
Petrochemicals are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as maize, palm fruit or sugar cane.

Polyethylene glycol (PEG; ) is a polyether compound derived from petroleum with many applications, from industrial manufacturing to medicine. PEG is also known as polyethylene oxide (PEO) or polyoxyethylene (POE), depending on its molecular weight. The structure of PEG is commonly expressed as H−(O−CH2−CH2)n−OH.
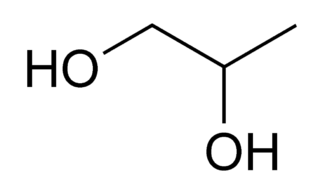
Propylene glycol (IUPAC name: propane-1,2-diol) is a viscous, colorless liquid, which is nearly odorless but possesses a faintly sweet taste. Its chemical formula is CH3CH(OH)CH2OH. Containing two alcohol groups, it is classed as a diol. It is miscible with a broad range of solvents, including water, acetone, and chloroform. In general, glycols are non-irritating and have very low volatility.
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups. An aliphatic diol is also called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified.

An antifreeze is an additive which lowers the freezing point of a water-based liquid. An antifreeze mixture is used to achieve freezing-point depression for cold environments. Common antifreezes also increase the boiling point of the liquid, allowing higher coolant temperature.
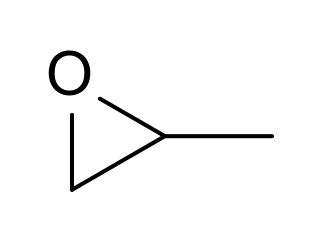
Propylene oxide is an organic compound with the molecular formula CH3CHCH2O. This colourless volatile liquid with an odour resembling ether, is produced on a large scale industrially. Its major application is its use for the production of polyether polyols for use in making polyurethane plastics. It is a chiral epoxide, although it is commonly used as a racemic mixture.

Ethyl butyrate, also known as ethyl butanoate, or butyric ether, is an ester with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3. It is soluble in propylene glycol, paraffin oil, and kerosene. It has a fruity odor, similar to pineapple, and is a key ingredient used as a flavor enhancer in processed orange juices. It also occurs naturally in many fruits, albeit at lower concentrations.
Mace is the brand name of an early type of aerosol self-defense spray invented by Alan Lee Litman in the 1960s. The first commercial product of its type, Litman's design packaged phenacyl chloride (CN) tear gas dissolved in hydrocarbon solvents into a small aerosol spray can, usable in many environments and strong enough to act as a deterrent and incapacitant when sprayed in the face. Its popularity led to the name "mace" being used commonly for other defense sprays regardless of their composition, and for the term "maced" to be used to reference being pepper sprayed. It is unrelated to the spice mace.

2-Butoxyethanol is an organic compound with the chemical formula BuOC2H4OH (Bu = CH3CH2CH2CH2). This colorless liquid has a sweet, ether-like odor, as it derives from the family of glycol ethers, and is a butyl ether of ethylene glycol. As a relatively nonvolatile, inexpensive solvent, it is used in many domestic and industrial products because of its properties as a surfactant. It is a known respiratory irritant and can be acutely toxic but animal studies did not find it to be mutagenic, and no studies suggest it is a human carcinogen. A study of 13 classroom air contaminants conducted in Portugal reported a statistically significant association with increased rates of nasal obstruction, the study also reported a positive association below the level of statistical significance with a higher risk of obese asthma and increased child BMI.
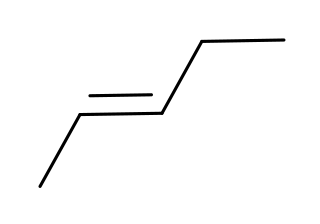
Pentenes are alkenes with chemical formula C
5H
10. Each contains one double bond within its molecular structure. There are a total of six different compounds in this class, differing from each other by whether the carbon atoms are attached linearly or in a branched structure, and whether the double bond has a cis or trans form.

A carbonate ester (organic carbonate or organocarbonate) is an ester of carbonic acid. This functional group consists of a carbonyl group flanked by two alkoxy groups. The general structure of these carbonates is R1O(C=O)OR2 and they are related to esters R1O(C=O)R, ethers R1OR2 and also to the inorganic carbonates.
Glycol ethers are a group of solvents based on alkyl ethers of ethylene glycol or propylene glycol commonly used in paints and cleaners. These solvents typically have a higher boiling point, together with the favorable solvent properties of lower-molecular weight ethers and alcohols. The word "Cellosolve" was registered in 1924 as a United States trademark by Carbide & Carbon Chemicals Corp. for "Solvents for Gums, Resins, Cellulose Esters, and the Like". The first one was ethyl cellosolve, with the name now generic for glycol ethers.

Dimethyl carbonate (DMC) is an organic compound with the formula OC(OCH3)2. It is a colourless, flammable liquid. It is classified as a carbonate ester. This compound has found use as a methylating agent and more recently as a solvent that is exempt from the restrictions placed on most volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the US. Dimethyl carbonate is often considered to be a green reagent.
The molecular formula C6H12O3 may refer to:
Calcium Lime Rust, more commonly known as CLR, is a household cleaning product used for dissolving stains, such as calcium, lime, and iron oxide deposits.
The molecular formula C7H16O3 (molar mass: 148.20 g/mol, exact mass: 148.1099 u) may refer to:
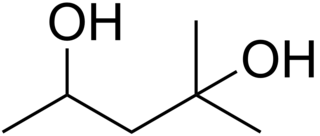
2-Methyl-2,4-pentanediol (MPD) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2C(OH)CH2CH(OH)CH3. This colourless liquid is a chiral diol. It is produced industrially from diacetone alcohol by hydrogenation. Total European and USA production was 15000 tonnes in 2000.

Propylene glycol methyl ether acetate is a P-type glycol ether used in inks, coatings, and cleaners. It is sold by Dow Chemical under the name Dowanol PMA, by Shell Chemical under the name methyl proxitol acetate, and by Eastman under the name PM Acetate.

Propylene glycol methyl ether is an organic solvent with a wide variety of industrial and commercial uses. Similar to other glycol ethers, it is used as a carrier/solvent in printing/writing inks and paints/coatings. It also finds use as an industrial and commercial paint stripper. It is used as an antifreeze in diesel engines.
Chalkboard paint is a specialized paint that creates a chalkboard like coating that can be utilized as a writing surface in the same manner as a traditional chalkboard or blackboard. Chalkboard paint is commonly made out of a mixture of talc, acrylic, water, glycol, titanium dioxide, carbon black, opacifiers, silica, and esters. It may also contain acetone, propane, butane, xylene, ethylbenzene, amorphous silica, n-butyl acetate, and propylene glycol methyl ether acetate which are industrial standard ingredients used in inks and paints as thinners, olfactory, and pigmentation agents.













