
Delhi has significant reliance on its transport infrastructure. The city has developed a highly efficient public transport system with the introduction of the Delhi Metro, which is undergoing a rapid modernization and expansion since 2006. There are 16.6 million registered vehicles in the city as of 30 June 2014, which is the highest in the world among all cities, most of which do not follow any pollution emission norm, while the Delhi metropolitan region has 11.2 million vehicles. Delhi and NCR lose nearly 42 crore man-hours every month while commuting between home and office through public transport, due to the traffic congestion. Therefore, serious efforts, including a number of transport infrastructure projects, are under way to encourage usage of public transport in the city.
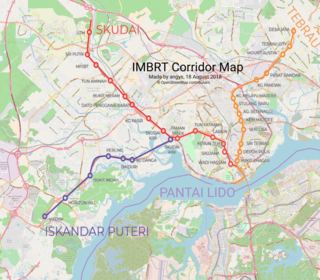
The Iskandar Malaysia Bus Rapid Transit (IMBRT) was a bus rapid transit system to be built in and around Iskandar Malaysia, Johor, Malaysia. It was to have consisted of trunk, direct, and feeder bus rapid transit corridors. The project was cancelled in 2024 due to insufficient capacity to handle projected traffic.
Chennai BRTS was a bus rapid transit system taken up as an integrated part of Circular Corridor Project in India. Beginning at Adyar, the route will cover Saidapet, Jafferkanpet, Ramavaram, Puzhal, Manali, Chennai Central Railway Station, Lighthouse and will return to Adyar. The corridor will cover a distance of 70.3 kilometres (43.7 mi). The route of the elevated BRTS corridor was planned to run along the banks of Adyar river and Buckingham canal. The project was expected to be completed by 2013.

Janmarg, also known as Ahmedabad BRTS, is a bus rapid transit system in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. It is operated by Ahmedabad Janmarg Limited, a subsidiary of Ahmedabad Municipal Corporation and others. It is designed by CEPT University. It was inaugurated in October 2009. The network expanded to 89 kilometres (55 mi) by December 2017 and 160 km by March 2023; with daily ridership of 3,49,000 passengers. BRTS won several nation and international awards for design, implementation and operation. It was rated Silver on BRT Standard in 2013.
Bangalore BRTS was a proposed bus rapid transit system in Bangalore, Karnataka. Beginning with a comprehensive report in 2007, and even earlier, several proposals were made to implement a BRTS in Bangalore.

Bengaluru Suburban Railway is an under-construction suburban rail network for the city of Bangalore. A suburban rail system for the city was first proposed in 1983. Since then, several different route proposals were made but no suburban rail project took shape. It was finally approved in the 2019 Railway Budget.
The Delhi BRTS was a bus rapid transit system in Delhi. The first route opened in 2008 ahead of the 2010 Commonwealth Games, which were held in the city. The project was well used but was criticised for the difficulty of access to the bus platforms, which were in the middle of the road, for lack of enforcement and for the effect it had on other motor traffic. A legal challenge was defeated in 2012. The Aam Aadmi Party Government had announced the scrapping of bus rapid transit system and it was dismantled in 2016, because of traffic congestion and accidents.

The Institute for Transportation and Development Policy (ITDP) is a non-governmental non-profit organization that focuses on developing bus rapid transit (BRT) systems, promoting biking, walking, and non-motorized transport, and improving private bus operators margins. Other programs include parking reform, traffic demand management, and global climate and transport policy. According to its mission statement, ITDP is committed to "promoting sustainable and equitable transportation worldwide."

Urban rail transit in India plays an important role in intracity transportation in the major cities which are highly populated. It consists of Regional Rapid Transit System, suburban rail, monorail, and tram systems.

The Cebu Bus Rapid Transit System is a mass transit system under construction in Cebu City, Philippines. It is expected to become the first operational bus rapid transit project in the Philippines. Only one line has been planned in detail so far, but scheme developers note the potential to develop a larger network comprising the adjacent cities of Lapu-Lapu, Mandaue, and Talisay, all of which, together with Cebu City, form part of the Cebu metropolitan area.

