Related Research Articles

The Order of Preachers, commonly known as the Dominican Order, is a Catholic mendicant order of pontifical right that was founded in France by a Castilian priest named Dominic de Guzmán. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull Religiosam vitam on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as Dominicans, generally display the letters OP after their names, standing for Ordinis Praedicatorum, meaning 'of the Order of Preachers'. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, active sisters, and lay or secular Dominicans. More recently, there have been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries.

The Sisters of St. Joseph, also known as the Congregation of the Sisters of St. Joseph, abbreviated CSJ or SSJ, is a Catholic religious congregation of women founded in Le Puy-en-Velay, France, in 1650. This congregation, named for Saint Joseph, has approximately 14,000 members worldwide: about 7,000 in the United States; 2,000 in France; and are active in 50 other countries.

Edward Dominic Fenwick, was an American prelate of the Catholic Church, a Dominican friar and the first Bishop of Cincinnati.
The Congregation of Sisters of St. Dominic of St. Catherine of Siena is a Catholic religious institute for women founded in 1862 in Racine, Wisconsin, USA, in the Archdiocese of Milwaukee.

St. Catharine College was a small Roman Catholic liberal arts college near Springfield, Kentucky. The college was accredited by the Commission on Colleges of the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools and had a peak enrollment of 750 students.
The Dominican Sisters of Mary, Mother of the Eucharist, is a Catholic female religious institute of diocesan right, rather than Pontifical right, based in Ann Arbor, Michigan which follows the charism of the Dominican Order. The congregation was founded in 1997 by four members of the Dominican Sisters of St. Cecilia in Nashville, Tennessee. As of 2021, it has 155 members.

The Congregation of St. Cecilia, commonly known as the Nashville Dominicans, is a religious institute of the Roman Catholic Church located in Nashville, Tennessee. It is a member of the Council of Major Superiors of Women Religious, one of the two organizations which represent women religious in the United States. The sisters combine a monastic communal lifestyle of contemplation in the Dominican tradition with an active apostolate in Catholic education. As of 2018, the congregation has 300 sisters.

The Adrian Dominican Sisters is a Catholic religious institute of Dominican sisters in the United States. Their motherhouse is in Adrian, Michigan.

The Sisters of the Holy Family are a Catholic religious order of African-American nuns based in New Orleans, Louisiana. They were founded in 1837 as the Congregation of the Sisters of the Presentation of the Blessed Virgin Mary by Henriette DeLille. They adopted the current name in 1842.

The Third Order of Saint Dominic, also referred to as the Lay Fraternities of Saint Dominic or Lay Dominicans since 1972, is a Catholic third order which is part of the Dominican Order.

St. Agnes Academy-St. Dominic School (SAA-SDS) is an independent Catholic school in Memphis, Tennessee, consisting of an all-girls PK2-12th school and an all-boys PK2-8th school. The school is located in the Diocese of Memphis and follows Catholic principles but is not run by the diocese. It was founded by 6 Dominican sisters.
The Dominican Sisters of Blauvelt are a religious congregation within the Dominican Order of religious sisters founded in 1890. They are based in the town of Blauvelt, New York, a northern suburb of New York City. Their traditional service has been childcare, both through teaching and caring for orphans.

The Dominican Order was first established in the United States by Edward Fenwick in the early 19th century. The first Dominican institution in the United States was the Province of Saint Joseph, which was established in 1805. Additionally, there have been numerous institutes of Dominican Sisters and Nuns.
Catholic sisters and nuns in the United States have played a major role in American religion, education, nursing and social work since the early 19th century. In Catholic Europe, convents were heavily endowed over the centuries, and were sponsored by the aristocracy. Religious orders were founded by entrepreneurial women who saw a need and an opportunity, and were staffed by devout women from poor families. The number of Catholic nuns grew exponentially from about 900 in the year 1840, to a maximum of nearly 200,000 in 1965, falling to 56,000 in 2010. According to an article posted on CatholicPhilly.com, the website of the Archdiocese of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in October 2018, National Religious Retirement Office statistics showed that number as 47,160 in 2016, adding that “about 77 percent of women religious are older than 70.” In March 2022, the NRRO was reporting statistics from 2018, citing the number of professed sisters as 45,100. The network of Catholic institutions provided high status lifetime careers as nuns in parochial schools, hospitals, and orphanages. They were part of an international Catholic network, with considerable movement back and forth from Britain, France, Germany and Canada.
The Dominican Congregation of Our Lady of the Rosary, better known as the Dominican Sisters of Sparkill, is an institute of religious sisters of the Third Order of Saint Dominic based in Sparkill, New York, which was founded in 1876. The congregation developed to care for indigent women but now works primarily in education as well.

St. Dominic Church is a parish of the Roman Catholic Church, established in 1852. It is located in Southwest Washington, D.C., in the Archdiocese of Washington, and is administered by the Order of Preachers, more commonly known as the Dominicans, in the Province of St. Joseph (Eastern).
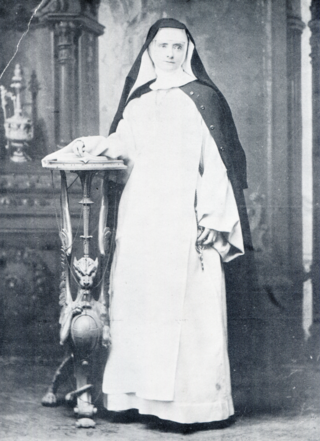
Lucy Eaton Smith, OP (1845-1894), known in religion as Mother Mary Catherine De Ricci of the Sacred Heart, was an American Catholic nun who founded the Dominican Sisters of St. Catherine de' Ricci, a pontifical institute in Albany, New York.
References
- ↑ "New Congregation of Dominican Sisters Founded," Catholic Times (Diocese of Columbus, Ohio), Vol. 58, April 26, 2009, p. 3. The new Congregation is listed as Dominican Sisters of Peace in the Official Catholic Directory (Berkeley Heights, NJ: P. J. Kenedy & Sons, 2011), p. 336, and #1115, p. 1691.
- ↑ Ryan, Zoe. "Dominican Sisters of St. Catherine de’ Ricci merge with Dominican Sisters of Peace", National Catholic Reporter , 19 October 2012. Retrieved 20 August 2013.
- ↑ McGreal, Mary Nona, OP, Ed. Dominicans at Home in a Young Nation: 1786-1865 Strasbourg, France: Editions du Signe, 2001: 97-99.
- ↑ Noonan, Paschala, OP. Signadou: History of the Kentucky Dominican Sisters. Manhasset, NY: Brookville Books, 1997.
- ↑ McGreal, Mary Nona, OP, Ed. Dominicans at Home in a Young Nation: 1786-1865 Strasbourg, France: Editions du Signe, 2001: 126-9.
- ↑ Mullay, Camilla, OP. A Place of Springs: A History of the Dominican Sisters of St. Mary of the Springs 1830-1970. Ed Ruth Caspar, OP. Columbus, Ohio: Dominican Sisters of St. Mary of the Springs, 2005.
- ↑ Dawes, Dorothy, OP. "Sister Mary Dominic O'Brien (1846-1900): Cabra's Gift to New Orleans," in Religious Pioneers: Building the Faith in the Archdiocese of New Orleans, Dorothy Dawes and Charles Nolan, Eds, Archdiocese of New Orleans, 2004: 163-178.
- ↑ McGreal, Mary Nona, OP. "Dominicans (O.P.)", in Encyclopedia of American Catholic History, Michael Glazier and Thomas J. Shelley, Eds. Collegeville, Minn: Liturgical Press, 1997: 443.
- ↑ Hartman, Sister Irene, OP. The Dominican Women of the Sunflower State: A History of the Great Bend, Kansas Dominicans 1902-1989. Dominican Sisters Great Bend, Kansas, 1997.
- ↑ Richard, Sister Paula, OP. "Eucharistic Missionaries of St. Dominic," in Religious Pioneers: Building the Faith in the Archdiocese of New Orleans, Dorothy Dawes and Charles Nolan, Eds, Archdiocese of New Orleans, 2004: 335-46.
- ↑ Bearers of the Word: A Brief History and Biographies, 1929-2008, Ed. Rebecca Betz, OP, Loretta Petit, OP, Barbara Wilhelm. Sisters of St. Dominic, Akron, Ohio, 2009.
- ↑ Paulus, Rosalia, OP. History of the Sisters of Saint Dominic of Akron, Ohio: 1923-1979. MS, Archives, Our Lady of the Elms Motherhouse, Akron, Ohio
- ↑ Culbertson, Diana, OP. Ed. A Journey of Faith: The Story of the Dominican Sisters of Oxford, Michigan. (Based on congregational chronicles, letters and annals). Dominican Sisters of Oxford, MI, 2010.
- ↑ Cf Melanie Blair, OSF and Jordan Hite, TOR, "The Merger and Union of Religious Institutes." Bulletin on Issues of Religious Law 3 (April 1987).
- ↑ Vatican Council II, Perfectae Caritatis, (#22).
- ↑ "Religious Ministries - Directory".
- ↑ "Leadership - Dominican Sisters of Peace" . Retrieved 2022-03-14.
- ↑ Decree Prot. n. C 244-2 / 2009, Franc Card. Rodé, CM to Sister Margaret Ormond, OP, Prioress, Dominican Sisters of Peace, 2 March 2010.
- ↑ Constitutions, Dominican Sisters of Peace, #1 and #3.
- ↑ Constitutions, Dominican Sisters of Peace, #26.