
Basalt is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars.

Vesta is one of the largest objects in the asteroid belt, with a mean diameter of 525 kilometres (326 mi). It was discovered by the German astronomer Heinrich Wilhelm Matthias Olbers on 29 March 1807 and is named after Vesta, the virgin goddess of home and hearth from Roman mythology.

Johnstown is a home rule municipality in Weld and Larimer counties in the U.S. state of Colorado. The population was 17,303 at the 2020 United States Census.
A V-type asteroid or Vestoid is an asteroid whose spectral type is that of 4 Vesta. Approximately 6% of main-belt asteroids are vestoids, with Vesta being by far the largest of them. They are relatively bright, and rather similar to the more common S-type asteroid, which are also made up of stony irons and ordinary chondrites, with V-types containing more pyroxene than S-types.

In meteoritics, a meteorite classification system attempts to group similar meteorites and allows scientists to communicate with a standardized terminology when discussing them. Meteorites are classified according to a variety of characteristics, especially mineralogical, petrological, chemical, and isotopic properties.
3494 Purple Mountain, provisional designation 1980 XW, is a bright Vestian asteroid and a formerly lost minor planet from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 6.5 kilometers in diameter. First observed in 1962, it was officially discovered on 7 December 1980, by Chinese astronomers at the Purple Mountain Observatory in Nanking, China, and later named in honor of the discovering observatory. The V-type asteroid has a rotation period of 5.9 hours.

An achondrite is a stony meteorite that does not contain chondrules. It consists of material similar to terrestrial basalts or plutonic rocks and has been differentiated and reprocessed to a lesser or greater degree due to melting and recrystallization on or within meteorite parent bodies. As a result, achondrites have distinct textures and mineralogies indicative of igneous processes.
The Vesta family is a family of asteroids. The cratering family is located in the inner asteroid belt in the vicinity of its namesake and principal body, 4 Vesta. It is one of the largest asteroid families with more than 15,000 known members and consists of mostly bright V-type asteroids, so-called "vestoids".
J-type asteroids are asteroids with spectra similar to that of diogenite meteorites and so, presumably, to the deeper layers of the crust of 4 Vesta.
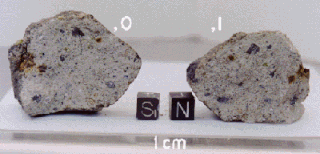
HED meteorites are a clan (subgroup) of achondrite meteorites. HED stands for "howardite–eucrite–diogenite". These achondrites came from a differentiated parent body and experienced extensive igneous processing not much different from the magmatic rocks found on Earth and for this reason they closely resemble terrestrial igneous rocks.

Howardites are achondritic stony meteorites that originate from the surface of the asteroid 4 Vesta, and as such are part of the HED meteorite clan. There are about 200 distinct members known.

Eucrites are achondritic stony meteorites, many of which originate from the surface of the asteroid 4 Vesta and are part of the HED meteorite clan. They are the most common achondrite group with over 100 meteorites found.
51829 Williemccool (provisional designation 2001 OD41) is a Vestian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 2 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 21 July 2001, by astronomers of the Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking program at Palomar Observatory in California, United States. The asteroid was named in memory of American astronaut and pilot William C. McCool, who died in the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster.

9951 Tyrannosaurus, provisional designation 1990 VK5, is a stony Vestian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 17 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 15 November 1990, by Belgian astronomer Eric Elst at ESO's La Silla Observatory in northern Chile. It was named after Tyrannosaurus, a genus of dinosaurs.
7794 Sanvito, provisional designation 1996 AD4, is a bright Vestian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 4.6 kilometers (2.9 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 15 January 1996, by Italian astronomers Ulisse Munari and Maura Tombelli at the Cima Ekar Observing Station in Tuscany, Italy. The likely V-type asteroid was named after Italian amateur astronomer Roberto di San Vito.

6257 Thorvaldsen, provisional designation 4098 T-1, is a bright Vestian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 4.3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered during the Palomar–Leiden Trojan survey on 26 March 1971, by Ingrid and Cornelis van Houten at Leiden, and Tom Gehrels at Palomar Observatory in California. The asteroid was named for Danish sculptor Bertel Thorvaldsen.
10244 Thüringer Wald, provisional designation 4668 P-L, is a Vestian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 3.3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 26 September 1960, by Ingrid and Cornelis van Houten at Leiden, and Tom Gehrels at Palomar Observatory in California, United States. The asteroid was named after the Thuringian Forest, a German mountain range.
This is a glossary of terms used in meteoritics, the science of meteorites.

274301 Wikipedia, provisional designation 2008 QH24, is a Vestian asteroid orbiting in the inner region of the asteroid belt, approximately 1 kilometer (0.6 mi) in diameter. It was discovered on 25 August 2008 by astronomers at the Andrushivka Astronomical Observatory in northern Ukraine. The asteroid was named after the online encyclopedia Wikipedia in January 2013.
Bunburra Rockhole is an anomalous basaltic achondritic meteorite. Originally classified as a eucrite, it was thought to belong to a group of meteorites that originated from the asteroid 4 Vesta, but has since been reclassified based on oxygen and chromium isotopic compositions. It was observed to fall on July 21, 2007, 04:43:56 local time, by the Desert Fireball Network (DFN). Two fragments weighing 150g and 174g were recovered by the DFN at 31°21.0′S, 129°11.4′E in the Nullarbor Desert region, South Australia in November of the same year. This is the first meteorite to be recovered using the Desert Fireball Network observatory.











