
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its phase, as in phase modulation.

An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements. An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Linear electrical networks, a special type consisting only of sources, linear lumped elements, and linear distributed elements, have the property that signals are linearly superimposable. They are thus more easily analyzed, using powerful frequency domain methods such as Laplace transforms, to determine DC response, AC response, and transient response.
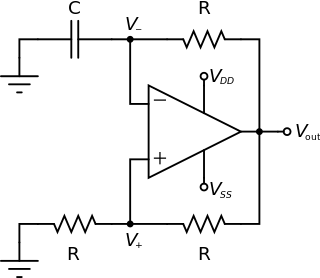
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave or a triangle wave. Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supply to an alternating current (AC) signal. They are widely used in many electronic devices ranging from simplest clock generators to digital instruments and complex computers and peripherals etc. Common examples of signals generated by oscillators include signals broadcast by radio and television transmitters, clock signals that regulate computers and quartz clocks, and the sounds produced by electronic beepers and video games.

An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the power of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.
In engineering, a transfer function of a system, sub-system, or component is a mathematical function that theoretically models the system's output for each possible input. They are widely used in electronics and control systems. In some simple cases, this function is a two-dimensional graph of an independent scalar input versus the dependent scalar output, called a transfer curve or characteristic curve. Transfer functions for components are used to design and analyze systems assembled from components, particularly using the block diagram technique, in electronics and control theory.
In signal processing, group delay and phase delay are delay times experienced by a signal's various frequency components when the signal passes through a linear time-invariant system (LTI), such as a microphone, coaxial cable, amplifier, loudspeaker, telecommunications system or ethernet cable. These delays are generally frequency dependent, which means that different frequency components experience different delays. As a result, the signal's waveform experiences distortion as it passes through the system. This distortion can cause problems such as poor fidelity in analog video and analog audio, or a high bit-error rate in a digital bit stream. For a modulation signal, the information carried by the signal is carried exclusively in the wave envelope. Group delay therefore operates only with the frequency components derived from the envelope.

In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of resistance and reactance in a circuit.

In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves.

A crystal radio receiver, also called a crystal set, is a simple radio receiver, popular in the early days of radio. It uses only the power of the received radio signal to produce sound, needing no external power. It is named for its most important component, a crystal detector, originally made from a piece of crystalline mineral such as galena. This component is now called a diode.

In electronics, negative resistance (NR) is a property of some electrical circuits and devices in which an increase in voltage across the device's terminals results in a decrease in electric current through it.
This is an index of articles relating to electronics and electricity or natural electricity and things that run on electricity and things that use or conduct electricity.
The Hartley oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit in which the oscillation frequency is determined by a tuned circuit consisting of capacitors and inductors, that is, an LC oscillator. The circuit was invented in 1915 by American engineer Ralph Hartley. The distinguishing feature of the Hartley oscillator is that the tuned circuit consists of a single capacitor in parallel with two inductors in series, and the feedback signal needed for oscillation is taken from the center connection of the two inductors.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to electrical engineering.

A variable capacitor is a capacitor whose capacitance may be intentionally and repeatedly changed mechanically or electronically. Variable capacitors are often used in L/C circuits to set the resonance frequency, e.g. to tune a radio, or as a variable reactance, e.g. for impedance matching in antenna tuners.
This is an alphabetical list of articles pertaining specifically to electrical and electronics engineering. For a thematic list, please see List of electrical engineering topics. For a broad overview of engineering, see List of engineering topics. For biographies, see List of engineers.
A radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves with frequencies between about 30 Hz and 300 GHz. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary parts of all systems that use radio: radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, wireless networks, radar, two way radios like walkie talkies, radio navigation systems like GPS, remote entry systems, among numerous other uses.
Radio-frequency (RF) engineering is a subset of electronic engineering involving the application of transmission line, waveguide, antenna and electromagnetic field principles to the design and application of devices that produce or use signals within the radio band, the frequency range of about 20 kHz up to 300 GHz.

In electronics, a plate detector is a vacuum tube circuit in which an amplifying tube having a control grid is operated in a non-linear region of its grid voltage versus plate current transfer characteristic, usually near plate current cutoff, to demodulate amplitude modulated carrier signal. This differs from the grid leak detector, which utilizes the non-linearity of the grid voltage versus grid current characteristic for demodulation. It also differs from the diode detector, which is a two-terminal device.

Electronics engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering which emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flow. Previously electrical engineering only used passive devices such as mechanical switches, resistors, inductors, and capacitors.
This glossary of electrical and electronics engineering is a list of definitions of terms and concepts related specifically to electrical engineering and electronics engineering. For terms related to engineering in general, see Glossary of engineering.











