Related Research Articles

Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at 1,904,569 square kilometres. With around 280 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population.

Jakarta, officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta, is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta is the largest city in Southeast Asia and serves as the diplomatic capital of ASEAN.
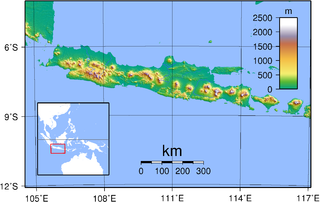
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's most populous island, home to approximately 56% of the Indonesian population.

Gamelan is the traditional ensemble music of the Javanese, Sundanese, and Balinese peoples of Indonesia, made up predominantly of percussive instruments. The most common instruments used are metallophones played by mallets and a set of hand-played drums called kendhang/Kendang, which register the beat. The kemanak and gangsa are commonly used gamelan instruments in Bali. Other instruments include xylophones, bamboo flutes, a bowed instrument called a rebab, a zither-like instrument siter and vocalists named sindhen (female) or gerong (male).
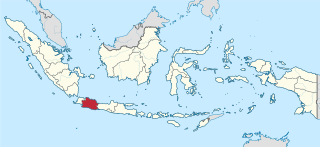
West Java is a province of Indonesia on the western part of the island of Java, with its provincial capital in Bandung. West Java is bordered by the province of Banten and the country's capital region of Jakarta to the west, the Java Sea to the north, the province of Central Java to the east and the Indian Ocean to the south. With Banten, this province is the native homeland of the Sundanese people, the second-largest ethnic group in Indonesia.

The Javanese are an Austronesian ethnic group native to the central and eastern part of the Indonesian island of Java. With approximately 100 million people, Javanese people are the largest ethnic group in both Indonesia and in Southeast Asia as a whole. Their native language is Javanese, it is the largest of the Austronesian languages in number of native speakers and also the largest regional language in Southeast Asia. The Javanese as the largest ethnic group in the region have dominated the historical, social, and political landscape in the past as well as in modern Indonesia and Southeast Asia.

Wayang, also known as wajang, is a traditional form of puppet theatre play originating from the Indonesian island of Java. Wayang refers to the entire dramatic show. Sometimes the leather puppet itself is referred to as wayang. Performances of wayang puppet theatre are accompanied by a gamelan orchestra in Java, and by gender wayang in Bali. The dramatic stories depict mythologies, such as episodes from the Hindu epics the Ramayana and the Mahabharata, as well as local adaptations of cultural legends. Traditionally, a wayang is played out in a ritualized midnight-to-dawn show by a dalang, an artist and spiritual leader; people watch the show from both sides of the screen.

Betawi people, or Betawis, are an Austronesian ethnic group native to the city of Jakarta and its immediate outskirts, as such often described as the native inhabitants of the city. They are the descendants of the people who inhabited Batavia from the 17th century onwards.

The bedug is one of the drums used in the gamelan. It is also used among Muslims in Indonesia and Malaysia to signal mosque prayer times. The hitting of the instrument is particularly done according to a rhythm that goes in an increasingly rapid pace.

Yogyakarta is the capital city of Special Region of Yogyakarta in Indonesia, in the south-central part of the island of Java. As the only Indonesian royal city still ruled by a monarchy, Yogyakarta is regarded as an important centre for classical Javanese fine arts and culture such as ballet, batik textiles, drama, literature, music, poetry, silversmithing, visual arts, and wayang puppetry. Renowned as a centre of Indonesian education, Yogyakarta is home to a large student population and dozens of schools and universities, including Gadjah Mada University, the country's largest institute of higher education and one of its most prestigious.

Poerbatjaraka was a Javanese/Indonesian self-taught philologist and professor, specialising in Javanese literature. The eldest son of a Surakarta royal courtier in the Dutch East Indies, he showed interest in Javanese literature at an early age, reading from books in the court's collection. Despite attending only primary school, his knowledge of Dutch and Javanese literature allowed him to take a position at the colony's Archaeology Service, and then at Leiden University in the Netherlands. He was allowed to obtain a doctor's degree at Leiden. He then returned to the colony to work at a Batavia museum, cataloguing Javanese texts and writing scholarly works. After Indonesia's independence, he became a professor at the universities of Indonesia, Gajah Mada, and Udayana.

Prijono was an Indonesian politician and academic. Prijono was a leading figure of the Murba Party and the Indonesian Peace Committee. Prijono served as Minister of Education and Culture between 1957 and 1966. He was one of the intellectual ideologues who surrounded President Sukarno.

Gandrung is a traditional dance from Indonesia. Gandrung has many variations and is popular in Bali, Lombok and Eastern Java among the Balinese, Sasak and Javanese. The most popular variation is gandrung from the Banyuwangi region in the eastern peninsula of Java, so much that the city is often referred as Kota Gandrung or "the city of gandrung". Originally a ritual dance dedicated to the goddess of rice and fertility, Dewi Sri, it is currently performed as a social dance of courtship and love in communal and social events, or as a tourist attraction. Gandrung Sewu Festival is held at Banyuwangi annually.

