
John Harrison was an English carpenter and clockmaker who invented the marine chronometer, a long-sought-after device for solving the problem of calculating longitude while at sea.
A pendulum clock is a clock that uses a pendulum, a swinging weight, as its timekeeping element. The advantage of a pendulum for timekeeping is that it is an approximate harmonic oscillator: It swings back and forth in a precise time interval dependent on its length, and resists swinging at other rates. From its invention in 1656 by Christiaan Huygens, inspired by Galileo Galilei, until the 1930s, the pendulum clock was the world's most precise timekeeper, accounting for its widespread use. Throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, pendulum clocks in homes, factories, offices, and railroad stations served as primary time standards for scheduling daily life, work shifts, and public transportation. Their greater accuracy allowed for the faster pace of life which was necessary for the Industrial Revolution. The home pendulum clock was replaced by less-expensive synchronous electric clocks in the 1930s and '40s. Pendulum clocks are now kept mostly for their decorative and antique value.

The Worshipful Company of Clockmakers was established under a royal charter granted by King Charles I in 1631. It ranks sixty-first among the livery companies of the City of London, and comes under the jurisdiction of the Privy Council. The company established a library and its museum in 1813, which is the oldest specific collection of clocks and watches worldwide. This is administered by the company's affiliated charity, the Clockmakers' Charity, and is presently housed on the second floor of London's Science Museum. The modern aims of the company and its museum are charitable and educational, in particular to promote and preserve clockmaking and watchmaking, which as of 2019 were added to the HCA Red List of Endangered Crafts.

A watchmaker is an artisan who makes and repairs watches. Since a majority of watches are now factory-made, most modern watchmakers only repair watches. However, originally they were master craftsmen who built watches, including all their parts, by hand. Modern watchmakers, when required to repair older watches, for which replacement parts may not be available, must have fabrication skills, and can typically manufacture replacements for many of the parts found in a watch. The term clockmaker refers to an equivalent occupation specializing in clocks.
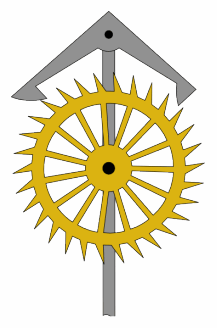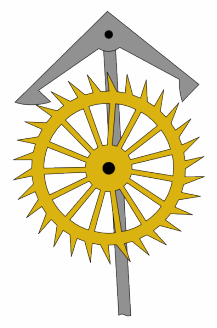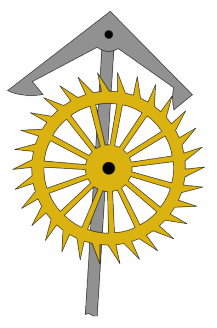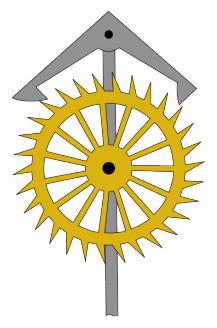
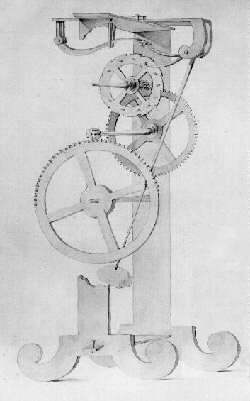
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy to the clock's timekeeping element to replace the energy lost to friction during its cycle and keep the timekeeper oscillating. The escapement is driven by force from a coiled spring or a suspended weight, transmitted through the timepiece's gear train. Each swing of the pendulum or balance wheel releases a tooth of the escapement's escape wheel, allowing the clock's gear train to advance or "escape" by a fixed amount. This regular periodic advancement moves the clock's hands forward at a steady rate. At the same time, the tooth gives the timekeeping element a push, before another tooth catches on the escapement's pallet, returning the escapement to its "locked" state. The sudden stopping of the escapement's tooth is what generates the characteristic "ticking" sound heard in operating mechanical clocks and watches.

John Arnold was an English watchmaker and inventor.

The Clockmakers’ Museum in London, England, is believed to be the oldest collection specifically of clocks and watches in the world. The collection belongs to and is administered by the Clockmakers’ Charity, affiliated to the Worshipful Company of Clockmakers, founded in 1631 by Royal Charter. Since 2015 it has been housed in a gallery provided by the Science Museum in South Kensington, having formerly been located in the Guildhall complex in the City of London since 1874, where it first opened to the public. Admission is free.

Chronometry or horology is the science of the measurement of time, or timekeeping. Chronometry provides a standard of measurement for time, and therefore serves as a significant reference for many and various fields of science.

Jaffa Gate is one of the seven main open gates of the Old City of Jerusalem.

A balance spring, or hairspring, is a spring attached to the balance wheel in mechanical timepieces. It causes the balance wheel to oscillate with a resonant frequency when the timepiece is running, which controls the speed at which the wheels of the timepiece turn, thus the rate of movement of the hands. A regulator lever is often fitted, which can be used to alter the free length of the spring and thereby adjust the rate of the timepiece.

Charles Frodsham was a distinguished English horologist, establishing the firm of Charles Frodsham & Co, which remains in existence as the longest continuously trading firm of chronometer manufacturers in the world. In January 2018, the firm launched a new chronometer wristwatch, after sixteen years in development. It is the first watch to use the George Daniels double-impulse escapement.

Edward John Dent (1790–1853) was a famous English watchmaker noted for his highly accurate clocks and marine chronometers.

The British Horological Institute (BHI) is the representative body of the horological industry in the United Kingdom. It was founded by a group of clockmakers in 1858, and has its current premises at Upton Hall in Nottinghamshire, which includes a museum of clock history.

A chronometer is an extraordinarily accurate mechanical timepiece, with an original focus on the needs of maritime navigation. In Switzerland, timepieces certified by the Contrôle Officiel Suisse des Chronomètres (COSC) may be marked as Certified Chronometer or Officially Certified Chronometer. Outside Switzerland, equivalent bodies, such as the Japan Chronometer Inspection Institute, have in the past certified timepieces to similar standards, although use of the term has not always been strictly controlled.
Edward Martin Burgess FSA FBHI, known as Martin Burgess, was an English horologist and master clockmaker.
Jonathan Betts MBE is Curator Emeritus at the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, a horological scholar and author, and an expert on the first marine timekeepers created by John Harrison in the middle of the 18th century. He was formerly Senior Specialist in horology at Greenwich. Between 2016 and 2019 he served on the board of trustees of the Institute of Conservation.

A nautical chronometer made by Thomas Earnshaw (1749–1828), and once part of the equipment of HMS Beagle, the ship that carried Charles Darwin on his voyage around the world, is held in the British Museum. The chronometer was the subject of one episode of the BBC's series A History of the World in 100 Objects.
Thomas Mercer Chronometers is a British company specialising in the design and production of bespoke chronometers.

The Dingwall Beloe Lecture Series is the result of bequests by Eric Dingwall, formerly an Assistant Keeper of Printed Books in the British Museum, and to the Clockmakers Company by Reginald Beloe TD, the noted horological collector and Master of the Company in 1977.

Newham Town Hall, formerly East Ham Town Hall, is a municipal building in Barking Road, East Ham, London. The town hall, which is the headquarters of Newham London Borough Council, is a Grade II* listed building.

















