
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the largest Egyptian pyramid. It served as the tomb of pharaoh Khufu, who ruled during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Built c. 2600 BC, over a period of about 26 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only wonder that has remained largely intact. It is the most famous monument of the Giza pyramid complex, which is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Memphis and its Necropolis". It is situated at the northeastern end of the line of the three main pyramids at Giza.

Khufu or Cheops was an ancient Egyptian monarch who was the second pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty, in the first half of the Old Kingdom period. Khufu succeeded his father Sneferu as king. He is generally accepted as having commissioned the Great Pyramid of Giza, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, but many other aspects of his reign are poorly documented.

Zahi Abass Hawass is an Egyptian archaeologist, Egyptologist, and former Minister of Tourism and Antiquities, serving twice. He has worked at archaeological sites in the Nile Delta, the Western Desert and the Upper Nile Valley.

The pyramid of Khafre or of Chephren is the middle of the three Ancient Egyptian Pyramids of Giza, the second tallest and second largest of the group. It is the only pyramid out of the three that still has cladding at the top. It is the tomb of the Fourth-Dynasty Pharaoh Khafre (Chefren), who ruled c. 2558−2532 BC.

The pyramid of Menkaure is the smallest of the three main pyramids of the Giza pyramid complex, located on the Giza Plateau in the southwestern outskirts of Cairo, Egypt. It is thought to have been built to serve as the tomb of the Fourth Dynasty King Menkaure.

The Giza pyramid complex in Egypt is home to the Great Pyramid, the Pyramid of Khafre, and the Pyramid of Menkaure, along with their associated pyramid complexes and the Great Sphinx. All were built during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom of ancient Egypt, between c. 2600 – c. 2500 BC. The site also includes several temples, cemeteries, and the remains of a workers' village.

Hemiunu was an ancient Egyptian prince who is believed to have been the architect of the Great Pyramid of Giza. As vizier, succeeding his father, Nefermaat, and his uncle, Kanefer, Hemiunu was one of the most important members of the court and responsible for all the royal works. His tomb lies close to west side Khufu's pyramid.

The construction of the Egyptian pyramids can be explained with well-established scientific facts, however there are some aspects that are even today considered controversial hypotheses. The construction techniques used seem to have developed over time; later pyramids were not constructed in the same way as earlier ones. It is believed that huge stones were carved from quarries with copper chisels, and these blocks were then dragged and lifted into position. Disagreements chiefly concern the methods used to move and place the stones.

The Khufu ship is an intact full-size solar barque from ancient Egypt. It was sealed into a pit alongside the Great Pyramid of pharaoh Khufu around 2500 BC, during the Fourth Dynasty of the ancient Egyptian Old Kingdom. Like other buried Ancient Egyptian ships, it was part of the extensive grave goods intended for use in the afterlife. The Khufu ship is one of the oldest, largest, best preserved vessels from antiquity. It is 43.4 metres (142 ft) long, 5.9 metres (19 ft) wide, and 1.78 meters deep, and is the world's oldest intact ship. It has been described as "a masterpiece of woodcraft" that could sail today if put into a lake or a river.
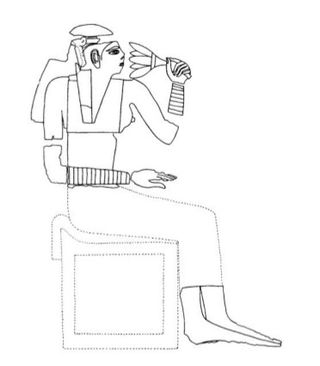
Hetepheres I was a queen of Egypt during the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt who was a wife of one king, the mother of the next king, the grandmother of two more kings, and the figure who tied together two dynasties.
The Upuaut Project was a scientific exploration of the so-called "air shafts" of the Great Pyramid of Giza, which was built as a tomb for Fourth Dynasty pharaoh Khufu. The Upuaut Project was led by Rudolf Gantenbrink under the auspices of the German Archaeological Institute in Cairo during three campaigns. According to Bauval, it was "marshalled into two stages: the first stage, to improve ventilation in the Great Pyramid using the shafts in the King's Chamber, and the second stage to explore the presumed 'abandoned' shafts in the Queen's Chambers." The latter was accomplished by sending a miniature mobile robot designed by Rudolph Gantenbrink, named Upuaut-2, into the shafts.

Selim Hassan was an Egyptian Egyptologist.

Henutsen is the name of an ancient Egyptian queen consort who lived during the 4th dynasty of the Old Kingdom Period. She was the second or third wife of pharaoh Khufu and most possibly buried at Giza.

Rahotep,, was a prince, the son of pharaoh Snofru and his first wife Hetepheres I, in ancient Egypt during the 4th Dynasty, reign of his father Snofru possibly his brother Khufu too..

Chasing Mummies: The Amazing Adventures of Zahi Hawass is a reality television series that aired on The History Channel in the United States. Produced by Boutique TV, the series depicted the adventures of archaeologist and Egyptologist Dr. Zahi Hawass and his discoveries in Egypt as he is followed by young archeological fellows and a camera crew. The series ran Wednesdays on the History Channel from July 14, 2010 until its end on September 15, 2010. The shows illustrates the complexities in the almost never-ending quest to preserve and discover artifacts from ancient Egypt.

G1-c is one of the subsidiary pyramids of the Giza East Field of the Giza Necropolis immediately to the eastern side of the Great Pyramid of Giza, built during the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt. It is the southern of the three pyramids of the queens and is the one of Queen Henutsen. It is 46.25 metres wide and had a height of 29.6 metres. A niche, four inches deep was dug in the south wall of the burial chamber. Pyramid G1-c was originally not a part of Khufu's pyramid complex, as its southern side is aligned not with the side of the Great Pyramid, but with Khufukhaf I's mastaba tomb nearby. Pyramid G1-c was at some point thought to possibly be a satellite pyramid, because it did not come with a boat pit like pyramids G1-a and G1-b. It was later determined to be an unfinished pyramid which was constructed in a hurry. Henutsen is thought to have been buried in the tomb. Dr. Rainer Stadelmann believes Khufukhaf is the same person as Khafra and the pyramid was built by him for his mother, but this identification is doubtful.

Pyramid G1-d is a satellite pyramid within the Khufu pyramid complex on the Giza plateau.

"Star shafts", or sometimes "air shafts", commonly refers to two narrow ducts leading out of the King's Chamber of the Great Pyramid of Giza. It may also refer to two similar shafts in the walls of the Queen's Chamber, though these are discussed less frequently due to being blocked off on both the outside and inside of the pyramid.

The Khufu Statuette or the Ivory figurine of Khufu is an ancient Egyptian statue. Historically and archaeologically significant, it was found in 1903 by Sir William Matthew Flinders Petrie during excavation of Kom el-Sultan in Abydos, Egypt. It depicts Khufu, a Pharaoh of the Fourth dynasty, and the builder of the Great Pyramid, though it may have been carved much later, in the Twenty-Sixth Dynasty, 664 BC–525 BC.

Mostafa Waziri is an Egyptian archaeologist, Egyptologist, and the former secretary-general of the Supreme Council of Antiquities of Egypt.
