The Srimpi is a ritualised dance of Java, Indonesia, associated with the royal palaces of Yogyakarta and Surakarta. The srimpi dance is one of the classical dances of Central Java. Along with the bedhaya, srimpi epitomised the elegant character of the royal Javanese court, becoming a symbol of the ruler's power as well as the refinement of Javanese culture.

Gordon Lumban Tobing was an Indonesian singer of folk songs, particularly those in the Batak language. Born to a Batak family in Medan, North Sumatra, Tobing moved to Jakarta in 1950 and began working in the entertainment industry. While with Radio Republik Indonesia, he participated in an Indonesian cultural envoy to the 4th World Festival of Youth and Students. Over the remainder of his life Tobing was included in numerous similar envoys, ultimately travelling to five continents.
Bagong Kussudiardja was an Indonesian artist, contemporary dance choreographer and painter. Bagong’s career kicked off after Indonesia’s independence in 1945. As a dance choreographer, Bagong has choreographed more than 200 dances. Bagong perfected his skills by studying Japanese and Indian dances. In 1957 and 1958, Bagong trained under the well-known dance choreographer Martha Graham, known for her boundary-breaking techniques. Bagong then combined the modern moves with traditional Indonesian dances. After his training, he founded Pusat Latihan Tari Bagong Kussudiardja in 1958, followed by Padepokan Seni Bagong Kussudiardja in 1978.

Pencalang is a traditional merchant ship from Nusantara. Historically it was called as pantchiallang or pantjalang. It was originally built by Malay people from the area of Riau and the Malay Peninsula, but has been copied by Javanese shipwrights. By the end of the 17th century this ship has been built by Javanese and Chinese shipbuilders in and around Rembang. However it was a popular choice for Balinese skippers followed by Sulawesian skippers.

Melati Suryodarmo is an Indonesian durational performance artist. Her physically demanding performances make use of repetitive motions and often last for many hours, sometimes reaching "a level of factual absurdity". Suryodarmo has performed and exhibited throughout Europe and Asia as well as in North America. Born in Surakarta, she attended Padjadjaran University, graduating with a degree in international relations before moving to Germany. She lived there for 20 years, studying performance art at the Braunschweig University of Art with Butoh choreographer Anzu Furukawa and performance artist Marina Abramović.

Buda Script or (Aksara Buda) or Gunung Script is an archaic script. Based on its shape, the Buda Script still has a close relationship with the Kawi script. This script was previously used on the island of Java and Bali. This type of script is called the Buda script because it is considered to have originated from the pre-Islamic era which is called the Buddhist Age. The word Buda is based on the Buddha word. Manuscripts containing writing using the Buda script are commonly found in mountainous areas. Because of that, this type of script is also called the "Mountain script".

Sri Koesnapsijah was a Javanese language writer and activist of the Dutch East Indies and Indonesia who was among the generation of Indonesian women writers active in the 1930s. She was known for her short stories and articles which she published in the magazine Panjebar Semangat in the 1930s and 1940s, where she was also an assistant editor. After Indonesian independence she was active in the Communist Party-affiliated Gerwani movement, and was briefly a representative of the Communist Party in the Jakarta-area consultative body DPR-GR. She was arrested in late 1965 during the anti-communist repression of the Transition to the New Order and imprisoned without charge for the following decade.
References
- ↑ "RIP: Prof. Dr. Edi Sedyawati (1938–2022)". Jakarta Institute of Arts. 12 November 2022. Archived from the original on 1 December 2022. Retrieved 4 February 2023.
- ↑ Juliana Harsianti, Going back to tradition. The Nation, 1 May 2017. Accessed 27 June 2018.
- ↑ Rita Widiadana, NH Dini and her endless soul-searching journey. Jakarta Post, 27 November 2017. Accessed 27 June 2018.
- ↑ Masajeng Rahmiasri, Cultural movement seeks Indonesian women to wear, preserve kebaya. Jakarta Post, 4 March 2017. Accessed 27 June 2018.
- ↑ Véronique Degroot, Candi, Space and Landscape: A Study on the Distribution, Orientation and Spatial Organization of Central Javanese Temple Remains, p. v. Leiden: Sidestone Press, 2009. ISBN 9789088900396
- ↑ Jennifer Sidharta, Passing down history through art. Global Indonesian Voices, 2 December 2015. Accessed 27 June 2018.
- ↑ Art of Indonesia, p. 233. Ed. Haryati Soebadio-Noto Soebagio. Periplus Editions, 1998. ISBN 9789625932378
- 1 2 Jennifer Lindsay, Heirs to World Culture: Being Indonesian, 1950-1965, p. 213. Leiden: Brill Publishers, 2012. ISBN 9789004253513
- ↑ Gunawan Mohamad, Celebrating Indonesia: Fifty Years with the Ford Foundation, 1953-2003, p. 173. New York City: Ford Foundation, 2003. ISBN 9789799796417
- ↑ Jennifer Lindsay, Heirs to World Culture, p. 214.
- ↑ Jennifer Lindsay, Heirs to World Culture, pp. 213-214.
- ↑ Masatoshi Iguchi, Java Essay: The History and Culture of a Southern Country, p. 110. Leicester: Troubador Publishing, 2017. ISBN 9781784628857