
Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the electronic or mechanical conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a scene photo or from subtitle text superimposed on an image.
A document management system (DMS) is usually a computerized system used to store, share, track and manage files or documents. Some systems include history tracking where a log of the various versions created and modified by different users is recorded. The term has some overlap with the concepts of content management systems. It is often viewed as a component of enterprise content management (ECM) systems and related to digital asset management, document imaging, workflow systems and records management systems.

An image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting or an object and converts it to a digital image. Commonly used in offices are variations of the desktop flatbed scanner where the document is placed on a glass window for scanning. Hand-held scanners, where the device is moved by hand, have evolved from text scanning "wands" to 3D scanners used for industrial design, reverse engineering, test and measurement, orthotics, gaming and other applications. Mechanically driven scanners that move the document are typically used for large-format documents, where a flatbed design would be impractical.
DjVu is a computer file format designed primarily to store scanned documents, especially those containing a combination of text, line drawings, indexed color images, and photographs. It uses technologies such as image layer separation of text and background/images, progressive loading, arithmetic coding, and lossy compression for bitonal (monochrome) images. This allows high-quality, readable images to be stored in a minimum of space, so that they can be made available on the web.
In library and archival science, digital preservation is a formal process to ensure that digital information of continuing value remains accessible and usable in the long term. It involves planning, resource allocation, and application of preservation methods and technologies, and combines policies, strategies and actions to ensure access to reformatted and "born-digital" content, regardless of the challenges of media failure and technological change. The goal of digital preservation is the accurate rendering of authenticated content over time.
Enterprise content management (ECM) extends the concept of content management by adding a timeline for each content item and, possibly, enforcing processes for its creation, approval, and distribution. Systems using ECM generally provide a secure repository for managed items, analog or digital. They also include one methods for importing content to manage new items, and several presentation methods to make items available for use. Although ECM content may be protected by digital rights management (DRM), it is not required. ECM is distinguished from general content management by its cognizance of the processes and procedures of the enterprise for which it is created.
DocuShare is a content management system developed by Xerox Corporation. DocuShare makes use of open standards and allows for managing content, integrating it with other business systems, and developing customized and packaged software applications.
The Extensible Metadata Platform (XMP) is an ISO standard, originally created by Adobe Systems Inc., for the creation, processing and interchange of standardized and custom metadata for digital documents and data sets.
PaperPort is commercial document management software published by Kofax, used for working with scanned documents. It uses a built-in optical character recognition to create files in searchable Portable Document Format (PDF); text in these files is indexed and can be searched for with appropriate software, such as Microsoft's Windows Search. Earlier versions of PaperPort used OmniPage to provide this function. It provides image editing tools for these files.

Adobe LiveCycle Enterprise Suite (ES4) is a service-oriented architecture Java EE server software product from Adobe Systems used to build applications that automate a broad range of business processes for enterprises and government agencies. LiveCycle ES4 is an enterprise document and form platform that helps you capture and process information, deliver personalized communications, and protect and track sensitive information. It is utilized for purposes such as account opening, services, and benefits enrollment, correspondence management, requests for proposal processes, and other manual-based workflows. LiveCycle ES4 incorporates new features with a particular focus on mobile devices. LiveCycle applications function in both online and offline environments. These capabilities are enabled through the use of Adobe Reader, HTML/PhoneGap, and Flash Player clients to reach desktop computers and mobile devices.
Data extraction is the act or process of retrieving data out of data sources for further data processing or data storage. The import into the intermediate extracting system is thus usually followed by data transformation and possibly the addition of metadata prior to export to another stage in the data workflow.
Documentum is an enterprise content management platform currently developed by OpenText. EMC acquired Documentum for US$1.7 billion in December 2003. The Documentum platform was part of EMC's Enterprise Content Division (ECD) business unit, one of EMC's four operating divisions.
Sidecar files, also known as buddy files or connected files, are computer files that store data which is not supported by the format of a source file.
hOCR is an open standard of data representation for formatted text obtained from optical character recognition (OCR). The definition encodes text, style, layout information, recognition confidence metrics and other information using Extensible Markup Language (XML) in the form of Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) or XHTML.
Forms processing is a process by which one can capture information entered into data fields and convert it into an electronic format. This can be done manually or automatically, but the general process is that hard copy data is filled out by humans and then "captured" from their respective fields and entered into a database or other electronic format.
AnyDoc Software, founded in 1989 as Microsystems Technology, Inc., was a company based in Tampa, Florida that developed, sold, installed, and supported enterprise content management (ECM) software which captures data from scanned documents or images into machine-readable text for back-office applications and content/document management systems. The company’s flagship product, OCR for Forms debuted in 1991 after two years of product research and development. AnyDoc Software was purchased in 2013 by Hyland Software, which is best known for its document management and content services software, OnBase. AnyDoc users can find more information about their products on the AnyDoc Community Page.
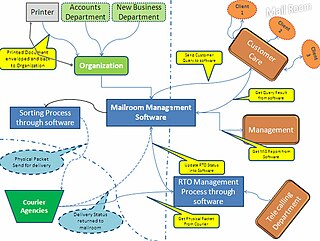
Digital mailroom is the automation of incoming mail processes. Using document scanning and document capture technologies, companies can digitise incoming mail and automate the classification and distribution of mail within the organization. Both paper and electronic mail (email) can be managed through the same process allowing companies to standardize their internal mail distribution procedures and adhere to company compliance policies.
Xena is open-source software for use in digital preservation. Xena is short for XML Electronic Normalising for Archives.

agorum core is a free and open-source Enterprise Content Management system by agorum Software GmbH from Germany. One of the main features is the Document-Network-Share. With that the documents within the ECM are shown as a normal network share. So it is usable like any other fileserver, you can use any program, that is able to access a normal drive. From the users' view the benefit is, that everything is working like before.
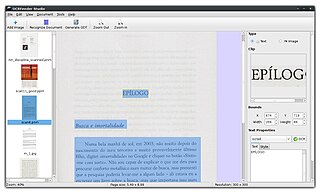
OCRFeeder is an optical character recognition suite for GNOME, which also supports virtually any command-line OCR engine, such as CuneiForm, GOCR, Ocrad and Tesseract. It converts paper documents to digital document files and can serve to make them accessible to visually impaired users.




