In music, solfège or solfeggio, also called sol-fa, solfa, solfeo, among many names, is a music education method used to teach aural skills, pitch and sight-reading of Western music. Solfège is a form of solmization, though the two terms are sometimes used interchangeably.

Finale is a proprietary music notation software developed and released by MakeMusic for Microsoft Windows and macOS since 1988.

Cubase is a digital audio workstation (DAW) developed by Steinberg for music and MIDI recording, arranging and editing. The first version, which was originally only a MIDI sequencer and ran on the Atari ST computer, was released in 1989. Cut-down versions of Cubase are included with almost all Yamaha audio and MIDI hardware, as well as hardware from other manufacturers. These versions can be upgraded to a more advanced version at a discount.
Ear training or aural skills is a music theory study in which musicians learn to identify pitches, intervals, melody, chords, rhythms, solfeges, and other basic elements of music, solely by hearing. The application of this skill is analogous to taking dictation in written/spoken language. As a process, ear training is in essence the inverse of sight-reading, the latter being analogous to reading a written text aloud without prior opportunity to review the material. Ear training is typically a component of formal musical training and is a fundamental, essential skill required in music schools.

GarageBand is a line of digital audio workstations developed by Apple Inc. for macOS, iPadOS, and iOS devices that allows users to create music or podcasts. GarageBand is developed by Apple for macOS, and was once part of the iLife software suite, along with iMovie and iDVD. Its music and podcast creation system enables users to create multiple tracks with pre-made MIDI keyboards, pre-made loops, an array of various instrumental effects, and voice recordings.

Logic Pro is a digital audio workstation (DAW) and MIDI sequencer software application for the macOS platform. It was originally created in the early 1990s as Notator Logic, or Logic, by German software developer C-Lab which later went by Emagic. Apple acquired Emagic in 2002 and renamed Logic to Logic Pro. It is the second most popular DAW – after Ableton Live – according to a survey conducted in 2015.

Guitar Pro is a multitrack editor of guitar and bass tablature and musical scores, possessing a built-in MIDI-editor, a plotter of chords, a player, a metronome and other tools for musicians. It has versions for Windows and Mac OS X and is written by the French company Arobas Music.
Band-in-a-Box is a music creation software package for Windows and macOS produced by PG Music Incorporated, founded in 1988 in Victoria, British Columbia. Even though reviewers have described the software interface as awkward or outdated, it nevertheless features the ability of enabling a user to create songs and have them accompanied by professional musicians playing real instruments. The user enters four basic keyboard inputs consisting of: chords; a key; a tempo; a musical style. The screen resembles a blank page of music onto which the user enters the names of chords using standard chord notation. The software generates a song typically played by four or five studio musicians using those chords; the user can specify whether to create solo parts over these chords as well. The developers have enlisted musicians as supporting instrumentalists to build huge databases of phrases in many styles of music. The software retrieves and customizes groups of musical phrases that are appropriate for soloing or comping over a particular chord at a chosen key, genre and tempo. It can create backgrounds, melodies or solos for almost any chord progressions used in Western popular music, and can play them in any of thousands of different music styles.
Nodal is a generative software application for composing music. The software was produced at the Centre for Electronic Media Art (CEMA), Monash University, Australia. It uses a novel method for the notation and playing of MIDI based music. This method is based around the concept of a user-defined graph. The graph consists of nodes and edges. The composer interactively defines the graph, which is then traversed by any number of virtual players that play the musical events as they encounter them on the graph. The time taken by a player to travel from one node to another is based on the length of the edges that connect the nodes.

Logic Studio is a discontinued professional music production suite by Apple Inc. The first version of Logic Studio was unveiled on September 12, 2007. It claims to be the largest collection of modeled instruments, sampler instruments, effect plug-ins, and audio loops ever put in a single application.
Musition is an educational music theory software program. Musition contains 34 topics and allows students to improve their theory knowledge and musicianship. Teachers can tailor the drills and testing features of Musition, to assist students in reaching specific goals, or to help them prepare for particular assessment tasks. Musition allows teachers to track students' progress using the syllabus, test and record keeping features.
Richard Dean Grove was an American musician, composer, arranger, and educator. He is best known as the founder of the Dick Grove School of Music. Its students include Michael Jackson, Linda Ronstadt, and Barry Manilow, and its teachers Henry Mancini, Bill Conti, and Lalo Schifrin.

A Chromebook is a laptop or tablet running the Linux-based ChromeOS as its operating system. Initially designed to heavily rely on web applications for tasks using the Google Chrome browser, Chromebooks have since expanded to be able to run Android and full-fledged Linux apps since 2017 and 2018, respectively. All supported apps can be installed and launched alongside each other.
BlueStacks is an American technology company known for the BlueStacks App Player and other cloud-based cross-platform products. The BlueStacks App Player allows Android applications to run on computers running Microsoft Windows or macOS. The company was founded in 2009 by Jay Vaishnav, Suman Saraf, and Rosen Sharma.

GNU Solfege is an ear training program written in Python intended to help musicians improve their skills and knowledge. It is free software and part of the GNU Project.
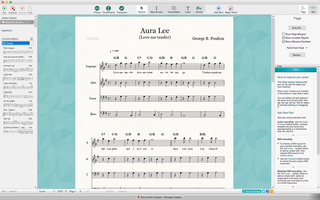
ScoreCloud is a software service and web application for creating, storing, and sharing music notation, created by Doremir for macOS, Microsoft Windows, iPhone and iPad.

B-Step Sequencer is a multitrack software MIDI step sequencer that is available as either a standalone application or in audio plug-in format. Primarily used to create melodical sequences to trigger soft or hardware synthesizer, whether in a studio environment or live on stage, it has a user interface based on pattern and TR music sequencers.