Kozhikode Light Metro is a proposed Light Metro system for the city of Kozhikode, in India. In 2010, the State government explored the possibility of implementing a metro rail project for Kozhikode city and its suburbs. The proposal was to have a corridor connecting Meenchanda to the Kozhikode Medical College Hospital through the heart of the city. An inception report was submitted by a Bangalore-based consultant, Wilber Smith, on the detailed feasibility study on the prospect of implementing the Mass Rapid Transport System (MRTS) and Light Rail Transit System (LRTS) in the city. However, the project has been scrapped to be replaced by Kozhikode Monorail project.

Hubli-Dharwad Bus Rapid Transit System (HDBRTS) is a bus rapid transit system built to serve the twin cities of Hubali and Dharwad, located in the North-Western part of Karnataka state in India. Hubali-Dharwad BRTS (HDBRTS) project is a Government of Karnataka initiative to foster long-term economic growth in the region. The project promotes fast, safe, comfortable, convenient and affordable public transportation between the twin cities and aims to reduce congestion and air pollution in the region.

Rainbow BRTS is a bus rapid transit system in the city of Pune. The system is operated by the Pune Mahanagar Parivahan Mahamandal Limited (PMPML). The infrastructure has been developed by the Pune Municipal Corporation & Pimpri Chinchwad Municipal Corporation, Pune. The project currently envisages 113 km of dedicated bus corridors along with buses, bus stations, terminals and intelligent transit management system.

The Meerut Metro is an under-construction rapid transit system, which will serve the city of Meerut, Uttar Pradesh, India. It is being built in two phases, of which the first phase with the first line will cover 23.6 km (14.7 mi) with 13 stations, from Modipuram to Meerut South. It will have nine elevated, three underground stations, one at-grade station as the depot station at Modipuram, and four stations integrated with the Delhi–Meerut Regional Rapid Transit System on a single corridor, making the metro the first such rapid transit system in India to be merged directly with a regional transit system. The second phase will include a second line covering 15 km (9.3 mi) from Shradhapuri Phase-II to Jagrati Vihar, with 12 stations, out of which seven will be elevated and five will be underground, thereby taking the overall length to 38.6 km (24.0 mi). The metro will also be the fastest metro of India, at an operational speed of 120 km/h (75 mph).
The Lagos Metropolitan Area Transport Authority (LAMATA) is the Lagos State Government agency created to coordinate transport planning, policies, and public transport infrastructure implementation in the Lagos Metropolitan Area, Nigeria. The organisation oversees wide range of transport planning and implementation of transport strategies and plans in Lagos, as well as the Lagos Rail Mass Transit and the Lagos Bus Rapid Transit System. It is based in Ikeja.
TransPeshawar or Zu Peshawar is a bus rapid transit system in Peshawar, capital of Pakistan's Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP) province. TransPeshawar BRT system consists of two parts: the first encompasses an east–west corridor served by 30 stations on a dedicated lane for exclusive use by buses, while the second part consists of a network of feeder routes in which buses can enter and exit the system to travel on city streets. The system was inaugurated on 13 August 2020, and is the fourth BRT system in Pakistan.
Coimbatore Metro, also known as Kovai Metro, is a proposed rapid transit system for Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu.

Urban Mass Transit Company Limited (UMTC) is an urban transport consultancy company to develop sustainable urban mobility methods and solutions. It focuses on planning, designing, project management and implementation supervision of urban transportation projects. It was founded on 13 April 1993 as a partnership between Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation and Infrastructure Leasing & Financial Services Limited (IL&FS).

The RapidX is a rapid rail system operated by the National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC) in India's National Capital Region (NCR). The objective of RapidX is to replace the conventional non-air-conditioned MEMU-operated local train network with a rapid rail system. The semi-high-speed trainsets operating on RapidX are named Namo Bharat and have an average speed of 100 km/h.
The Ghaziabad–Jewar Regional Rapid Transit System is a proposed 72.44 km (45.01 mi) semi high-speed rail and regional transit corridor that will connect the National Capital Region cities of Ghaziabad and Noida with Noida International Airport at Jewar. It is the fourth of the four rapid rail corridors planned under the first phase of the RapidX project managed by the National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC). It will be built to allow a maximum speed of 180 km/h (110 mph), and the distance between Ghaziabad, Noida and the airport will be covered in less than 40–50 minutes. The project is estimated to cost approximately ₹20,640 crore. It will originate from Ghaziabad, run through Noida, Greater Noida, YEIDA City and end at the Noida International Airport at Jewar. It will have 12 stations and two depots on both the northern and southern ends of the corridor.













