Related Research Articles
Papular mucinosis is a rare skin disease. Localized and disseminated cases are called papular mucinosis or lichen myxedematosus while generalized, confluent papular forms with sclerosis are called scleromyxedema. Frequently, all three forms are regarded as papular mucinosis. However, some authors restrict it to only mild cases. Another form, acral persistent papular mucinosis is regarded as a separate entity.

Lupus erythematosus is a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the human immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, and lungs. The most common and most severe form is systemic lupus erythematosus.
Madarosis is a condition that results in the loss of eyelashes, and sometimes eyebrows. The term "madarosis" is derived from the ancient Greek "madaros", meaning "bald". It originally was a disease of only losing eyelashes but it currently is the loss of both eyelashes and eyebrows. Eyebrows and eyelashes are both important in the prevention of bacteria and other foreign objects from entering the eye. A majority of patients with madarosis have leprosy, and it was reported that 76% of patients with varying types of leprosy had madarosis.
Alopecia mucinosa, also known as Follicular mucinosis, Mucinosis follicularis, Pinkus' follicular mucinosis, and Pinkus' follicular mucinosis–benign primary form, is a skin disorder that generally presents, but not exclusively, as erythematous plaques or flat patches without hair primarily on the scalp, neck and face. This can also be present on the body as a follicular mucinosis and may represent a systemic disease.
Lichen myxedematosus is a group of cutaneous disorders considered mucinoses. Conditions included in this group are:
Mucinoses are a group of cutaneous diseases caused by fibroblasts producing abnormally large amounts of acid mucopolysaccharides, usually hyaluronic acid.
Discrete papular lichen myxedematosus is a skin condition caused by fibroblasts producing abnormally large amounts of mucopolysaccharides characterized by the occurrence of waxy, flesh-colored papules.
Acral persistent papular mucinosis (APPM) is a rare form of lichen myxedematosus. It is characterized by small papules on the backs of the hands, wrists, and extensor aspects of the distal forearms, with no further clinical or laboratory indications. Lesions tend to persist and may grow in number gradually. Because there are no symptoms, treatment is rarely required.
Self-healing papular mucinosis is a skin condition caused by fibroblasts producing abnormally large amounts of mucopolysaccharides, and may present in adult and juvenile forms. The juvenile variant is also called self-healing juvenile cutaneous mucinosis.
Self-healing juvenile cutaneous mucinosis is a skin condition caused by fibroblasts producing abnormally large amounts of mucopolysaccharides, and is characterized by the sudden onset of skin lesions and polyarthritis.
Papular mucinosis of infancy is a skin condition caused by fibroblasts producing abnormally large amounts of mucopolysaccharides, characterized by skin-colored or translucent papules.
Reticular erythematous mucinosis (REM) is a skin condition caused by fibroblasts producing abnormally large amounts of mucopolysaccharides. It is a disease that tends to affect women in the third and fourth decades of life.
Cutaneous focal mucinosis is a skin condition characterized by a solitary nodule or papule.
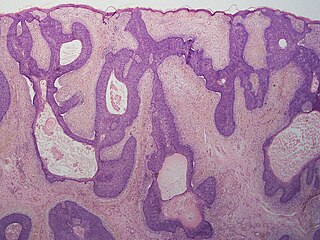
Basaloid follicular hamartoma is a cutaneous condition characterized as distinctive benign adnexal tumor that has several described variants. It manifest as small tan or brown coloured papules in the trunk, pubic area, face, scalp, and axilla.
Urticaria-like follicular mucinosis is a rare cutaneous disorder that occurs primarily in middle-aged men.
Stiff skin syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by ‘rock hard’ induration, thickening of the skin and subcutaneous tissues, limited joint mobility, and mild hypertrichosis in infancy or early childhood. Immunologic abnormalities or vascular hyperactivity are not present in patients.
Nodular lichen myxedematosus is a cutaneous condition characterized by multiple nodules on the limbs and trunk, with a mild or absent papular component.
Cutaneous lupus mucinosis is a cutaneous condition characterized by lesions that present as asymptomatic skin-colored, at times reddish, 0.5–2 cm papules and nodules.
Perifollicular mucinosis is a cutaneous condition characterized by mucinosis, and described in HIV-infected patients. It is usually found in adults and rarely seen in children. It can have many causes.
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.