
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road for which a fee is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically implemented to help recoup the costs of road construction and maintenance.
King's Highway 407, commonly referred to as Highway 407 and colloquially as the "four-oh-seven", is a tolled 400-series highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. Comprising a privately leased segment as well as a publicly owned segment, the route spans the entire Greater Toronto Area (GTA) around the city of Toronto, travelling through the suburbs of Burlington, Oakville, Mississauga, Brampton, Vaughan, Markham, Pickering, Whitby, and Oshawa before ending in Clarington, north of Orono. At 151.4 km long, this is the fourth longest freeway in Ontario's 400 series network, after Highways 417, 400, and 401. The segment between Burlington and Brougham in Pickering is leased to and operated by the 407 ETR Concession Company Limited and is officially known as the 407 Express Toll Route (407 ETR). It begins at the junction of the Queen Elizabeth Way (QEW) and Highway 403 in Burlington, and travels 108.0 km (67.1 mi) across the GTA to Brock Road in Pickering. East of Brock Road, the tollway continues east as Highway 407, a toll route operated by the provincial government, for 43.4 km (27.0 mi) to Highway 35/115 in Clarington. The route interchanges with nine freeways: the QEW, Highway 403, Highway 401, Highway 410, Highway 427, Highway 400, Highway 404, Highway 412, and Highway 418. Highway 407 is an electronically operated toll highway; there are no toll booths along the length of the route. Distances are calculated automatically using transponders or automatic number-plate recognition, which are scanned at entrance and exit portals.

The Metropolitan Rapid Transit or MRT is a mass rapid transit system serving the Bangkok Metropolitan Region in Thailand. The MRT system comprises two rapid transit lines, with a further three lines currently under construction and due to open in 2023. The MRT Blue Line, officially the Chaloem Ratchamongkhon Line, between Hua Lamphong and Bang Sue was the first to open in 2004 as Bangkok's second metro system. The MRT Blue line is officially known in Thai as rotfaifa mahanakhon (รถไฟฟ้ามหานคร) or "metropolitan electric train", but it is more commonly called rotfai taidin (รถไฟใต้ดิน), literally, "underground train".

The South Luzon Expressway (SLEX), signed as E2 of the Philippine expressway network and R-3 of the Metro Manila arterial road network, is a limited-access toll expressway that connects Metro Manila to the provinces in the Calabarzon region on the island of Luzon in the Philippines. The expressway has a length of 46.9 km, traveling from its northern terminus at the Magallanes Interchange in Makati to its southern terminus at Santo Tomas, Batangas, connecting it to the Southern Tagalog Arterial Road. A portion of the expressway from the Magallanes Interchange to the Calamba Exit is part of Asian Highway 26 of the Asian highway network.

The Illinois State Toll Highway Authority (ISTHA) is an administrative agency of the U.S. state of Illinois charged with building, operating, and maintaining toll roads in the state. The roads, as well as the authority itself, are sometimes referred to as the Illinois Tollway. The system opened in 1958 in the Chicago area, and has subsequently expanded to include the eastern and central sections of Interstate 88 (I-88) extending into the northwestern part of the state. Beginning in 2005, the system was reconstructed to include more lanes and open road tolling, the latter of which uses I-Pass transponders to collect revenue as vehicles pass antennas at toll plazas or designated entrance or exit ramps. As of 2017, ISTHA maintains and operates 294 miles (473 km) of tollways in 12 counties in Northern Illinois.
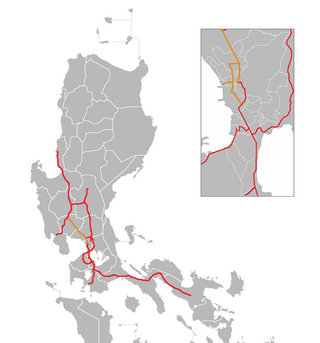
The North Luzon Expressway (NLEX), signed as E1 of the Philippine expressway network, partially as N160 of the Philippine highway network, and R-8 of the Metro Manila arterial road network, is a limited-access toll expressway that connects Metro Manila to the provinces of the Central Luzon region in the Philippines. The expressway, which includes the main segment and its various spurs, has a total length of 101.8 kilometers (63.3 mi) and travels from its northern terminus at Sta. Ines Interchange to its southern terminus in Balintawak Interchange, which is adjacent to its connection to Skyway, an elevated toll road that connects the NLEX to its counterpart in the south, the South Luzon Expressway. The segment of the expressway between Santa Rita Exit in Guiguinto and the Balintawak Interchange in Quezon City is part of Asian Highway 26 of the Asian highway network.

