Region of Ghana. It was opened in 1957 by Kwame Nkrumah, Ghana's first president. The iconic crescent-shaped arch bridge is featured in Ghanaian stamps and currency.

The Worms Rhine Bridge is a two-track railway bridge that spans the Rhine river to the north of Worms, Germany, forming part of the Worms–Biblis railway.

The Germersheim Rhine Bridge is a two-track railway bridge that crosses the Rhine near Germersheim in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. It forms part of the Germersheim–Bruchsal railway.



















