The Explorers program is a NASA exploration program that provides flight opportunities for physics, geophysics, heliophysics, and astrophysics investigations from space. Launched in 1958, Explorer 1 was the first spacecraft of the United States to achieve orbit. Over 90 space missions have been launched since. Starting with Explorer 6, it has been operated by NASA, with regular collaboration with a variety of other institutions, including many international partners.
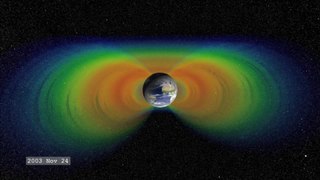
Van Allen radiation belt is a zone of energetic charged particles, most of which originate from the solar wind, that are captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetosphere. Earth has two such belts, and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The belts are named after James Van Allen, who is credited with their discovery.

Helios-A and Helios-B are a pair of probes that were launched into heliocentric orbit to study solar processes. As a joint venture between German Aerospace Center (DLR) and NASA, the probes were launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, on December 10, 1974, and January 15, 1976, respectively.

Advanced Composition Explorer is a NASA Explorer program satellite and space exploration mission to study matter comprising energetic particles from the solar wind, the interplanetary medium, and other sources.

Explorer 6, or S-2, was a NASA satellite, launched on 7 August 1959, at 14:24:20 GMT. It was a small, spheroidal satellite designed to study trapped radiation of various energies, galactic cosmic rays, geomagnetism, radio propagation in the upper atmosphere, and the flux of micrometeorites. It also tested a scanning device designed for photographing the Earth's cloud cover. On 14 August 1959, Explorer 6 took the first photos of Earth from a satellite.

Explorer 11 was a NASA satellite that carried the first space-borne gamma-ray telescope. This marked the beginning of space gamma-ray astronomy. Launched on 27 April 1961 by a Juno II, the satellite returned data until 17 November 1961, when power supply problems ended the science mission. During the spacecraft's seven-month lifespan it detected twenty-two events from gamma-rays and approximately 22,000 events from cosmic radiation.

Explorer 7 was a NASA satellite launched on 13 October 1959, at 15:30:04 GMT, by a Juno II launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) to an orbit of 573 × 1,073 km (356 × 667 mi) and inclination of 50.27°. It was designed to measure solar X-ray and Lyman-alpha flux, trapped energetic particles, and heavy primary cosmic rays. Secondary objectives included collecting data on micrometeoroid penetration, molecular sputtering and studying the Earth-atmosphere heat balance.

Proton ('proton') was a Soviet series of four cosmic ray and elementary particle detecting satellites. Orbited 1965–68, three on test flights of the UR-500 ICBM and one on a Proton-K rocket, all four satellites completed their missions successfully, the last reentering the Earth's atmosphere in 1969.

The European Space Research Organisation (ESRO) was an international organisation founded by 10 European nations with the intention of jointly pursuing scientific research in space. It was founded in 1964. As an organisation ESRO was based on a previously existing international scientific institution, CERN. The ESRO convention, the organisations founding document outlines it as an entity exclusively devoted to scientific pursuits. This was the case for most of its lifetime but in the final years before the formation of ESA, the European Space Agency, ESRO began a programme in the field of telecommunications. Consequently, ESA is not a mainly pure science focused entity but concentrates on telecommunications, earth observation and other application motivated activities. ESRO was merged with ELDO in 1975 to form the European Space Agency.
Health threats from cosmic rays are the dangers posed by cosmic rays to astronauts on interplanetary missions or any missions that venture through the Van-Allen Belts or outside the Earth's magnetosphere. They are one of the greatest barriers standing in the way of plans for interplanetary travel by crewed spacecraft, but space radiation health risks also occur for missions in low Earth orbit such as the International Space Station (ISS).

OSO 7 or Orbiting Solar Observatory 7, before launch known as OSO H is the seventh in the series of American Orbiting Solar Observatory satellites launched by NASA between 1962 and 1975. OSO 7 was launched from Cape Kennedy on 29 September 1971 by a Delta N rocket into a 33.1° inclination, low-Earth orbit, and re-entered the Earth's atmosphere on 9 July 1974. It was built by the Ball Brothers Research Corporation (BBRC), now known as Ball Aerospace, in Boulder Colorado.

OSO 3, or Third Orbiting Solar Observatory was launched on March 8, 1967, into a nearly circular orbit of mean altitude 550 km, inclined at 33° to the equatorial plane. Its on-board tape recorder failed on June 28, 1968, allowing only the acquisition of sparse real-time data during station passes thereafter; the last data were received on November 10, 1969. OSO 3 reentered the Earth's atmosphere and burned up on April 4, 1982.
TD-1A, or Thor-Delta 1A, was a European astrophysical research satellite which was launched in 1972. Operated by the European Space Research Organisation, TD-1A made astronomical surveys primarily in the ultraviolet, but also using x-ray and gamma ray detectors.

Cosmic Ray Subsystem is an instrument aboard the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft of the NASA Voyager program, and it is an experiment to detect cosmic rays. The CRS includes a High-Energy Telescope System (HETS), Low-Energy Telescope System (LETS), and The Electron Telescope (TET). It is designed to detect energetic particles and some of the requirements were for the instrument to be reliable and to have enough charge resolution. It can also detect the energetic particles like protons from the Galaxy or Earth's Sun.

Explorer 12, also called EPE-A or Energetic Particles Explorer-A and as S3), was a NASA satellite built to measure the solar wind, cosmic rays, and the Earth's magnetic field. It was the first of the S-3 series of spacecraft, which also included Explorer 12, 14, 15, and 26. It was launched on 16 August 1961, aboard a Thor-Delta launch vehicle. It ceased transmitting on 6 December 1961 due to power failure.

Explorer 34, was a NASA satellite launched as part of Explorer program. Explorer 34 as launched on 24 May 1967 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, with Thor-Delta E1 launch vehicle. Explorer 34 was the fifth satellite launched as part of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform program, but was known as "IMP-4" because the preceding launch was more specifically part of the "Anchored IMP" sub-program. The spacecraft was put into space between the launches of Explorer 33 in 1966 and Explorer 35 in July 1967, but the next satellite to use Explorer 34's general design was Explorer 41, which flew in 1969.

Explorer 41, also called as IMP-G and IMP-5, was a NASA satellite launched as part of Explorer program. Explorer 41 as launched on 21 June 1969 on Vandenberg AFB, California, with a Thor-Delta E1 launch vehicle. Explorer 41 was the seventh satellite launched as part of the overall Interplanetary Monitoring Platform series, though it received the post-launch designation "IMP-5" because two previous flights had used the "AIMP" designation instead. It was preceded by the second of those flights, Explorer 35, launched in July 1967. Its predecessor in the strict IMP series of launches was Explorer 34, launched in May 1967, which shared a similar design to Explorer 41. The next launch was of an IMP satellite was Explorer 43 in 1971.

Explorer 43, also called as IMP-I and IMP-6, was a NASA satellite launched as part of Explorer program. Explorer 43 was launched on 13 March 1971 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), with a Thor-Delta M6 launch vehicle. Explorer 43 was the sixth satellite of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform.
Explorer 47, was a NASA satellite launched as part of Explorer program. Explorer 47 was launched on 23 September 1972 from Cape Canaveral, Florida, with a Thor-Delta 1604. Explorer 47 was the ninth overall launch of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform series, but received the launch designation "IMP-7" because two previous "Anchored IMP" flights had used "AIMP" instead.

Explorer 50, also known as IMP-J or IMP-8, was a NASA satellite launched to study the magnetosphere. It was the eighth and last in a series of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform.