
The combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP), often referred to as the birth control pill or colloquially as "the pill", is a type of birth control that is designed to be taken orally by women. It is the oral form of combined hormonal contraception. The pill contains two important hormones: a progestin and estrogen. When taken correctly, it alters the menstrual cycle to eliminate ovulation and prevent pregnancy.

Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior.

Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the major progestogen in the body. Progesterone has a variety of important functions in the body. It is also a crucial metabolic intermediate in the production of other endogenous steroids, including the sex hormones and the corticosteroids, and plays an important role in brain function as a neurosteroid.

Progestogens, also sometimes written progestins, progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the body. The progestogens are named for their function in maintaining pregnancy, although they are also present at other phases of the estrous and menstrual cycles.

Percy Lavon Julian was an American research chemist and a pioneer in the chemical synthesis of medicinal drugs from plants. Julian was the first person to synthesize the natural product physostigmine, and a pioneer in industrial large-scale chemical synthesis of the human hormones progesterone and testosterone from plant sterols such as stigmasterol and sitosterol. His work laid the foundation for the steroid drug industry's production of cortisone, other corticosteroids, and artificial hormones that led to birth control pills.

Dioscorea is a genus of over 600 species of flowering plants in the family Dioscoreaceae, native throughout the tropical and warm temperate regions of the world. The vast majority of the species are tropical, with only a few species extending into temperate climates. It was named by the monk Charles Plumier after the ancient Greek physician and botanist Dioscorides.
Russell Earl Marker was an American chemist who invented the octane rating system when he was working at the Ethyl Corporation. Later in his career, he went on to found a steroid industry in Mexico when he successfully made semisynthetic progesterone from chemical constituents found in Mexican yams in a process known as Marker degradation. This eventually led to the development at Syntex of the combined oral contraceptive pill and synthetic cortisone – and to the development of the Mexican barbasco trade.

Yam is the common name for some plant species in the genus Dioscorea that form edible tubers.
Laboratorios Syntex SA was a pharmaceutical company formed in Mexico City in January 1944 by Russell Marker, Emeric Somlo, and Federico Lehmann to manufacture therapeutic steroids from the Mexican yams called cabeza de negro and Barbasco. The demand for barbasco by Syntex initiated the Mexican barbasco trade.

George Rosenkranz was a pioneering Hungarian-born Mexican scientist in the field of steroid chemistry, who used native Mexican plant sources as raw materials. He was born in Hungary, studied in Switzerland and emigrated to the Americas to escape the Nazis, eventually settling in Mexico.

Dioscorea bulbifera is a species of true yam in the yam family, Dioscoreaceae. It is native to Africa, Asia and northern Australia. It is widely cultivated and has become naturalized in many regions.

Diosgenin, a phytosteroid sapogenin, is the product of hydrolysis by acids, strong bases, or enzymes of saponins, extracted from the tubers of Dioscorea wild yam species, such as the Kokoro. It is also present in smaller amounts in a number of other species. The sugar-free (aglycone) product of such hydrolysis, diosgenin is used for the commercial synthesis of cortisone, pregnenolone, progesterone, and other steroid products.
Barbasco is the name of several plants that contain poisonous chemical compounds that have been used for fishing by indigenous populations of the Americas:

Dioscorea mexicana, Mexican yam or cabeza de negro is a species of yam in the genus Dioscorea.
The Marker degradation is a three-step synthetic route in steroid chemistry developed by American chemist Russell Earl Marker in 1938–1940. It is used for the production of cortisone and mammalian sex hormones from plant steroids, and established Mexico as a world center for steroid production in the years immediately after World War II. The discovery of the Marker degradation allowed the production of substantial quantities of steroid hormones for the first time, and was fundamental in the development of the contraceptive pill and corticosteroid anti-inflammatory drugs. In 1999, the American Chemical Society and the Sociedad Química de México named the route as an International Historic Chemical Landmark.

Sarsasapogenin is a steroidal sapogenin, that is the aglycosidic portion of a plant saponin. It is named after sarsaparilla, a family of climbing plants found in subtropical regions. It was one of the first sapogenins to be identified, and the first spirostan steroid to be identified as such. The identification of the spirostan structure, with its ketone spiro acetal functionality, was fundamental in the development of the Marker degradation, which allowed the industrial production of progesterone and other sex hormones from plant steroids.

The Mexican barbasco trade was the trade of the diosgenin-rich yam species Dioscorea mexicana, Dioscorea floribunda and Dioscorea composita which emerged in Mexico in the 1950s as part of the Mexican steroid industry. The trade consisted in Mexican campesinos harvesting the root in the jungle, selling it to middlemen who brought it to processing plants where the root was fermented and the diosgenin extracted and sold to pharmaceutical companies such as Syntex who used it to produce synthetic hormones.
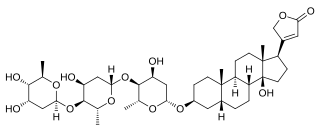
Phytosteroids, also known as plant steroids, are naturally occurring steroids that are found in plants. Examples include digoxin, digitoxin, diosgenin, and guggulsterone, as well as phytosterols like β-sitosterol and other phytoestrogens like isoflavones.
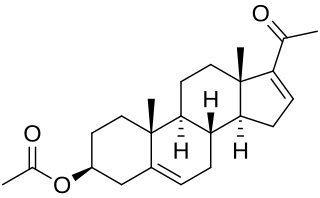
16-Dehydropregnenolone acetate (16-DPA) is a chemical compound used as an intermediate or synthon in the production of many semisynthetic steroids. As 7-ACA is for cephalosporins and 6-APA is for penicillins, 16-DPA is for steroids. While it is not easy to synthesize, it is a convenient intermediate which can be made from other more available materials, and which can then be modified to produce the desired target compound.

Mexico ranks fourth in the world in biodiversity and is one of the 17 megadiverse countries. With over 200,000 different species, Mexico is home of 10–12% of the world's biodiversity. Mexico ranks first in biodiversity in reptiles with 707 known species, second in mammals with 438 species, fourth in amphibians with 290 species, and fourth in flora, with 26,000 different species. Mexico is also considered the second country in the world in ecosystems and fourth in overall species. About 2,500 species are protected by Mexican legislation. In 2002, Mexico had the second fastest rate of deforestation in the world, second only to Brazil. It had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 6.82/10, ranking it 63rd globally out of 172 countries.













