Related Research Articles

Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Egypt to the north, Eritrea to the northeast, Ethiopia to the southeast, Libya to the northwest, South Sudan to the south, and the Red Sea. It has a population of 45.7 million people as of 2022 and occupies 1,886,068 square kilometres, making it Africa's third-largest country by area and the third-largest by area in the Arab League. It was the largest country by area in Africa and the Arab League until the secession of South Sudan in 2011; since then both titles have been held by Algeria. Its capital and most populous city is Khartoum.
DDD or Triple D may refer to:
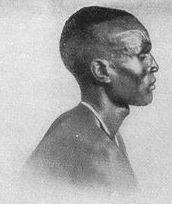
The Dinka people are a Nilotic ethnic group native to South Sudan. The Dinka mostly live along the Nile, from Mangalla-Bor to Renk, in the region of Bahr el Ghazal, Upper Nile, and the Abyei Area of the Ngok Dinka in South Sudan.

The Sudan national football team represents Sudan in international football and is controlled by the Sudan Football Association, the governing body for football in Sudan. Its home ground is Khartoum Stadium in the capital Khartoum. In 1957, it was one of the three teams to participate in the inaugural Africa Cup of Nations, the other two being Egypt and Ethiopia.

The Second Sudanese Civil War was a conflict from 1983 to 2005 between the central Sudanese government and the Sudan People's Liberation Army. It was largely a continuation of the First Sudanese Civil War of 1955 to 1972. Although it originated in southern Sudan, the civil war spread to the Nuba mountains and the Blue Nile. It lasted for almost 22 years and is one of the longest civil wars on record. The war resulted in the independence of South Sudan 6 years after the war ended.
The Eastern Nilotic languages are one of the three primary branches of the Nilotic languages, themselves belonging to the Eastern Sudanic subfamily of Nilo-Saharan; they are believed to have begun to diverge about 3,000 years ago, and have spread southwards from an original home in Equatoria in South Sudan. They are spoken across a large area in East Africa, ranging from Equatoria to the highlands of Tanzania. Their speakers are mostly cattle herders living in semi-arid or arid plains.

Juba is the capital and largest city of South Sudan. The city is situated on the White Nile and also serves as the capital of the Central Equatoria State. It is the most recently declared national capital and had a population of 525,953 in 2017. It has an area of 52 km2 (20 sq mi), with the metropolitan area covering 336 km2 (130 sq mi).
Lango is a community of Paranilotic languages-speaking people originating in South Sudan. They are nomadic agriculturists and Pastoralists. The Lango live in the Ikwoto County area of Eastern Equatoria State. This region borders Uganda to the South and their inhabitants are sharing ancestral lines with the Lango and Acholi of Uganda.

Salva Kiir Mayardit, also known as Salva Kiir, is a South Sudanese politician who has been the President of South Sudan since its independence on 9 July 2011. Prior to independence, he was the President of the Government of Southern Sudan, as well as First Vice President of Sudan, from 2005 to 2011. He was named Commander-in-Chief of the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA) in 2005, following the death of John Garang.

The Roman Catholic Diocese of Torit is a diocese located in Torit in the ecclesiastical province of Juba in South Sudan.

The South Sudan People's Defence Forces (SSPDF), formerly the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA), is the army of the Republic of South Sudan. The SPLA was founded as a guerrilla movement against the government of Sudan in 1983 and was a key participant of the Second Sudanese Civil War, led by John Garang. After Garang's death in 2005, Salva Kiir was named the SPLA's new Commander-in-Chief. As of 2010, the SPLA was divided into divisions of 10,000–14,000 soldiers.

The Lopit people are an ethnic group found in Eastern Equatoria State, South Sudan. Traditionally, they refer to themselves as donge (plural) or dongioni (singular). The Lopit number 160,000 to 200,000 people living in the Lopit area, in the Lopit mountains which extend from the east to the north of Torit.

The States of South Sudan were created out of the three historic former provinces of Bahr el Ghazal (northwest), Equatoria (southern), and Greater Upper Nile (northeast). The states are further divided into 79 counties.

The South Sudan national football team represents South Sudan in international football and is controlled by the South Sudan Football Association, the governing body for football in South Sudan.

South Sudan, officially the Republic of South Sudan, is a landlocked country in eastern Central Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, and Kenya, and includes the vast swamp region of the Sudd, formed by the White Nile and known locally as the Bahr al Jabal, meaning "Mountain Sea". The population was 11,088,796 in 2023, and Juba is the capital and largest city. South Sudan gained independence from Sudan on 9 July 2011, making it the most recent sovereign state or country with widespread recognition as of 2024.
Lobira is a community in Ikotos County, Eastern Equatoria state, South Sudan. It is on the southern road between Torit and Kapoeta, and lies to the north of Lobira hill.
Dongotono is an Eastern Nilotic language spoken by an estimated 5,000 people in South Sudan.

The South Sudanese Civil War was a multi-sided civil war in South Sudan between forces of the government and opposition forces. In December 2013, President Salva Kiir accused his former deputy Riek Machar and 10 others of attempting a coup d'état. Machar denied trying to start a coup and fled to lead the Sudan People's Liberation Movement-in-Opposition (SPLM-IO). Fighting broke out between the Sudan People's Liberation Movement (SPLM) and SPLM-IO, igniting the civil war. Ugandan troops were deployed to fight alongside the South Sudanese government. The United Nations has peacekeepers in the country as part of the United Nations Mission in South Sudan (UNMISS).
Beatrice Nyakaisiki Byenkya is a Ugandan politician, who serves as the Chairperson of the Uganda Land Commission. She was appointed to that position on 18 April 2019. Her appointment requires the approval of the Ugandan parliament.
References
- ↑ "Dongotona". Gurtong. Retrieved 2011-07-06.