Din Daeng is one of the 50 districts (khet) of Bangkok, Thailand. Its neighbours, clockwise from north, are Chatuchak, Huai Khwang, Ratchathewi, and Phaya Thai.
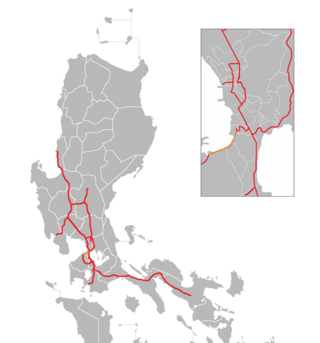
The Manila–Cavite Expressway, signed as E3 of the Philippine expressway network and R-1 of Metro Manila's arterial road network, is a 14-kilometer-long (8.7 mi) controlled-access toll expressway linking Manila to the southern province of Cavite in the Philippines. At its north end, it feeds into and from Roxas Boulevard in the city of Parañaque in Metro Manila, also part of R-1. At the south end, it splits into two termini, both along the north coast in Kawit, Cavite. The first feeds into the intersection of Tirona Highway and Antero Soriano Highway. The second southern terminus is on the intersection of Tirona Highway, Antero Soriano Highway and Covelandia Road in Kawit, Cavite.

Texas State Highway 130 (SH 130), also known as the Pickle Parkway, is a highway from Interstate 35 (I-35) in San Antonio along I-410 and I-10 to east of Seguin, then north as tollway from there to I-35 north of Georgetown. SH 130 runs in a 91-mile (146 km) corridor east and south of Austin. The route parallels I-35 and is intended to relieve the Interstate's traffic volume through the San Antonio–Austin corridor by serving as an alternate route.

The Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway (SCTEX), signed as E1 and E4 of the Philippine expressway network and R-8 of the Metro Manila arterial road network, is controlled-access toll expressway in the Central Luzon region of the Philippines. From its northern terminus in Tarlac City to its southern terminus at Tipo in Hermosa, Bataan, the SCTEX serves as one of the main expressways in Luzon. The expressway is also connected to the Central Luzon Link Expressway, North Luzon Expressway, Tarlac–Pangasinan–La Union Expressway, and the Subic Freeport Expressway. The SCTEX is the country's longest expressway at 93.77 kilometers (58.27 mi). The Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway was constructed to provide a more efficient transport corridor between Subic Bay Freeport, Clark, and the Central Techno Park in Tarlac, foster development on the municipalities served, and connect major infrastructures such as the Subic Seaport and Clark International Airport.

The Metro Manila Skyway, officially the Metro Manila Skyway System (MMSS) or simply the Skyway, is an elevated highway which is the main expressway in Metro Manila, Philippines. It connects the North and South Luzon Expressways with access to Ninoy Aquino International Airport via the NAIA Expressway (NAIAX). It is the first fully grade-separated highway in the Philippines and one of the longest elevated highways in the world, with a total length of approximately 39.2 kilometers (24.4 mi).

Interstate 90 (I-90) in the US state of Illinois runs roughly northwest-to-southeast through the northern part of the state. From the Wisconsin state line at South Beloit, it heads south to Rockford before heading east-southeast to the Indiana state line at Chicago. I-90 traverses 124 miles (200 km) through a variety of settings, from farmland west of the Fox River Valley through the medium-density suburbs west of O'Hare International Airport, through Downtown Chicago, and through the heart of the industrial southeast side of Chicago before entering Indiana.
There are approximately 25 current toll roads in the state of Texas. Toll roads are more common in Texas than in many other U.S. states, since the relatively low revenues from the state's gasoline tax limits highway planners' means to fund the construction and operation of highways.

The Red Line Mass Transit System Project is a commuter rail system serving the Bangkok Metropolitan Region in Thailand. The construction began in January 2009 and free public trial operation began on 2 August 2021, with full commercial service to begin in November 2021 when Bang Sue Grand Station opens. It is a part of the Mass Rapid Transit Master Plan in Bangkok Metropolitan Region.

Vibhavadi Rangsit Road or Highway 31, often informally called Vibhavadi Road (ถนนวิภาวดี), is a highway in Thailand.
Multiple toll-collecting controlled-access highway systems are operated in Thailand, currently serving the Greater Bangkok area and nearby provinces. The first expressway in Thailand is Chaloem Maha Nakhon Expressway, opened in 1981. Burapha Withi Expressway was the world's longest bridge from its opening in 2000 to 2010.
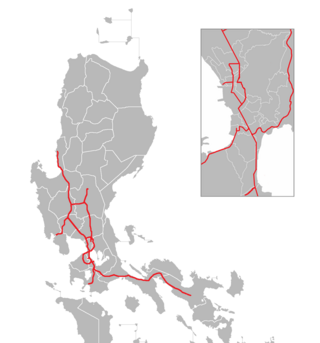
The Philippine expressway network, also known as the High Standard Highway Network, is a controlled-access highway network managed by the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH) which consists of all expressways and regional high standard highways in the Philippines.
Sam Liam Din Daeng or Din Daeng Junction is a road junction in the area of Thanon Phaya Thai Subdistrict, Ratchathewi District in downtown Bangkok. It is a three-way junction of Ratchawithi Road, Ratchaprarop Road and Din Daeng Road, being considered the beginning of the former two. The name of the junction refers to its triangular shape. On top of the junction is an overpass linking Ratchawithi Road and the nearby Victory Monument zone.

Lat Phrao Intersection is a major road junction in Chatuchak District of the Thai capital Bangkok. It is where Phahonyothin and Vibhavadi Rangsit roads—the city's two main northward highways—cross each other, and is also the beginning of Lat Phrao Road, which leads eastward through its highly populated suburbs. The junction carries the second-highest amount of road traffic in the city.














